Abstract
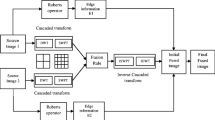
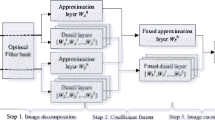
In this paper, the Gaussian Mixture Model and Mean Shift algorithm are used to detect and track moving objects in the visual perception network composed of multiple cameras. And on this basis, a target matching method based on wavelet transform, which is applied in a visual perception network composed by multiple camera, fusing visual information from different cameras is proposed. This method takes local features as basis of target matching, and applies wavelet transformation to detect the feature points that represent important information of the target image, and then extracts the color of the neighborhood of feature points as its salient features. The method of classification and clustering is applied by calculating the distance of salient features vector space to measure similarities of the target features and thus realize target recognition. The test result shows that the method can realize the matching and recognition of moving object with the cooperation among multiple cameras.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali MMN, Abdullah-Al-Wadud M, Lee SL (2014) Multiple object tracking with partial occlusion handling using salient feature points[J]. Inf Sci 278(18):448–465
Burdescu DD, Brezovan M, Ganea E, Stanescu L (2009) A new method for segmentation of images represented in a HSV color space[C]. In: ACIVS 2009, Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems. Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 606–617
Chen R (2015) Image segmentation and target tracking based on Meanshift algorithm[C]. In: International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics (ameii-15.2015.135)
Craglia M, de Bie K et al (2012) Digital earth 2020: towards the vision for the next decade[J]. Int J Digital Earth 5(1):4–21
Draisma J, Horobeţ E et al (2016) The Euclidean distance degree of an algebraic variety[J]. Found Comput Math 16(1):99–149
Riou L, Coudert S, Fayolle J, Ducottet C (2000) A wavelet based multiscale detection scheme of feature points[C]. In: Pattern Recognition, International Conference on, vol 3. pp 3425
Forbes C, Evans M, Hastings N, Peacock B (2010) Normal (Gaussian) Distribution[M]. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, pp 143–148
Girone G, D’Uggento AM (2016) About the mean difference of the inverse normal distribution[J]. Appl Math 7(14):1504–1509
Grzejszczak T, Kawulok M, Galuszka A (2016) Hand landmarks detection and localization in color images[J]. Multimedia Tools Appl 75(23):16363–16387
Gu H-Z, Lee S-Y (2013) A view-invariant and anti-reflection algorithm for car body extraction and color classification[J]. Multimedia Tools Appl 65(3):387–418
Hashem IAT, Chang V, Anuar NB, et al (2016) The role of big data in smart city[J]. Int J Inf Manag 36(5):748–758
X Hu, J Zheng (2016) An improved moving object detection algorithm based on Gaussian mixture models[J]. Open J Appl Sci 6(07):449–456
Hu M, Liu Y, Fan Y (2015) Robust image feature point matching based on structural distance[C]. In: Chinese Conference on Image and Graphics Technologies, IGTA 2015: Advances in Image and Graphics Technologies. pp 142–149
S Kannappan, Y Liu, BP Tiddeman (2016) Performance Evaluation of Video Summaries Using Efficient Image Euclidean Distance[M]. Adv Vis Comput 2016:33–42
Karney C.F.F. (2016) Sampling exactly from the normal distribution[J]. ACM Trans Math Softw 42(1):1–14
Liao W, Zhao XM, Qian SY, Nie Y (2016) Combining with the three-frame difference and improved Gaussian mixture model of moving object detection method[J]. Comput Inf Technol
Liberti L, Lavor C, Maculan N (2012) Antonio Mucherino. Euclidean distance geometry and applications[J]. Quantit Biol 56(1):3–69
Mishchenko Y (2015) A fast algorithm for computation of discrete Euclidean distance transform in three or more dimensions on vector processing architectures[J]. Signal Image Video Process 9(1):19–27
Neirotti P, De Marco A, Cagliano A, Mangano G, Scorrano F (2014) Current trends in Smart City initiatives: some stylised facts[J]. Cities 38:25–36
Pan Z, Liu S, Fu W (2017) A review of visual moving target tracking[J]. Multimedia Tools Appl 76(16):16989–17018
Pasupa K, Pantuwong N, Nopparit S (2015) A comparative study of feature point matching versus foreground detection for computer detection of dairy cows in video frames[J]. Artif Life Robotics 20(4):320–326
