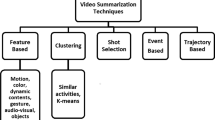
Abstract
Video scene analysis is a recent research topic due to its vital importance in many applications such as real-time vehicle activity tracking, pedestrian detection, surveillance, and robotics. Despite its popularity, the video scene analysis is still an open challenging task and require more accurate algorithms. However, the advances in deep learning algorithms for video scene analysis have been emerged in last few years for solving the problem of real-time processing. In this paper, a review of the recent developments in deep learning and video scene analysis problems is presented. In addition, this paper also briefly describes the most recent used datasets along with their limitations. Moreover, this review provides a detailed overview of the particular challenges existed in real-time video scene analysis that has been contributed towards activity recognition, scene interpretation, and video description/captioning. Finally, the paper summarizes the future trends and challenges in video scene analysis tasks and our insights are provided to inspire further research efforts.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulnabi AH, Wang G, Lu J, Jia K (2015) Multi-task CNN model for attribute prediction. IEEE Trans Multimedia 17(11):1949–1959. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2015.2477680
Acar E, Hopfgartner F, Albayrak S (2016) A comprehensive study on mid-level representation and ensemble learning for emotional analysis of video material. J Multimedia Tools Appl 76(9):11809–11837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3618-5
Ba J, Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K (2015) Multiple object recognition with visual attention. In: Proceedings of Int Conf on Learning Representations (ICLR'15). San Diego, California, USA
Baccouche M, Mamalet F, Wolf C, Garcia C, Baskurt A (2012) Sparse shift-invariant representation of local 2D patterns and sequence learning for human action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 21st Int Conf on pattern recognition (ICPR'12), pp 3823–3826. doi:10.11385.6048
Ballan L, Bertini M, Bimbo AD, Seidenari L, Serra G (2012) Effective codebooks for human action representation and classification in unconstrained videos. IEEE Trans Multimedia 14(4):1234–1245. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2012.2191268
Ballas N, Yao L, Pal C, Courville AC (2016) Delving deeper into convolutional networks for learning video representations. In: Proceedings of Int Conf on Learning Representations (ICLR'16), San Juan, Puerto Rico
Barros P, Jirak D, Weber C, Wermter S (2015) Multimodal emotional state recognition using sequence dependent deep hierarchical features. J Neural Netw 72:140–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2015.09.009.
Bengio Y, Lamblin P, Popovici D, Larochelle H (2006) Greedy layer-wise training of deep networks. In: Proceedings of the 19th Int Conf on neural information processing systems (NIPS'06). MIT Press, Canada, pp 153–160
Chan C-S, Chen S-Z, Xie P-X, Chang C-C, Sun M (2016) Recognition from hand cameras: a revisit with deep learning. In: Proceedings part IV of 14th European Conf computer vision (ECCV'16). Springer Int Publishing, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp 505–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0 31
Charalampous K, Gasteratos A (2016) On-line deep learning method for action recognition. J of. Pattern Anal Applic 19(2):337–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-014-0404-8.
