Abstract
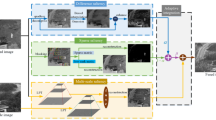
Saliency detection aims to locate the distinctive regions in images and can be extensively applied to many applications. Up to now, most of effort has put into visible images and the related methods usually encounter difficulty for images with complex background. In this paper, we propose a semantic feature based multi-spectral saliency detection method using the complementarity of infrared and visible images. We use the thermal infrared image to relieve the difficulty of visible images with complex background, while still utilizing the rich texture and color information in visible images. Specifically, we firstly uses the Convolutional Neural Network to extract high-level feature from superpixels obtained by segmenting visible and infrared images, and then the initial saliency maps of both spectrums are computed, respectively. After that, two initial saliency maps are fused via a Total Variation (TV) minimization model and finally the fused result is linearly combined with the enhanced foreground salient object map to obtain the final saliency detection result. Experiment results reveal that the proposed method outperforms the baseline methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achanta R, Estrada F, Wils P, Süsstrunk S (2008) Salient region detection and segmentation. In: 6th international conference on computer vision systems (ICVS 2008). Springer, pp 66–75
Bao L, Lu J, Li Y, Shi Y (2015) A saliency detection model using shearlet transform. Multimedia Tools Appl 74(11):4045–4058
Borji A, Cheng MM, Jiang H, Li J (2014) Salient object detection: a survey. arXiv:1411.5878
Borji A, Cheng MM, Jiang H, Li J (2015) Salient object detection: a benchmark. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5706–5722
Chan TF, Esedoglu S (2005) Aspects of total variation regularized l 1 function approximation. SIAM J Appl Math 65(5):1817–1837
Chang X, Ma Z, Lin M, Yang Y, Hauptmann A (2017) Feature interaction augmented sparse learning for fast kinect motion detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(8):3911–3920
Chang X, Ma Z, Yang Y, Zeng Z, Hauptmann AG (2017) Bi-level semantic representation analysis for multimedia event detection. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(5):1180–1197
Chang X, Yang Y (2016) Semisupervised feature analysis by mining correlations among multiple tasks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst PP(99):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2582746
Chang X, Yang Y, Hauptmann AG, Xing EP, Yu Y (2015) Semantic concept discovery for large-scale zero-shot event detection. In: Twenty-fourth international joint conference on artificial intelligence, vol 2. AAAI Press, p 6
Chang X, Yu YL, Yang Y, Xing EP (2017) Semantic pooling for complex event analysis in untrimmed videos. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39 (8):1617–1632. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2608901
Cheng MM, Mitra NJ, Huang X, Torr PH, Hu SM (2015) Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(3):569–582
Felzenszwalb PF, Huttenlocher DP (2004) Efficient graph-based image segmentation. Int J Comput Vis 59(2):167–181
Gao C, Du Y, Liu J, Lv J, Yang L, Meng D, Hauptmann AG (2016) Infar dataset: infrared action recognition at different times. Neurocomputing 212:36–47
Goferman S, Zelnik-Manor L, Tal A (2012) Context-aware saliency detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(10):1915–1926
Han A, Han F, Hao J, Yuan Y (2017) An improved saliency detection method based on non-uniform quantification and channel-weighted color distance. Multimedia Tools Appl 76(8):11,037–11,050
Harel J, Koch C, Perona P et al (2006) Graph-based visual saliency. In: Advances in neural information processing systems 19 (NIPS 2006), vol 1. Curran Associates, Inc, p 5
Hiremath P, Pujari J (2008) Content based image retrieval using color boosted salient points and shape features of an image. Intern J Image Process 2(1):10–17
Itti L (2004) Automatic foveation for video compression using a neurobiological model of visual attention. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(10):1304–1318
Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E (1998) A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20(11):1254–1259
Jiang B, Zhang L, Lu H, Yang C, Yang MH (2013) Saliency detection via absorbing markov chain. In: 2013 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1665–1672
Jiang R, Crookes D (2014) Deep salience: visual salience modeling via deep belief propagation. In: AAAI. AAAI Press, pp 2773–2779
Jiang H, Wang J, Yuan Z, Wu Y, Zheng N, Li S (2013) Salient object detection: a discriminative regional feature integration approach. In: 2013 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 2083–2090