Pathak RS, Singh A (2016) Distributional wavelet transform[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect A 86(2):273–277
Priambodo B, Ani N (2016) Count vehicle over region of interest using euclidean distance[J]. Int Res J Comp Sci 3(05). http://www.irjcs.com/volumes/Vol3/iss5/03.MYCS10081.pdf
Rahman MM, Harun-Or-Roshid, Mozid Pk MA, Mamun MAA (2011) A comparative study of wavelet transform and Fourier transform[J]. J Phys Sci 15:149–160
Ratanasanya S, Polvichai J, Sirinaovakul B (2015) Feature point matching with matching distribution. In: Unger H, Meesad P, Boonkrong S (eds) Recent advances in information and communication technology 2015. Advances in intelligent systems and computing, vol. 361. Springer, Cham, pp 9–18
Saravanan G, Yamuna G, Nandhini S (2016) Real time implementation of RGB to HSV/HSI/HSL and its reverse color space models[C]. In: International conference on communication and signal processing(ICCSP). pp 0462–0466
Sattar F, Karray F, Kamel M, Nassar L, Golestan K (2016) Recent advances on context-awareness and data/information fusion in ITS[J]. Int J Intell Transp Syst Res 14(1):1–19
Sindhuja G, Renuka DSM (2015) Comparative analysis of mean shift in object tracking[C]. In: (IEEE 2015) Conference on Power, Control, Communication and Computational Technologies for Sustainable Growth (PCCCTSG). pp 283–287
Skoneczny S (2012) Nonlinear sharpening in the HSV color space[J]. Przegląd Elektrotechniczny 2012(2):140–144
Sriharsha KV, Rao NV (2015) Dynamic scene analysis using Kalman filter and Mean shift tracking algorithms[C]. In: 2015 6th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT). pp 1–8
Sun Y, Feng X (2012) Local feature image fusion algorithm based on wavelet transform[C]. Lect Notes Electr Eng 124(2):711–716
Surkutlawar S, Kulkarni RK (2013) Shadow suppression using RGB and HSV color space in moving object detection[J]. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 4(1):164–169
Utomo FS (2016) Multiple vehicle tracking using adaptive Gaussian mixture model and Kalman filter[J]. Am J Appl Sci 13(12):1407–1412
Vogler N, Bocklitz T, Mariani M et al (2010) Separation of CARS image contributions with a Gaussian mixture model[J]. J Opt Soc Am A 27(6):1361–1371
Wang D, Sun W, Yu S, Li L, Liu W (2016) A novel background-weighted histogram scheme based on foreground saliency for mean-shift tracking[C]. Multimedia Tools Appl 75(17):10271–10289
Xiong T, Zhang L (2016) Double Gaussian mixture model for image segmentation with spatial relationships[J]. J Vis Commun Image Represent 34:135–145
Xu Y, Zhou C, Xu S, Xing C (2014) Moving region detection based on background difference[C]. In: 2014 I.E. Workshop on Electronics, Computer & Applications (IWECA). IEEE, Ottawa, pp 518–521
Yadav D K (2014) Efficient method for moving object detection in cluttered background using Gaussian Mixture Model[C]. In: 2014 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI). IEEE, New Delhi, pp 943–948
Yager RR (2016) Multi-source information fusion using measure representations[M]. In: On Logical, Algebraic, and Probabilistic Aspects of Fuzzy Set Theory, Part of the Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing book series (STUDFUZZ), vol 336. p 199–214
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Bowen DU, Juhua PU, Xiong Z (2016) Multimodal data fusion model for smart city[J]. J Beijing Univ Aeronaut Astronaut 42(12):2683–2690
Zheng Y, Xiao S (2016) Performance analysis of a moving target tracking method based on computer vision[C]. In: 2016 I.E. Eighth International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (ICMTMA). pp 467–470
Zhou Z, Zhou M, Shi X (2016) Target tracking based on foreground probability[J]. Multimedia Tools Appl 75(6):3145–3160
Acknowledgments
The work was supported in part by the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U1536203), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61572214), and the independent innovation research foundation of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Grant No. 2016YXMS089).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, F., Tianjiang, W., Fang, L. et al. Research on multi-camera information fusion method for intelligent perception. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 15003–15026 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5085-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5085-z