Chen DL, Dolan WB (2011) Collecting highly parallel data for paraphrase evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL'11), Portland, OR, USA
Cho K, Courville A, Bengio Y (2015) Describing multimedia content using attention-based encoder-decoder networks. IEEE Tran Multimedia 17(11):1875–1886. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2015.2477044
Ciresan DC, Giusti A, Gambardella LM, Schmidhuber J (2012) Deep neural networks segment neuronal membranes in electron microscopy images. In: Proceedings of Conf on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA, pp. 2852–2860
Couprie C, Farabet C, Najman L, LeCun Y (2013) Indoor semantic segmentation using depth information. In: Internatinal Conf on Learning Representation (ICLR'13), Scottsdale, AZ, USA, pages 8
Dollar P, Wojek C, Schiele B, Perona P (2012) Pedestrian detection: an evaluation of the state of the art. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(4):743–761. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2011.155
Donahue J, Hendricks LA, Guadarrama S, Rohrbach M, Venugopalan S, Saenko K, Darrell T (2016) Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conf on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR'15). MA, USA, Boston, pp 2625–2634
Etezadifar P, Farsi H (2016) Scalable video summarization via sparse dictionary learning and selection simultaneously. J Multimedia Tools Appl 76(6):7947–7971. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3433-z
Evans KK, Horowitz TS, Howe P, Pedersini R, Reijnen E, Pinto Y, Kuzmova Y, Wolfe JM (2011) Visual Attention. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci 2(5):503–514
Farabet C, Couprie C, Najman L, LeCun Y (2013) Learning hierarchical features for scene labeling. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(8):1915–1929. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.231
Farrajota M, Rodrigues JMF, du Buf, JMH (2016) A Deep Neural Network Video Framework for Monitoring Elderly Persons. In: Proceedings Part II of 10th International Conference Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction (UAHCI2016), pp. 370–381, Toronto, ON, Canada, July 2016
Fukushima K (1980) Neocognitron: a self-organizing neural network model for a mechanism of pattern recognition unaffected by shift in position. J of. Biol Cybern 36(4):193–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00344251
Gao X, Zhang T (2015) Unsupervised learning to detect loops using deep neural networks for visual SLAM system. J of. Auton Robot 41(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-015-9516-2
Gilani SO, Jamil M, Fazal Z, Naveed MS, Sakina R (2016) Automated scene analysis by image feature extraction. In: Proceedings of IEEE 14th Intl Conf on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure. Computing:530–536. https://doi.org/10.1109/DASC-PICom-DataCom-CyberSciTec.2016.102
Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, Malik J (2014) Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'14), IEEE computer society, Columbus, Ohio, USA, pp. 580–587, doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.81
Graves A, Mohamed AR, Hinton G (2013) Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks. Proceedings of the IEEE Int Conf on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing:6645–6649. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2013.6638947
Guadarrama S, Krishnamoorthy N, Malkarnenkar G, Venugopalan S, Mooney R, Darrell T, Saenko K (2013) YouTube2Text: recognizing and describing arbitrary activities using semantic hierarchies and zero-shot recognition. In: Proceedings of IEEE Int Conf on computer vision (ICCV'13), pp. 2712–2719, doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2013.337
Guo Y, Liu Y, Oerlemans A, Lao S, Wu S, Lew MS (2016) Deep learning for visual understanding. J of Neurocomput 187(C):27–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.09.116
Hasan M, Roy-Chowdhury AK (2015) A continuous learning framework for activity recognition using deep hybrid feature models. IEEE Trans Multimedia 17(11):1909–1922. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2015.2477242
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2015) Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. In: IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 37(9):1904–1916. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824
Hinton GE (2007) Learning multiple layers of representation. Trends Cogn Sci 11(10):428–434
Hinton G, Deng L, Yu D, Dahl GE, Mohamed RA, Jaitly N, Senior A, Vanhoucke V, Nguyen P, Sainath TN, Kingsbury B (2012) Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: the shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal Proc. Magaz 29(6):82–97. https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2012.2205597
Ho C-T, Lin Y-H, Wu J-L (2016) Emotion prediction from user-generated videos by emotion wheel guided deep learning. In: Proceedings of 23rd Int Conf on Neural Information Processing (ICONIP'16), springer Int publishing, Kyoto, Japan, pp. 3–12, doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46687-3 1
Hong C, Yu J, Wan J, Tao D, Wang M (2015) Multimodal deep autoencoder for human pose recovery. IEEE Trans Image Proc 24(12):5659–5670. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2487860
Huang S, Li X, Zhang Z, He Z, Wu F, Liu W, Tang J, Zhuang Y (2016) Deep learning driven visual path prediction from a single image. IEEE Trans Image Proc. 25(12):5892–5904. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2613686
Husain F, Dellen B, Torras C (2016) Action recognition based on E_cient deep feature learning in the Spatio-temporal domain. IEEE Robo Auto Lett 1(2):984–991. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2016.2529686
Ji S, Xu W, Yang M, Yu K (2013) 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):221–231. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59
Jiang Y-G, Ye G, Chang S-F, Ellis D, Loui AC (2011) Consumer video understanding: a benchmark database and an evaluation of human and machine performance. In: Proceedings of ACM Int Conf on Multimedia Retrieval (ICMR'11), Trento, Italy
Jiu M, Wolf C, Taylor G, Baskurt A (2014) Human body part estimation from depth images via spatially-constrained deep learning. Pattern Recogn Lett 50(C:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2013.09.021
Kaya H, Salah AA (2016) Combining modality-specific extreme learning Machines for Emotion Recognition in the wild. J on Multimodal User. Interfaces 10(2):139–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12193-015-0175-6.
