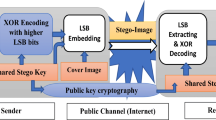
Abstract
Information hiding is an active area of research where secret information is embedded in innocent-looking carriers such as images and videos for hiding its existence while maintaining their visual quality. Researchers have presented various image steganographic techniques since the last decade, focusing on payload and image quality. However, there is a trade-off between these two metrics and keeping a better balance between them is still a challenging issue. In addition, the existing methods fail to achieve better security due to direct embedding of secret data inside images without encryption consideration, making data extraction relatively easy for adversaries. Therefore, in this work, we propose a secure image steganographic framework based on stego key-directed adaptive least significant bit (SKA-LSB) substitution method and multi-level cryptography. In the proposed scheme, stego key is encrypted using a two-level encryption algorithm (TLEA); secret data is encrypted using a multi-level encryption algorithm (MLEA), and the encrypted information is then embedded in the host image using an adaptive LSB substitution method, depending on secret key, red channel, MLEA, and sensitive contents. The quantitative and qualitative experimental results indicate that the proposed framework maintains a better balance between image quality and security, achieving a reasonable payload with relatively less computational complexity, which confirms its effectiveness compared to other state-of-the-art techniques.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Hiding a fixed size message inside multiple images of same resolution, e.g., embedding 8 KB data in 50 images of resolution 256 × 256 pixels
Hiding variable amount of message inside multiple images of same resolution
Hiding fixed size message in same images of varying resolutions
Discrete Wavelength Transform
Discrete Cosine Transform
References
Al-Taani AT, Al-Issa AM (2009) A novel steganographic method for gray-level images. Int J Comput, Inform Syst Sci, Eng 3: 1 2009
Aziz M, Tayarani-N MH, Afsar M (2015) A cycling chaos-based cryptic-free algorithm for image steganography. Nonlinear Dyn 80:1271–1290
Bailey K, Curran K (2006) An evaluation of image based steganography methods. Multimed Tools Appl 30:55–88
Bin L, Ming W, Xiaolong L, Shunquan T, Jiwu H (2015) A strategy of clustering modification directions in spatial image steganography. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 10:1905–1917
Chai T, Draxler RR (2014) Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?–Arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci Model Dev 7:1247–1250
Cheddad A, Condell J, Curran K, Mc Kevitt P (2010) Digital image steganography: survey and analysis of current methods. Signal Process 90:727–752
Cheddad A, Condell J, Curran K, Mckevitt P (2014) Encryption method. ed: Google Patents
Chen W-Y (2008) Color image steganography scheme using DFT, SPIHT codec, and modified differential phase-shift keying techniques. Appl Math Comput 196:40–54
Chen W-J, Chang C-C, Le THN (2010) High payload steganography mechanism using hybrid edge detector. Expert Syst Appl 37:3292–3301
Chen P-Y, Lin H-J (2006) A DWT based approach for image steganography. Int J Appl Sci Eng 4:275–290
Cheng W-C, Pedram M (2004) Chromatic encoding: a low power encoding technique for digital visual interface. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 50:320–328
El Hennawy HM, Omar AE, Kholaif SM (2015) LEA: link encryption algorithm proposed stream cipher algorithm. Ain Shams Eng J 6:57–65
El-Emam NN (2015) New data-hiding algorithm based on adaptive neural networks with modified particle swarm optimization. Comput Secur 55:21–45
Emam NNE, Diabat MA (2015) A novel algorithm for colour image steganography using a new intelligent technique based on three phases. Appl Soft Comput
Eng PMKM, Zaynab Najeeb Abdulhameed (2014) High capacity steganography based on chaos and contourlet transform for hiding multimedia data. Int J Electron Comm Eng Technol (IJECET) 5:26–42
Fakhredanesh M, Rahmati M, Safabakhsh R (2013) Adaptive image steganography using contourlet transform. J Electron Imaging 22:043007
Grover N, Mohapatra A (2013) Digital image authentication model based on edge adaptive steganography. In: Advanced Computing, Networking and Security (ADCONS), 2013 2nd International Conference on, p 238–242
Gutub AA-A (2010) Pixel indicator technique for RGB image steganography. Journal of Emerging Technologies in Web Intelligence 2:56–64
Hong W (2013) Adaptive image data hiding in edges using patched reference table and pair-wise embedding technique. Inform Sci 221:473–489
Hong W, Chen T-S (2012) A novel data embedding method using adaptive pixel pair matching. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 7:176–184
Ioannidou A, Halkidis ST, Stephanides G (2012) A novel technique for image steganography based on a high payload method and edge detection. Expert Syst Appl 39:11517–11524
Ishtiaq M, Jaffar MA, Khan MA, Jan Z, Mirza AM (2009) Robust and imperceptible watermarking of video streams for low power devices. In: Signal Processing, Image Processing and Pattern Recognition, ed: Springer, p 177–184
Jassim FA (2013) A novel steganography algorithm for hiding text in image using five modulus method. Int J ComputAppl 72
Jiang N, Zhao N, Wang L (2015) LSB based quantum image steganography algorithm. Int J Theor Phys, p 1–17
