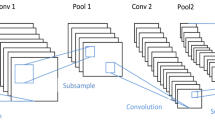
Abstract
The recognition of human actions in a video sequence still remains a challenging task in the computer vision community. Several techniques have been proposed until today such as silhouette detection, local space-time features and optical flow techniques. In this paper, a supervised way followed by an unsupervised learning using the principle of the auto-encoder is proposed to address the problem. We introduce a new foreground detection architecture based on information extracted from the Gaussian mixture model (GMM) incorporating with the uniform motion of Magnitude of Optical Flow (MOF). Thus, we use a fast dynamic frame skipping technique to avoid frames that contain irrelevant motion, making it possible to decrease the computational complexity of silhouette extraction. Furthermore a new technique of representations to construct an informative concept for human action recognition based on the superposition of human silhouettes is presented. We called this approach history of binary motion image (HBMI).Our method has been evaluated by a classification on the Ixmas, Weizmann, and KTH datasets, the Sparce Stacked Auto-encoder (SSAE), an instance of a deep learning strategy, is presented for efficient human activities detection and the Softmax (SMC) for the classification. The objective of this classifier in deep learning is the learning of function hierarchies with higher-level functions at lower-level functions of the hierarchy to provide an agile, robust and simple method. The results prove the efficiency of our proposed approach with respect to the irregularity in the performance of an action shape distortion, change of point of view as well as significant changes of scale.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdessamad J, ElAdel A, Zaied M (2017) A sparse representation-based approach for copy-move image forgery detection in smooth regions. In: Ninth international conference on machine vision (ICMV 2016). International Society for Optics and Photonics, vol 10341, p 1034129
Abidine MB, Fergani B Evaluating a new classiffication method using pca to human activity recognition.. In: Proceeding of International Conference on Computer Medical Applications (ICCMA). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCMA.2013.6506158
Bellil W, Amar C, Ben ZM et al (2004) La fonction Beta et ses dérivées: vers une nouvelle famille d’ondelettes. In: First international conference on signal, system and design, SCS, pp 201–207
Benezeth Y, Jodoin PM, Kulkarni BM (2010) Histogram based foreground object extraction for indoor and outdoor scenes, ICVGIP
Blank M, Gorelick L, Shechtman E et al (2005) Actions as space-time shapes. In: Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2005. ICCV 2005. IEEE, pp 1395–1402
Bobick A, Davis J The recognition of human movement using temporal templates, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence
Bradski1 GR, Davis JW (2002) Motion segmentation and pose recognition with motion history gradients. Mach Vis Appl 13:174–184
Chaaraoui A, Climent-Prez P (2013) Silhouette-based human action recognition using sequences of key poses. In: Pattern Recogn Lett Elsevier, vol 34, pp 1799–1807
Chandrashekhar V, Venkatesh K (2006) Action energy images for reliable human action recognition. Action energy images for reliable human action recognition
Chang Z, Ban X, Shen JG (2015) Research on three-dimensional motion history image model and extreme learning machine for human body movement trajectory recognition. Mathematical Problems in Engineering
Chaudhry R, Oi F, Kurillo G, Bajcsy R (2014) Bio-inspired dynamic 3D discriminative skeletal features for human action recognition. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW 315 ’13), pp 471–478
Chen C-Y, Hsu C-T, Yeh C-H, Chen M-J (2007) Arbitrary frame skipping transcoding through spatialtemporal complexity analysis. In: IEEE Conference on Region 10 Conference TENCON, pp 1–4
Cheriyadat AM (2014) Unsupervised feature learning for aerial scene classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 52:439–451
Dobhal T, Shitole V, Thomas G, Navada G (2015) Human activity recognition using binary motion image and deep learning. In: Proceeding of Computer Science Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.08.050, vol 58
Ejbali R, et Zaied M (2018) A dyadic multi-resolution deep convolutional neural wavelet network for image classification. Multimed Tool Appl 77(5):6149–6163
Ejbali R, Zaied M, et Amar CB (2010) Intelligent approach to train wavelet networks for recognition system of arabic words. In: KDIR, pp 518–522
Ejbali R, Zaied M, et Amar CB (2013) Face recognition based on beta 2D elastic bunch graph matching. In: 2013 13th International Conference on Hybrid Intelligent Systems (HIS). IEEE, pp 88–92
ElAdel A, Ejbali R, Zaied M, Amar CB (2016) A hybrid approach for Content-Based Image Retrieval based on Fast Beta Wavelet network and fuzzy decision support system. Mach Vis Appl 27(6):781–799
Fast DCNN based on FWT, intelligent dropout and layer skipping for image retrieval
Gnouma M, Ejbali R, et Zaied M (2017) Human fall detection based on block matching and silhouette area. In: Ninth International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2016). International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 1034105
Gnouma M, Ejbali R, et Zaied M (2018) Abnormal events’ detection in crowded scenes. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 1–22
Hassairi S, Ejbal R, Zaied M (2015) A deep convolutional neural wavelet network to supervised arabic letter image classiffication. In: 15th International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications (ISDA). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISDA.2015.7489226
Hassairi S, Ejbal R, Zaied M (2016) Supervised image classiffication using deep convolutional wavelets network. In: 27th International Conference on Tools with Artifficial Intelligence (ICTAI). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTAI.2015.49
Hassairi S, Ejbal R, Zaied M (2017) A deep stacked wavelet auto-encoders to supervisedfeature extraction to pattern classiffication. In: Multimedia Tools and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4461-z. Springer