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, and Hinton GE (2012) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS'12) vol 1, USA, p 1097–1105
Kong Y, Fu Y (2016) Human activity recognition and prediction, springer Int publishing, Switzerland, chapter "action recognition and human interaction", pp. 23-48. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27004-3 2
Koppula HS, Gupta R, Saxena A (2013) Learning human activities and object affordances from RGB-D videos. Int J Rob Res (IJRR) 32(8):951–970
Lai K, Bo L, Ren X, Fox D (2011) A large-scale hierarchical multi-view RGB-D object dataset. In: proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA'11), shanghai, China, pp. 1817–1824, doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2011.5980382
Le QV, Zou WY, Yeung SY, Ng AY (2011) Learning hierarchical invariant Spatio-temporal features for action recognition with independent subspace analysis. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'11), Colorado Springs, USA, pp. 3361-3368, 24 https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995496
LeCun Y, Boser B, Denker JS, Henderson D, Howard RE, Hubbard W, Jackel LD (1989) Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. J of Neural Comput 1(4):541–551. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1989.1.4.541
Lee K, Su Y, Kim T-K, Demiris Y (2013) A syntactic approach to robot imitation learning using probabilistic activity grammars. J of Robot Auton Syst 61(12):1323–1334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.robot.2013.08.003
Lee JT, Lim K-T, Chung Y, Sugimoto A (2016) Moving shadow detection from background image and deep learning. In: Proceedings of Image and Video Technology (IVT'15), workshops, Auckland, New Zealand, pp. 299–306, doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-30285-0 24
Li S, Zhang W, Chan AB (2015a) Maximum-margin structured learning with deep networks for 3D human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of IEEE Int Conf on computer vision(ICCV), pp. 2848–2856, doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.326g
Li S-Z, Yu B, Wu W, Su S-Z, Ji R (2015b) Feature learning based on SAE-PCA network for human gesture recognition in RGBD images. J Neurocomputing 151:565–573
Li T, Chang H, Wang M, Ni B, Hong R, Yan S (2015c) Crowded scene analysis: a survey. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 25(3):367–386. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2014.2358029
Li H, Li Y, Porikli F (2016) DeepTrack: learning discriminative feature representations online for robust visual tracking. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(4):1834–1848. ISSN 1057-7149. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2510583
Lin Z, Yuan C (2016) A very deep sequences learning approach for human action recognition. In: Proceedings of 22nd Int Conf on MultiMedia Modeling, springer Int publishing, Miami, FL, USA, pp. 256–267. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27674-8 23
Lin T et al (2014) Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. In: Proceedings of the 13th European conference on computer vision (ECCV'14), Zurich, Switzerland, pp. 740–755. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
Lin L, Wang K, Zuo W, Wang M, Luo J, Zhang L (2016) A deep structured model with radius-margin bound for 3D human activity recognition. Int J Comput Vision 118(2):256–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-015-0876-z.
Liu N, Han J, Zhang D, Wen S, Liu T (2015a) Predicting eye fixations using convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conf on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR'15), pp. 362–370. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298633
Liu Y, Guo Y, Wu S, Lew M (2015b) DeepIndex for accurate and efficient image retrieval. In: Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval (ICMR'15), shanghai, China, pp. 43–50, doi:https://doi.org/10.1145/2671188.2749300
Liu J, Shahroudy A, Xu D, Wang G (2016a) Spatio-temporal LSTM with trust gates for 3D human action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conf computer vision (ECCV'16). Netherlands, Amsterdam, pp 816–833. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46487-9-50
Liu M, Wang R, Li S, Huang Z, Shan S, Chen X (2016b) Video modeling and learning on Riemannian manifold for emotion recognition in the wild. J on Multimodal User. Interfaces 10(2):113–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12193-015-0204-5.
