Abstract
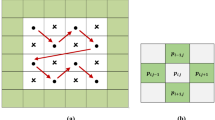
The performance of prediction-error expansion (PEE) for reversible data hiding (RDH) is excellent. 2D and 3D PEE has a great improvement than the conventional PEE. However, the PEE-based method used in each channel of a color image cannot make full use of the correlation among three channels. In the paper, a reversible data hiding algorithm based on 3D PEE mapping is proposed. Firstly, a prediction-error triple is generated from three channels of a color image. Next, the prediction error triples can shift freely in 3D space. Finally, specific error triples have been shifted to embed secret data and other triples are expanded to make room for data embedding. By using the proposed reversible 3D PEE mapping, the inter-correlation of RGB channels is better exploited. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms the traditional RDH methods for color images.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai S, Li X, Liu J, et al (2016) A new reversible data hiding scheme exploiting high-dimensional prediction-error histogram. In: IEEE international conference on image processing. IEEE, pp. 2732–2736
Celik MU, Sharma G, Tekalp AM et al (2005) Lossless generalized-LSB data embedding. IEEE Trans Image Process 14(2):253
Coltuc D (2012) Low distortion transform for reversible watermarking. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(1):412
Coltuc D, Chassery JM (2007) Very Fast Watermarking by Reversible Contrast Mapping. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 14(4):255–258
Fridrich J, Goljan M, Du R (2002) Lossless data embedding: new paradigm in digital watermarking. Eurasip Journal on Advances in Signal Processing 2002(2):986842
Hong W, Chen TS (2011) Reversible data embedding for high quality images using interpolation and reference pixel distribution mechanism. J Vis Commun Image Represent 22(2):131–140
Hu Y, Lee HK, Li J (2009) DE-Based Reversible Data Hiding With Improved Overflow Location Map. IEEE Transactions on Circuits & Systems for Video Technology 19(2):250–260
Lee S, Chang DY, Kalker T (2007) Reversible Image Watermarking Based on Integer-to-Integer Wavelet Transform. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics & Security 2(3):321–330
Li J, Li X, Yang B (2013) Reversible data hiding scheme for color image based on prediction-error expansion and cross-channel correlation. Signal Process 93(9):2748–2758
Li X, Zhang W, Gui X et al (2013) A Novel Reversible Data Hiding Scheme Based on Two-Dimensional Difference-Histogram Modification. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics & Security 8(7):1091–1100
Lin CC, Tai WL, Chang CC (2008) Multilevel reversible data hiding based on histogram modification of difference images. Pattern Recogn 41(12):3582–3591
Ma B, Shi YQ (2017) A Reversible Data Hiding Scheme Based on Code Division Multiplexing. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics & Security 11(9):1914–1927
Ni Z, Shi YQ, Ansari N et al (2004) Reversible data hiding. IEEE Transactions on Circuits & Systems for Video Technology 16(3):354–362
Coatrieux G, Pan W, Cuppens-Boulahia N, et al (2013) Reversible watermarking based on invariant image classification and dynamic histogram shifting. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 8(1):111–120
Qin C, Zhang X (2015) Effective reversible data hiding in encrypted image with privacy protection for image content. J Vis Commun Image Represent 31(C):154–164
Sachnev V, Kim HJ, Nam J et al (2009) Reversible Watermarking Algorithm Using Sorting and Prediction. IEEE Transactions on Circuits & Systems for Video Technology 19(7):989–999
Tai WL, Yeh CM, Chang CC (2009) Reversible data hiding based on histogram modification of pixel differences. IEEE Transactions on Circuits & Systems for Video Technology 19(6):906–910
Thodi DM, Rodriguez JJ (2007) Expansion embedding techniques for reversible watermarking. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(3):721–730
Tian J (2003) Reversible data embedding using a difference expansion. IEEE Transactions on Circuits & Systems for Video Technology 13(8):890–896
Tsai P, Hu YC, Yeh HL (2009) Reversible image hiding scheme using predictive coding and histogram shifting. Signal Process 89(6):1129–1143
Tsai YY, Tsai DS, Liu CL (2013) Reversible data hiding scheme based on neighboring pixel differences. Digital Signal Processing 23(3):919–927
Wang X, Ding J, Pei Q (2015) A novel reversible image data hiding scheme based on pixel value ordering and dynamic pixel block partition. Inf Sci 310:16–35
Wang X, Li X, Yang B et al (2010) Efficient Generalized Integer Transform for Reversible Watermarking. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 17(6):567–570
Wang J, Ni J, Hu Y (2014) An efficient reversible data hiding scheme using prediction and optimal side information selection. J Vis Commun Image Represent 25(6):1425–1431
Wu H Z, Wang H X, Shi Y Q (2017) Dynamic content selection-and-prediction framework applied to reversible data hiding. In: IEEE international workshop on information forensics and security. IEEE, pp. 1–6
Yang WJ, Chung KL, Liao HYM (2012) Efficient reversible data hiding for color filter array images. Inf Sci 190(3):208–226
Yao H, Qin C, Tang Z et al (2017) Guided filtering based color image reversible data hiding. J Vis Commun Image Represent 43(C):152–163
Zhang X (2013) Reversible Data Hiding With Optimal Value Transfer. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 15(2):316–325
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants (Nos. 61772281, 61502241, 61272421, 61232016, 61402235 and 61572258), in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China under Grant BK20141006, and in part by the Natural Science Foundation of the Universities in Jiangsu Province under Grant 14KJB520024, the PAPD fund and the CICAEET fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Li, J. 3D PEE mapping based reversible data hiding for color images. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 8003–8016 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6486-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6486-3