Hassairi S, Ejbali R, et Zaied M (2016) Sparse wavelet auto-encoders for image classification. In: 2016 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA). IEEE, pp 1–6
Horn BKP, Schunck BG (1981) Determining optical flow. Artif Intell 17:185–203
Hwang J-N, Wu T-D, Lin C-W (1998) Dynamic frame-skipping in video transcoding. In: IEEE Conference on Works Multimedia Signal Processing, pp 616–621
Jalal A, Uddin M, Kim T (2012) Depth video-based human activity recognition system using translation and scaling invariant features for life logging at smart home. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 58(3):863–871
Jemai O, Ejbali R, Zaied M et al (2015) A speech recognition system based on hybrid wavelet network including a fuzzy decision support system. In: Seventh International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2014). International Society for Optics and Photonics, pp 944–503
Jia K, Yeung D (2008) Human action recognition using local spatio-temporal discriminant embedding, IEEE Conference Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Karthikeyan S, Gaur U, Manjunath B (2011) Probabilistic subspace-based learning of shape dynamics modes for multi-view action recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops)
Ke S, Thuc H, Lee Y, Hwang J, Yoo J (2013) A review on video based human activity recognition. https://doi.org/10.3390/280computers2020088
Khatrouch M, Gnouma M, Ejbali R et al (2018) Deep learning architecture for recognition of abnormal activities. In: Tenth International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2017). International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 106960F
Ladjailia A, BOUCHRIKA I, Harrati N et al (2018) Encoding human motion for automated activity recognition in surveillance applications. In: Computer vision: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications. IGI Global, pp 2042–2064
Ladjailia A, Bouchrika AL, Merouani H (2016) On the use of local motion information for human action recognition via feature selection. In: 4th International Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE). https://doi.org/10.1109/INTEE.2015.7416792
Li ZZW, Liu Z (2008) Expandable data-driven graphical modeling of human 320 actions based on salient postures. In: IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, pp 1499–1510
Liu H, Ju Z, Ji X et al (2017) Study of human action recognition based on improved spatio-temporal features. In: Human Motion Sensing and Recognition. springer, Berlin, pp 233–250
Lucas BD, Kanade T et al (1981) An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision
Lv F, Nevatia R (2007) Single view human action recognition using key pose matching and viterbi path searching. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1–8
Maity S, Bhattacharjee D, Amlan C (2016) A novel approach for human action recognition from silhouette images. Elsevier IETE Journal of Research
Mariem G, Ridha E, Mourad Z (2016) Detection of abnormal movements of a crowd in a video scene. In: International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering, pp 398–402
Meng B, Liu XJ, et Wang X (2018) Human action recognition based on quaternion spatial-temporal convolutional neural network and LSTM in RGB videos. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 1–18
Qi J, Yang Z Learning dictionaries of sparse codes of 3d movements of body joints for real-time human activity understanding, Journals PloS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114147
Schuldt C, Laptev I, Caputo B (2004) Recognizing human actions: a local svm approach. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2004. ICPR 2004, vol 3. IEEE, pp 32–36
Seo J-J, Kim H-I, De Neve W et al (2017) Effective and efficient human action recognition using dynamic frame skipping and trajectory rejection. Image Vis Comput 58:76–85
Singh V, Nevatia R (2011) Action recognition in cluttered dynamic scenes using pose-speciffic part models. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 113–120
Sivagami M, Revathi T, et Jeganathan L (2017) An optimised background modelling for efficient foreground extraction. Int J High Performance Comput Netw 10 (1-2):44–53
Teyeb I, Jemai O, Zaied M et al (2014) A novel approach for drowsy driver detection using head posture estimation and eyes recognition system based on wavelet network. In: The 5th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems and Applications, IISA 2014. IEEE, pp 379–384
The data is available on the perception website http://perception.inrialpes
Wang L, Tan T, Ning H, Hu W (2003) Silhouette analysis-based gait recognition for human identiffication. In: IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, pp 1505–1518
Wang ZL, Wu Y (2014) Learning actionlet ensemble for 3d human action recognition. Part Ser Springer Briefs Comput Sci 260:11–40
Willems TTG, Gool LV An eficient dense and scale-invariant spatio-temporal interest point detector, Proceeding of the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision
Willems TTG, Gool LV An eficient dense and scale-invariant spatio-temporal interest point detector, Proceeding of the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision
Yu S, Cheng Y, Su S et al (2017) Stratified pooling based deep convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. Multimed Tool Appl 76(11):13367–13382
Yu ZL, Yuan J (2014) Iscriminative orderlet mining for real-time recognition of human-object interaction. In: Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision
Zaied M, Mohamed R, et Amar CB (2012) A power tool for content-based image retrieval using multiresolution wavelet network modeling and dynamic histograms. In: International Review on Computers and Software (IRECOS), vol 7
Zhen X, Shao X (2014) Action recognition by spatio-temporal oriented energies, Information Sciences, Elsevier
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of this work by grants from General Direction of scientific Research (DGRST), Tunisia, under the ARUB program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gnouma, M., Ladjailia, A., Ejbali, R. et al. Stacked sparse autoencoder and history of binary motion image for human activity recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 2157–2179 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6273-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6273-1