Ma Z, Yang Y, Sebe N, Zheng K, Hauptmann AG (2013) Multimedia event detection using a classifier-specific intermediate representation. IEEE Trans on Multimedia 15(7):1628–1637. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2013.2264928
Marszalek M, Laptev I, Schmid C (2009) Actions in context. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conf on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR'09), pp. 2929–2936. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206557
Mathieu M, Couprie C, LeCun Y (2016) Deep multi-scale video prediction beyond mean square error. In: Proceedings of Int Conf on Learning Representations (ICLR'16), San Juan, Puerto Rico
Mnih V, Heess N, Graves A, Kavukcuoglu K (2014) Recurrent models of visual attention. In: Collections of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, No. 27, Curran Associates, Inc., pp. 2204–2212
Mocanu DC, Bou Ammar H, Lowet D, Driessens K, Liotta A, Weiss G, Tuyls K (2015) Factored four way conditional restricted Boltzmann Machines for Activity Recognition. Pattern Recogn Lett 66(C:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2015.01.013
Neumann B, Möller R (2008) On scene interpretation with description logics. J of. Image Vis Comput 26(1):82–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2007.08.013
Ouyang W, Zeng X, Wang X (2016) Learning mutual visibility relationship for pedestrian detection with a deep model. Int J Comput Vision 120(1):14–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-016-0890-9
Pan Y, Mei T, Yao T, Li H, Rui Y (2016) Jointly modeling embedding and translation to bridge video and language. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conf on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR'16), pp. 4594–4602, doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.497
Pei L, Ye M, Zhao X, Dou Y, Bao J (2016a) Action recognition by learning temporal slowness invariant features. J Visual Comput 32(11):1395–1404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-015-1090-2
Pei L, Ye M, Zhao X, Xiang T, Li T (2016b) Learning Spatio-temporal features for action recognition from the side of the video. J SIViP 10(1):199–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-014-0726-4.
Perez M, Avila S, Moreira D, Moraes D, Testoni V, Valle E, Goldenstein S, Rocha A (2017) Video pornography detection through deep learning techniques and motion information. J Neurocomput 230:279–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.12.017
Pigou L, van den Oord A, Dieleman S, Herreweghe MV, Dambre J (2016) Beyond temporal pooling: recurrence and temporal convolutions for gesture recognition in video. Int J of Computer Vision https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-016-0957-7
Poppe R (2010) A survey on vision-based human action recognition. J Image Vision Comput 28(6):976–990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2009.11.014.
