Abstract
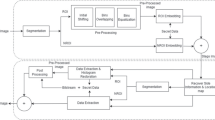
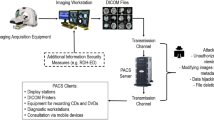
In this paper, we attempt to investigate the secure archiving of medical images which are stored on semi-trusted cloud servers, and focus on addressing the complicated and challenging integrity control and privacy preservation issues. With the intention of protecting the medical images stored on a semi-trusted server, a novel ROI-based high capacity reversible data hiding (RDH) scheme with contrast enhancement is proposed in this paper. The proposed method aims at improving the quality of the medical images effectively and embedding high capacity data reversibly meanwhile. Therefore, the proposed method adopts “adaptive threshold detector” (ATD) segmentation algorithm to automatically separate the “region of interest” (ROI) and “region of non-interest” (NROI) at first, then enhances the contrast of the ROI region by stretching the grayscale and embeds the data into peak bins of the stretched histogram without extending the histogram bins. Lastly, the rest of the required large of data are embedded into NROI region regardless its quality. In addition, the proposed method records the edge location of the segmentation instead of recording the location of the overflow and underflow. The experiment shows that the proposed method can improve the quality of medical images obviously whatever in low embedding rate or high embedding rate when compared with other contrast-based RDH methods.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Qershi OM, Khoo BE (2011) High capacity data hiding schemes for medical images based on difference expansion. J Syst Softw 84(1):105–112
Bao F, Deng RH, Ooi BC et al (2005) Tailored Reversible Watermarking Schemes for Authentication of Electronic Clinical Atlas. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 9(4):554–563
B.ou XL, Zhao Y, Ni R, Shi Y (2013) Pairwise Prediction-Error Expansion for Efficient Reversible Data Hiding. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(12):5010–5012
Dragoi I-C, Coltuc D (2014) Local-prediction-based difference expansion reversible watermarking. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(4):1779–1790
Fang YM, Ma K, Wang Z et al (2015) No-Reference Quality Assessment of Contrast-Distorted Images Based on Natural Scene Statistics. IEEE Signal Process Lett 22(7):838–842
Gao M, Wang L (2013) Comprehensive evaluation for HE based contrast enhancement. Adv Intell Syst Applicat 2:331–338
Gao G-Y, Shi Y-Q (2015) Reversible Data Hiding Using Controlled Contrast Enhancement and Integer Wavelet Transform. IEEE Signal Process Lett 22 (11):2078–2082
Gonzalez RC, Woods RE (2004) Digital Image Processing (Second Edition), Publishing House of Electronics Industry, pp 71
Hiary S, Jafar I, Hiary H (2016) An efficient multi-predictor reversible data hiding algorithm based on performance evaluation of different prediction schemes. Multimedia Tools Application, pp 1–27
Howard PG, Kossentini F, Martins B, Forchhammer S, Rucklidge WJ (1998) The emerging JBIG2 standard. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 8 (7):838–848
Hu Y, Lee H-K, Li J (2009) DE-based reversible data hiding with improved overflow location map. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 19(2):250–260
Hu X, Zhang W, Li X, Yu N (2015) Minimum rate prediction and optimized histograms modification for reversible data hiding. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 10 (3):653–664
Huang L-C, Tseng L-Y, Hwang M-S (2013) A reversible data hiding method by histogram shifting in high quality medical images. J Syst Softw 86(3):716–727
Jemmett DG, Miller GE (2012) Medical imaging archives delivered as Cloud-based service offerings, HP Business white paper, pp 1–11
Kamstra L, Heijmans HJAM (2005) Reversible data embedding into images using wavelet techniques and sorting. IEEE Trans Image Process 14(12):2082–2090
Lee S, Yoo CD, Kalker T (2007) Reversible image watermarking based on integer-to-integer wavelet transform. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 2(3):321–330
Li X, Yang B, Zeng T (2011) Effecient reversible watermarking based on adaptive prediction-error expansion and pixel selection. IEEE Trans Image Process 20 (12):3524–3533
Li X, Li J, Li B, Yang B (2013) High-fidelity reversible data hiding scheme based on pixel-value-ordering and prediction-error expansion. Signal Process 93 (1):198–205