Jinomeiq L, Baoduui W, Xinmei W (2007) One AES S-box to increase complexity and its cryptanalysis. J Syst Eng Electron 18:427–433
Kanan HR, Nazeri B (2014) A novel image steganography scheme with high embedding capacity and tunable visual image quality based on a genetic algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 41:6123–6130
Khan Muhammad IM, Sajjad M, Ahmad J, Yoo SJ, Han D, Baik SW (2015) Secure visual content labelling for personalized image retrieval. In: The 11th International Conference on Multimedia Information Technology and Applications (MITA 2015) June 30-July2, 2015, Tashkent, Uzbekistan, p 165–166
Khan A, Siddiqa A, Munib S, Malik SA (2014) A recent survey of reversible watermarking techniques. Inform Sci 279:251–272
Lee Y-P, Lee J-C, Chen W-K, Chang K-C, Su I-J, Chang C-P (2012) High-payload image hiding with quality recovery using tri-way pixel-value differencing. Inform Sci 191:214–225
Liu Q, Li P-y, Zhang M-c, Sui Y-x, Yang H-j (2015) A novel image encryption algorithm based on chaos maps with Markov properties. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 20:506–515
Luo W, Huang F, Huang J (2010) Edge adaptive image steganography based on LSB matching revisited. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 5:201–214
Mielikainen J (2006) LSB matching revisited. IEEE Signal Process Lett 13:285–287
Muhammad K, Ahmad J, Farman H, Jan Z, Sajjad M, Baik SW (2015) A secure method for color image steganography using gray-level modification and multi-level encryption. KSII T Internet Inf 9:1938–1962
Muhammad K, Ahmad J, Rehman NU, Jan Z, Qureshi RJ (2015) A secure cyclic steganographic technique for color images using randomization. Technical Journal UET Taxila, Pakistan 19(3):57–64
Muhammad K, Ahmad J, Sajjad M, Zubair M (2015) Secure image steganography using cryptography and image transposition. NED Univ J Res 12(4):81
Muhammad K, Jan Z, Ahmad J, Khan Z (2015) An adaptive secret key-directed cryptographic scheme for secure transmission in wireless sensor networks. Technical Journal, University of Engineering and Technology (UET) Taxila, Pakistan 20(3):48--53
Muhammad K, Mehmood I, Lee MY, Ji SM, Baik SW (2015) Ontology-based secure retrieval of semantically significant visual contents. J Kor Inst Next Gener Comput 11(3):87--96
Muhammad K, Mehmood I, Sajjad M, Ahmad J, Yoo SJ, Han D, Wook S (2015) Secure visual content labelling for personalized image retrieval. In: The 11th international conference on multimedia information technology and applications (MITA 2015), 2015, Tashkent, Uzbekistan, pp 165--166
Muhammad K, Sajjad M, Baik SW (2016) Dual-level security based cyclic18 steganographic method and its application for secure transmission of keyframes during wireless capsule endoscopy. J Med Syst 40:1--16
Muhammad K, Sajjad M, Mehmood I, Rho S, Baik SW (2015) A novel magic LSB substitution method (M-LSB-SM) using multi-level encryption and achromatic component of an image. Multimed Tools Appl:1–27
NguyenTD, Arch-int S, Arch-int N (2015) An adaptive multi bit-plane image steganography using block data-hiding. Multimed Tools Appl:1–27,
Nie T, Zhang T (2009) A study of DES and Blowfish encryption algorithm. In: TENCON 2009–2009 I.E. Region 10 Conference, p 1–4
Noda H, Niimi M, Kawaguchi E (2006) High-performance JPEG steganography using quantization index modulation in DCT domain. Pattern Recogn Lett 27:455–461
Parah SA, Sheikh JA, Hafiz AM, Bhat G (2014) Data hiding in scrambled images: a new double layer security data hiding technique. Comput Electr Eng 40:70–82
Parvez MT, Gutub AA-A (2011) Vibrant color image steganography using channel differences and secret data distribution. Kuwait J Sci Eng 38:127–142
Qazanfari K, Safabakhsh R (2014) A new steganography method which preserves histogram: generalization of LSB++. Inform Sci 277:90–101
Roy R, Sarkar A, Changder S (2013) Chaos based edge adaptive image steganography. Procedia Technol 10:138–146
Sajjad M, Mehmood I, Abbas N, Baik SW (2016) Basis pursuit denoising-based image superresolution using a redundant set of atoms. SIViP 10(1):181--188
Sajjad M, Mehmood I, Baik SW (2014) Sparse representations-based super-resolution of key-frames extracted from frames-sequences generated by a visual sensor network. Sensors 14:3652–3674
Tang M, Zeng S, Chen X, Hu J, Du Y (2015) An adaptive image steganography using AMBTC compression and Interpolation Technique. Op-Int J Light Electron Opt
Wang C-M, Wu N-I, Tsai C-S, Hwang M-S (2008) A high quality steganographic method with pixel-value differencing and modulus function. J Syst Softw 81:150–158
Wu S, Liu Y, Zhong S, Liu Y (2015) What makes the stego image undetectable?. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service, p 47
Wu D-C, Tsai W-H (2003) A steganographic method for images by pixel-value differencing. Pattern Recogn Lett 24:1613–1626
Zhang W, Zhang X, Wang S (2007) A double layered “plus-minus one” data embedding scheme. IEEE Signal Process Lett 14:848–851
Acknowledgments
We are sincerely thankful to the prolific suggestions and constructive comments of the associate editor and anonymous reviewers which improved the quality of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muhammad, K., Ahmad, J., Rehman, N.U. et al. CISSKA-LSB: color image steganography using stego key-directed adaptive LSB substitution method. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 8597–8626 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3383-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3383-5