Revathi AR, Kumar D (2016) An efficient system for anomaly detection using deep learning classifier. J of. SIViP 11(2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-016-0935-0
Rohrbach A, Rohrbach M, Schiele B (2015) The long-short story of movie description. In: Proceedings of 37th German Conf on Pattern Recognition (GCPR'15), springer Int publishing, Aachen, Germany, pp. 209–221, doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24947-6 17
Ronao CA, Cho S-B (2016) Human activity recognition with smartphone sensors using deep learning neural networks. J Expert Syst Appl 59:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.04.032
Salakhutdinov R, Hinton GE (2009) Deep Boltzmann Machines. In: Proceedings of the twelfth Int Conf on artificial intelligence and statistics (AISTATS'09), Clearwater Beach, Florida, USA, pp. 448–455
Sarkar S, Venugopalan V, Reddy K, Ryde J, Jaitly N, Giering M (2016) Deep learning for automated occlusion edge detection in RGB-D frames. J Signal Process Syst 88(2):205–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-016-1209-3
Schuldt C, Laptev I, Caputo B (2004) Recognizing human actions: a local SVM approach. In: Proceedings of the 17th Int Conf on Pattern Recognition (ICPR'04), vol 3, pp. 32–36
Sermanet P, Kavukcuoglu K, Chintala S, Lecun Y (2013) Pedestrian detection with unsupervised multistage feature learning. In: Proceedings of the 2013 I.E. Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'13), IEEE computer society, Portland, Oregon, pp. 3626–3633, doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.465
Shahroudy A, Liu J, Ng T-T, Wang G (2016) NTU RGB+D: a large scale dataset for 3D human activity analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'16), Las Vegas, NV, USA, pp. 1010–1019, doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.115
Shen J, Wang M, Chua T-S (2016) Accurate online video tagging via probabilistic hybrid modeling, journal of. Multimedia Systems 22(1):99–113
Shuai B, Wang G, Zuo Z, Wang B, Zhao L (2015) Integrating parametric and non-parametric models for scene labeling. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conf on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR'15). MA, USA, Boston, pp 4249–4258. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299053
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. Computing research repository (CoRR), vol abs/1409.1556
Singh S, Velastin SA, Ragheb H (2010) MuHAVi: a multicamera human action video dataset for the evaluation of action recognition methods. In: Proceedings of the 7th IEEE Int Conf on advanced video and signal based surveillance, pp. 48–55, doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/AVSS.2010.63
Singh S, Hoiem D, Forsyth D (2015) Learning a sequential search for landmarks. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conf on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR'15), pp. 3422–3430, doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298964
Soomro K, Zamir AR (2014) Computer vision in sports, Springer Int Publishing, chapter "action recognition in realistic sports videos", pp. 181-208. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09396-3 9
Sun B, Xu Q, He J, Yu L, Li L, Wei Q (2016) Audio-video based multimodal emotion recognition using SVMs and deep learning. In: Proceedings of 7th Chinese Conf on pattern recognition (CCPR2016). Springer Singapore, Chengdu, pp 621–631. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3005-5 51
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, 2015, pp 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594
Tome D, Monti F, Baroffo L, Bondi L, Tagliasacchi M, Tubaro S (2016) Deep convolutional neural networks for pedestrian detection. J of Signal Processing: Image Communication 47:482–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.image.2016.05.007
Trumble M, Gilbert A, Hilton A, Collomosse JP (2016) Learning Markerless human pose estimation from multiple viewpoint video. In: Proceedings part III of computer vision (ECCV'16). Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp 871–878. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49409-8 70
Varior RR, Wang G, Lu J, Liu T (2016) Learning invariant color features for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. on Image Proc. 25(7):3395–3410. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2531280
Venugopalan S, Rohrbach M, Donahue J, Mooney R, Darrell T, Saenko K (2015a) Sequence to Sequence-Video to Text. In: Proceedings of IEEE Int Conf on computer vision (ICCV'15), pp. 4534–4542, doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.515
Venugopalan S, Xu H, Donahue J, Rohrbach M, Mooney RJ, Saenko K (2015b) Translating videos to natural language using deep recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of Conf of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT'15), Denver, Colorado, USA, pp. 1494–1504
Vincent P, Larochelle H, Bengio Y, Manzagol P-A (2008) Extracting and composing robust features with Denoising autoencoders. In: Proceedings of the 25th Int Conf on Machine Learning (ICML'08), ACM, Helsinki, Finland, pp. 1096–1103, doi:https://doi.org/10.1145/1390156.1390294
Wang D (2007) Challenges for computational intelligence, springer, berlin, Germany, chapter "computational scene analysis", pp. 163-191
Wang L, Sng D (2015) Deep learning algorithms with applications to video analytics for a Smart City: a survey. CoRR, https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03131v1
Wang C, Yang H, Meinel C (2016) A deep semantic framework for multimodal representation learning. J of. Multimedia Tools Appl 75(15):9255–9276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3380-8.