Li X, Zhang W, Gui X, Yang B (2013) A novel reversible data hiding scheme based on two-dimensional difference-histogram modification. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 8(7):1091–1100
Lima JB, Madeiro F, Sales FJR (2015) Encryption of medical images based on the cosine number transform. Signal Process Image Commun 35:1–8
Luo L, Chen Z, Chen M, Zeng X, Xiong Z (2010) Reversible image watermarking using interpolation technique. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 5 (1):187–193
Ma X, Pan Z, Hu S, Wang L (2015) High-fidelity reversible data hiding scheme based on multi-predictor sorting and selecting mechanism. J Vis Commun Image Represent 28:71–82
Ni Z, Shi Y, Ansari N, Wei S (2006) Reversible Data Hiding. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 16(3):354–362
Ou B, Li X, Zhao Y, Ni R (2013) Reversible data hiding based on PDE predictor. J Syst Softw 86(10):2700–2709
Pai P-Y, Chang C-C, Chan Y-K, Tsai M-H (2011) An adaptable threshold detector. Inf Sci 181(8):1463–1483
Pei Q, Wang X, Li Y, Li H (2013) Adaptive reversible watermarking with improved embedding capacity. J Syst Softw 86(11):2841–2848
Qin C, Hu Y-C (2016) Reversible data hiding in VQ index table with lossless coding and adaptive switching mechanism. Signal Process 129:48–55
Qin C, Chang C-C, Jung H-T (2015) Reversible Data Hiding Scheme Based on Exploiting Modification Direction with Two Steganographic Images. Multimedia Tools and Appl 74(15):5861–5872
Qin C, Chang C-C, Huang Y-H, Liao L-T (2013) An inpaintingassisted reversible steganographic scheme using a histogram shifting mechanism. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 23(7):1109–1118
Sachnev V, Kim HJ, Nam J, Suresh S, Shi YQ (2009) Reversible Watermarking Algorithm using Sorting and Prediction. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 19(7):989–999
Shi Y-Q, Li X-L, Zhang X-P, Wu H-T, Ma B (2016) Reversible Data Hiding: Advances in the Past Two Decades. IEEE Access 4:3210–3237
Tian J (2002) Wavelet-based reversible watermarking for authentication. Proc SPIE 4675:679–690
Tian J (2003) Reversible data embedding using a difference expansion. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 13(8):890–896
Thodi DM, Rodriguez JJ (2004) Prediction-error based reversible watermarking Proceedings IEEE Int. Conference Inf. Processing, pp 1549–1552
Thodi DM, Rodriguez JJ (2007) Expansion embedding techniques for reversible watermarking. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(3):721–730
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR et al (2004) Image Quality Assessment: From Error Visibility to Structural Similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612
Willems F, Maas D, Kalker T (2004) Semantic Lossless Source Coding 42nd Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control and Computing, Monticello, Illinois, USA, pp 1411–1418
Wu H-T, Huang J (2012) Reversible image watermarking on prediction errors by efficient histogram modification. Signal Process 92(12):3000–3009
Wu H-T, Dugelay J-L, Shi Y-Q (2015) Reversible Image Data Hiding with Contrast Enhancement. IEEE Signal Process Lett 22(1):81–85
Yang Y, Ming J (2016) Image quality assessment based on the space similarity decomposition model. Signal Process 120:797–805
Yang Y, Zhang WM, Liang D, Yu NH (2016) Reversible Data Hiding in Medical Images with Enhanced contrast in Texture Area. Digital Signal Process 52:13–24
Yin Z-X, Luo B (2016) MDE-based Image Steganography with Large Embedding Capacity. Security and Communication Networks 9(8):721–728
Zhang W, Hu X, Yu N et al (2013) Recursive Histogram Modification: Establishing Equivalency Between Reversible data Hiding and Lossless Data Compression. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(7):2775–2785
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant U1636201,61572452,61502007, in part by the Natural Science Research Project of Anhui province under Grant 1608085MF125, in part by the NO.58 China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant 2015M582015, in part by the backbone teacher training program of Anhui University, in part by the Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Anhui University under Grant J01001319.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Zhang, W., Liang, D. et al. A ROI-based high capacity reversible data hiding scheme with contrast enhancement for medical images. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 18043–18065 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4444-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4444-0