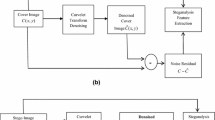
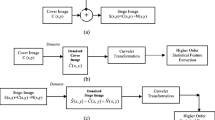
Abstract
Achieving high rates of detection in low rates of embedding is still a challenging problem in many steganalysis systems. The newly proposed steganalysis system based on sparse representation classifier has shown remarkable detection rates in low embedding rate. In this paper, we propose a new steganalysis system based on double sparse representation classifier. We compare our proposed method with other steganalysis systems which use different classifier (including nearest neighbor, support vector machine, ensemble support vector machine and sparse representation). In all of our experiments, input features to the classifier are fixed and the ability of classifier is examined. Also we provide a complexity analysis in terms of execution time for different classifier. In most of experiments, our proposed method shows superior performance in terms of detection rate and complexity for low embedding rates.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abavisani M, Joneidi M, Rezaeifar S, Shokouhi SB (2015) A robust sparse representation based face recognition system for smartphones. IEEE Sig Process Med Biol Symp 12:1–6
Aharon M, Elad M, Bruckstein A (2006) K-svd: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 54(11):4311–4322
Bas P, Filler T, Pevný T (2011) “Break our steganographic system”, The Ins and Outs of organizing BOSS. In Inf Hiding 5:59–70
Candes E, Tao T (2006) Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: universal encoding strategies? IEEE Trans Inf Theory 52(12):5406–5425
Candes E, Romberg J, Tao T (2006) Stable signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements. Comm Pure Appl Math 59(8):1207–1233
Chen S, Donoho D, Saunders M (2001) Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM Rev 43(1):129–159
Constantinos P, Aroukatos N (2014) LSB and DCT steganographic detection using compressive sensing. J Inf Hiding Multimedia Sig Process 5(1):20–32
Donoho D (2006) For most large underdetermined systems of linear equations the minimal l1-norm solution is also the sparsest solution. Comm Pure Appl Math 59(6):797–829
Donoho DL, Elad M, Temlyakov VN (2006) Stable recovery of sparse overcomplete representations in the presence of noise. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 52(1):6–18
Farhat F, Ghaemmaghami S (2015) Towards blind detection of low-rate spatial embedding in image steganalysis. IET Image Process 1:31–42
Friedman JH (2012) Fast sparse regression and classification. Int J Forecast 28(3):722–738
Gao S, Tsang IW, Chia L, Zhao P (2010) Local features are not lonely – Laplacian sparse coding for image classification. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit
Gemmeke JF, Virtanen T, Hurmalainen A (2011) Exemplarbased sparse representations for noise robust automatic speech recognition. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 19(7):2067–2080
Georghiades A, Belhumeur P, Kriegman D (2001) From few to many: Illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(6):643–660
Goljan M, Fridrich J (2015) CFA-aware features for steganalysis of color images. Proc. SPIE, Electronic Imaging, Media Watermarking, Security, and Forensics, San Francisco
Gong R, Wang H (2012) Steganalysis for GIF images based on colors-gradient co-occurrence matrix. Opt Commun, ELSVIER 11:4961–4965
Holub V, Fridrich J, Denemark T (2014) Universal distortion function for steganography in an arbitrary domain. EURASIP J Inf Secur 1:1–13
Huang J, Yang M (2010) Fast sparse representation with prototypes. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 3618–4625
Jiang Z, Lin Z, Davis LS (2011) Learning a discriminative dictionary for sparse coding via label consistent K-SVD. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit
Jinyang S, Xianting Z, Lei W (2015) Steganalysis using regional correlation and second-order Markov features. Int J Secur Appl 9(1):69–76