Wu C, Cheng H-P, Li S, Li HH, Chen Y (2016) ApesNet: a pixel-wise efficient segmentation network. In proceedings of the 14th ACM/IEEE symposium on embedded Systems for Real-Time Multimedia (ESTIMedia'16), pp. 2-8, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, October 2016. ACM. ISBN 978-1-4503-4543-9. doi:https://doi.org/10.1145/2993452.2994306
Wu G, Liu L, Guo Y, Ding G, Han J, Shen J, Shao L (2017). Unsupervised deep video hashing with balanced rotation. In processing of the twenty-sixth international joint conference on artificial intelligence (IJCAI’17), pp. 3076-3082, Melbourne, Australia, august 2016. 10.24963/ijcai.2017/429
Xia D-X, S-Z S, Geng L-C, G-X W, Li S-Z (2016) Learning rich features from Objectness estimation for human lying-pose detection. J Multimedia Syst 23(4):515–526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-016-0518-5
Xu W, Miao Z, Zhang J, Tian Y (2015) Learning Spatio-temporal features for action recognition with modified hidden conditional random field. In: Proceedings, Part I of Computer Vision (ECCV'14), workshops, springer Int publishing, Zurich, Switzerland, pp. 786–801, doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16178-5 55
Xu D, Yan Y, Ricci E, Sebe N (2017) Detecting anomalous events in videos by learning deep representations of appearance and motion. Elsevier J Comput Vis Image Underst 156:117–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2016.10.010.
Yao L, Torabi A, Cho K, Ballas N, Pal C, Larochelle H, Courville A (2015) Describing videos by exploiting temporal structure. In: Proceedings of IEEE Int Conf on computer vision (ICCV'15), pp. 4507–4515, doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.512
Young P, Lai A, Hodosh M, Hockenmaier J (2014), From image descriptions to visual denotations: new similarity metrics for semantic inference over event descriptions. Trans. of the Association for Computational Linguistics (TACL), 2(Feb.):67–78.
Zeiler MD, Fergus R (2014) Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In: Proceedings Part I of the 13th European Conf Computer Vision (ECCV'14), Zurich, Switzerland, pp. 818–833, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10590-1 53
Zhang Y, Li X, Zhang ZM, Wu F, Zhao L (2015) Deep learning driven Blockwise moving object detection with binary scene modeling. J Neurocomputing 168:454–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.05.082.
Zhang W, Duan P, Gong W, Lu Q, Yang S (2016a) A load-aware pluggable cloud framework for real-time video processing. IEEE Trans Industrial Inf 12(6):2166–2176. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2016.2560802
Zhang X, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Wang M, Luan H, Li J, Chua TS (2016b) Deep fusion of multiple semantic cues for complex event recognition. IEEE Trans Image Proc. 25(3):1033–1046. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2511585
Zhao F, Huang Y, Wang L, Xiang T, Tan T (2016) Learning relevance restricted Boltzmann machine for unstructured group activity and event understanding. Int J Comput Vis 119(3):329–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-016-0896-3
Zhou B, Tang X, Wang X (2015) Learning collective crowd behaviors with dynamic pedestrian-agents. Int J Comput Vis 111(1):50–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-014-0735-3
Zhu Y, Kiros R, Zemel R, Salakhutdinov R, Urtasun R, Torralba A, Fidler S (2015) Aligning books and movies: towards story-like visual explanations by watching movies and reading books. In: Proceedings of IEEE Int Conf on Computer Vision (ICCV'15), pp. 19-27, doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.11
Zhu F, Shao L, Xie J, Fang Y (2016a) From handcrafted to learned representations for human action recognition: a survey. J Image Vis Comput 55:42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2016.06.007.
Zhu X, Loy CC, Gong S (2016b) Learning from multiple sources for video summarisation. Int J Comput Vis 117(3):247–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-015-0864-3
Zuniga MD, Bremond F, Thonnat M (2013) Hierarchical and incremental event learning approach based on concept formation models. J of Neurocomputing 100:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2012.02.038
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbas, Q., Ibrahim, M.E.A. & Jaffar, M. Video scene analysis: an overview and challenges on deep learning algorithms. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 20415–20453 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5438-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5438-7