Judd T, Ehinger K, Durand F, Torralba A (2009) Learning to predict where humans look. In: 2009 IEEE 12th international conference on computer vision (ICCV). IEEE, pp 2106–2113
Kanan C, Cottrell G (2010) Robust classification of objects, faces, and flowers using natural image statistics. In: 2010 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 2472–2479
Li X, Lu H, Zhang L, Ruan X, Yang MH (2013) Saliency detection via dense and sparse reconstruction. In: 2013 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 2976– 2983
Lin Y, Kong S, Wang D, Zhuang Y (2014) Saliency detection within a deep convolutional architecture. In: Workshops at the twenty-eighth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
Liu T, Yuan Z, Sun J, Wang J, Zheng N, Tang X, Shum HY (2011) Learning to detect a salient object. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33 (2):353–367
Ma J, Chen C, Li C, Huang J (2016) Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization. Information Fusion 31:100–109
Ma YF, Hua XS, Lu L, Zhang HJ (2005) A generic framework of user attention model and its application in video summarization. IEEE Trans Multimedia 7(5):907–919
Oliva A, Torralba A, Castelhano MS, Henderson JM (2003) Top-down control of visual attention in object detection. In: Proceedings of international conference on image processing, 2003. ICIP 2003, vol 1. IEEE, pp I–253
Perazzi F, Krähenbühl P, Pritch Y, Hornung A (2012) Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 733–740
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv:1409.1556
Torralba A, Oliva A, Castelhano MS, Henderson JM (2006) Contextual guidance of eye movements and attention in real-world scenes: the role of global features in object search. Psychol Rev 113(4): 766
Wang L, Lu H, Ruan X, Yang MH (2015) Deep networks for saliency detection via local estimation and global search. In: 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 3183–3192
Wang Q, Yan P, Yuan Y, Li X (2013) Multi-spectral saliency detection. Pattern Recogn Lett 34(1):34– 41
Wang Q, Zhu G, Yuan Y (2013) Multi-spectral dataset and its application in saliency detection. Comput Vis Image Underst 117(12):1748–1754
Yan Q, Xu L, Shi J, Jia J (2013) Hierarchical saliency detection. In: 2013 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1155–1162
Yan Y, Nie F, Li W, Gao C, Yang Y, Xu D (2016) Image classification by cross-media active learning with privileged information. IEEE Trans Multimedia 18(12):2494–2502
Yan Y, Xu Z, Liu G, Ma Z, Sebe N (2013) Glocal structural feature selection with sparsity for multimedia data understanding. In: Proceedings of the 21st ACM international conference on multimedia. ACM, pp 537–540
Yan Y, Yang Y, Shen H, Meng D, Liu G, Hauptmann AG, Sebe N (2015) Complex event detection via event oriented dictionary learning. In: Twenty-ninth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence. AAAI Press, pp 3841–3847
Yang J, Yang MH (2017) Top-down visual saliency via joint crf and dictionary learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell PP(99):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2582746
Yang Y, Xu D, Nie F, Yan S, Zhuang Y (2010) Image clustering using local discriminant models and global integration. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(10):2761–2773
Zeiler MD, Fergus R (2014) Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 818–833
Zhai Y, Shah M (2006) Visual attention detection in video sequences using spatiotemporal cues. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM international conference on multimedia. ACM, pp 815–824
Zhang D, Han J, Jiang L, Ye S, Chang X (2017) Revealing event saliency in unconstrained video collection. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(4):1746–1758
Zhao R, Ouyang W, Li H, Wang X (2015) Saliency detection by multi-context deep learning. In: 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1265– 1274
Zhu W, Liang S, Wei Y, Sun J (2014) Saliency optimization from robust background detection. In: 2014 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 2814–2821
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61571071), Wenfeng innovationand start-up project of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications (No. WF201404), the National Social Science Foundation of China (No.15BGL2729), the Research Innovation Program for Postgraduate of Chongqing (No. CYS17222). The authors also thank NVIDIA corporation for the donation of GTX 980 GPU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Gao, C., Jian, J. et al. Semantic feature based multi-spectral saliency detection. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 3387–3403 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5152-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5152-5