Kuang-Yu C, Cheng-Fu L, Chu-Song C, Yi-Ping H (2014) Single-pass K-SVD for efficient dictionary learning, springer. Circuits Syst Signal Process 1:309–320
Li W, Zhou Y, Poh N et al (2013) Feature denoising using joint sparse representation for in-car speech recognition. IEEE Sig Process Lett 20(7):681–684
Liang RZ, Shi L, Wang H, Meng J, Wang JJY, Sun Q, Gu Y (2016) Optimizing top precision performance measure of content-based image retrieval by learning similarity function. In: Pattern Recogn (ICPR), 2016 23rd Int Conf (pp. 2954–2958) IEEE
Liu Q, Wang Q, Wu L (2004) Size of the dictionary in matching pursuit algorithm. IEEE Trans Signal Process 52(12):3403–3408
Mairal J, Bach F, Ponce J (2010) Task-driven dictionary learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(4):791–804
Malekmohammadi H, Ghaemmaghami S (2009) Steganalysis of LSB based image steganography using spatial and frequency domain features. IEEE Int Conf Multimedia Expo 7:1744–1747
Matinez AM, Kak AC (2001) PCA versus LDA. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(2):228–233
Nanni L, Brahnam S, Ghidoni S, Menegatti E, Barrier T (2013) A comparison of multi-scale approaches for extracting image descriptors from the co-occurrence matrix. PLoS One, Public Library of Science, Expert Systems with Applications 12:7457–7467
Nene S, Nayar S, Murase H (1996) Columbia object image library (coil-20), technical report CUCS-005-96. Tech Rep
Rubinstein R, Zibulevsky M, Elad M (2010) Double sparsity: Learning sparse dictionaries for sparse signal approximation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 58(3):1553–1564
Sigg CD, Dikk T, Buhmann JM (2010) Speech enhancement with sparse coding in learned dictionaries. Proc. ICASSP, Dallas, pp 4758–4761
Srinivas U, Suo Y, Dao M, Monga V, Tran TD (2015) Structured sparse priors for image classification. IEEE Trans Image Process 6:1763–1776
Tropp JA, Wright SJ (2010) Computational methods for sparse solution of linear inverse problems. Proc IEEE 98(6):948–958
Wang S, Yang J, Sun M, Peng X, Sun M, Zhou C (2012) Sparse tensor discriminant color space for face verification. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23(6):876–888
Wright J, Yang AY, Ganesh A, Sastry SS, Ma Y (2009) Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31(2):210–227
Wright J, Ma Y, Mairal J, Sapiro G, Huwang TS, Yan S (2010) Sparse representation for computer vision and pattern recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 6:1031–1044
Xu B, Wang J, Liu X, Zhang Z (2007) Passive steganalysis using image quality metrics and multi-class support vector machine. Third Int Conf Nat Comput, ICNC 8:215–220
Yamini B, Sabitha R (2013) Blind steganalytic attack as pattern recognition, using K-nearest neighbor classification technique. IEEE 5th Int Conf Adv Comput(ICoAC) 12:543–546
Yu XY, Wang A (2009) An Investigation of genetic algorithm on steganalysis techniques. IEEE Int Conf Intell Inf Hiding Multimedia Sig Process 9:1118–1121
Yu XY, Wang A (2009) Steganalysis based on regression model and bayesion network. IEEE Int Conf Multimedia Inf Netw Secur, MINES'09 11:41–44
Zhang Z, Hu D, Yang Y, Su B (2013) A universal digital image steganalysis method based on sparse representation. Int Conf Comput Intell Secur (CIS) 12:437–441
Zhang S, Wang H, Huang W (2017) Two-stage plant species recognition by local mean clustering and weighted sparse representation classification [J]. Clust Comput:1–9
Zheng Z (2015) A survey of sparse representation: algorithms and applications. IEEE Access 3:490–530
Zou D, Shi YQ, Su W, Xuan G (2006) Steganalysis based on Markov model of thresholded prediction-error image. IEEE Int Conf Multimedia Expo 7:1365–1368
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jalali, A., Farsi, H. & Ghaemmaghami, S. A Universal Image Steganalysis System Based On Double Sparse Representation Classification (DSRC). Multimed Tools Appl 77, 16347–16366 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5201-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5201-0