Abstract
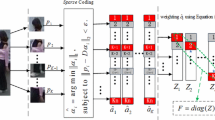
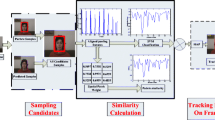
There are many visual tracking algorithms that are based on sparse representation appearance model. Most of them are modeled by local patches with fixed patch scale, which make trackers less effective when objects undergone appearance changes such as illumination variation, pose change or partial occlusion. To solve the problem, a novel appearance representation model is proposed via multi-scale patch based sparse coding histogram for robust visual tracking. In this paper, the appearance of an object is modeled by different scale patches, which are represented by sparse coding histogram with different scale dictionaries. Then a similarity measure is applied to the calculation of the distance between the sparse coding histograms of target candidate and target template. Finally, the similarity score of the target candidate is passed to a particle filter to estimate the target state sequentially in the tracking process. Additionally, in order to decrease the visual drift caused by partial occlusion, an occlusion handling strategy is adopted, which takes the spatial information of multi-scale patches and occlusion into account. Based on the experimental results on some benchmarks of video sequences, our tracker outperforms state-of-the-art tracking methods.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam A, Rivlin E, Shimshoni I et al. (2006) Robust fragments-based tracking using the integral histogram. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit 798-805
Arulampalam MS, Maskell S, Gordon N, Clapp T (2002) A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-gaussian bayesian tracking. IEEE Trans Signal Process 50(2):174–188
Avidan S (2007) Ensemble tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(2):261–271
Babenko B, Ming-Hsuan Y, Belongie S (2011) Robust object tracking with online multiple instance learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(8):1619–1632
Bai T, Li YF (2012) Robust visual tracking with structured sparse representation appearance model. Pattern Recognit 45(6):2390–2404
Bao C, Wu Y, Ling H et al. (2012) Real time robust L1 tracker using accelerated proximal gradient approach. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit 1830-1837
Cabido R, Montemayor JAS, Pantrigo J, Martínez-Zarzuela M, Payne BR (2012) High-performance template tracking. J Vis Commun Image Represent 23(2):271–286
Chen F, Wang Q, Wang S, Zhang W, Xu W (2011) Object tracking via appearance modeling and sparse representation. Image Vis Comput 29(11):787–796
Comaniciu D, Ramesh V, Meer P (2003) Kernel-based object tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(5):564–577
Doucet A, Freitas N, Gordon N et al. (2001) Sequential monte carlo methods in practice
Everingham M, Gool LV, Williams C, Winn J, Zisserman A (2010) The pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge. Int J Comput Vis 88(2):303–338
Fukunaga K (1990) Introduction to statistical pattern recognition, second ed., Academic Press
Grabbner H, Bischof H (2006) On-line boosting and vision. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit 260–267
Guoheng H, Chi-Man P, Cong L, Yicong Z (2015) Non-rigid visual object tracking using user-defined marker and Gaussian kernel. Multimed Tools Applic. doi:10.1007/s11042-015-2516-6
He SF, Yang QX, Lau R et al. (2013)Visual tracking via locality sensitive histograms. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit 2427-2434
Jia X, Lu H, Yang MH et al. (2012) Visual tracking via adaptive structural local sparse appearance model. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit 1822-1829
Kalal Z, Mikolajczyk K, Matas J (2012) Tracking-learning-detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(7):1409–1422
Kwon J, Lee KM (2011) Tracking by sampling trackers. Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vision 1195-1202
Li X, Hu W, Shen C, Zhang Z, Dick A, Hengel A (2013) A survey of appearance models in visual object tracking. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol (TIST) 4(4):1–58
Liu B, Huang J (2011) Robust tracking using local sparse appearance model and K-selection. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit 1313-1320
Matthews I, Ishikawa T, Baker S (2004) The template update problem. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 26(6):810–815
Mei X, Ling H (2011) Robust visual tracking and vehicle classification via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell (PAMI) 33(11):2259–2272
Nejhum SMS, Ho J, Yang M-H et al. (2008) Visual tracking with histograms and articulating blocks. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit 1-8
Parag T, Porikli F, Elgammal A et al. (2008) Boosting adaptive linear weak classifiers for online learning and tracking. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit 1-8
Perez P, Hue C, Vermaak J et al. (2002) Color-based probabilistic tracking. Proc Europ Conf Comput Vision 661-675
Ren X, Ramanan D (2013) Histograms of sparse codes for object detection. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit 3246- 3253
Ross D, Lim J, Lin R-S, Yang M-H (2008) Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int J Comput Vis 77(1):125–141
Tropp JAA, Gilbert C (2007) Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 53(12):4655–4666
Wang Q, Chen F, Xu W, Yang M-H (2012) Object tracking via partial least squares analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(10):4454–4465
Wang S, Lu H, Yang F et al. (2011) Superpixel tracking. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision 1323-1330
Wang J, Yang J, Yu K et al. (2010) Locality constrained linear coding for image classification. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit 3360-3367
Wright J, Ma Y, Mairal J, Sapiro G, Huang T, Yan S (2010) Sparse representation for computer vision and pattern recognition. Proc IEEE 98(6):1031–1044
Wright J, Yang A, Ganesh A, Sastry S, Ma Y (2008) Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell (PAMI) 31(2):210–227
Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M-H et al. (2013) Online object tracking: a benchmark. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit 2411-2418
Xie CJ, Tan JQ, Chen P, Zhang J, He L (2013) A multiple instance learning tracking method with local sparse representation. IET Comput Vis 7(5):320–334
Yilmaz A, Javed O, Shah M (2006) Object tracking: a survey. ACM Comput Surv 38(4):13
Zhang KH, Zhang L, Yang MH et al. (2012) Real-time compressive tracking. Proc Europ Conf Comput Vision 864–877
Zhong W, Lu H, Yang M.-H et al. (2012) Robust object tracking via sparsity-based collaborative model. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit 1838-1845
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61070227, 61300058, 61472282, 31401293 and 41302261), the NSFC-Guangdong Joint Foundation Key Project under Grant (No. U1135003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Wang, H., Tan, J. et al. Robust object tracking via multi-scale patch based sparse coding histogram. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 12181–12203 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3289-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3289-2