Abstract
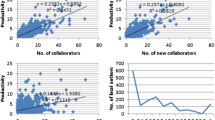
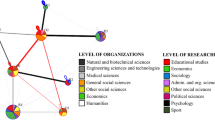
Social networks (SN) consist of a set of actors and connections between them. A collaboration network (ColNet) is a special type of SN, in which the actors represent researchers and the link between them indicate that they have co-authored at least one paper. ColNet analysis reveals how researchers interact and behave. A wide range of applications can be based on such studies. The current works on ColNet usually focus on a specific domain/discipline, country/geographical region or time interval. In our study, we focus on one of the understudied regions (the Arab world), and present a novel study on the ColNet of researchers in this region. The domain of interest in our study is biomedicine. We construct, analyze, and study ColNet of biomedical researchers in the Arab world. We divide the region of interest (the Arab world) into four geographical regions and look into the evolution of ColNet of each region separately over time. Our analysis reveals that there is an increase in the number of both authors and publications over time, and that authors tend to work in increasingly larger groups rather than working individually, which is consistent with what is assumed about the nature of research in this field. Our analysis also reveals that a researcher’s productivity is correlated with the amount of change in his/her circle of collaborators over time. For example, researchers working in stable or fixed groups and researchers who have completely different research group every few years are not necessarily the most productive ones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Ayyoub M, Arkok B, Jararweh Y (2018) An extended study of collaboration networks of levantine biomedical researchers. J Ambient Intell Humanized Comput 9(1):3–18
Al-Sadi A, Al-Ayyoub M (2018) Identifying influential positively perceived users in co-purchase networks. In: 2018 9th international conference on information and communication systems (ICICS). IEEE, pp 78–83
Alawneh E (2015) Collaboration networks of Arab biomedical researchers. Master’s thesis, Jordan University of Science and Technology
Andrade MTT, Braga P, Carneiro TKG, Ribeiro NM, Moret MA, de Barros Pereira HB (2014) Contextualized analysis of social networks: collaboration in scientific communities. Social Networking 2014
Arkok B, Al-Ayyoub M, Jararweh Y, Alsmadi I, Benkhelifa E (2014) Collaboration networks of levantine biomedical researchers. In: 2014 IEEE/ACM 7th international conference on utility and cloud computing (UCC). IEEE, pp 658–663
Benckendorff P (2009) Themes and trends in Australian and New Zealand tourism research: a social network analysis of citations in two leading journals (1994–2007). J Hosp Tour Manag 16(1):1–15
Cotta C, Merelo JJ (2006) The complex network of ec authors. ACM SIGEVOlution 1(2):2–9
Day MY, Shih SP, Chang W (2011) Understanding scientific collaboration with social network analysis. In: The 17th cross-strait conference on information and management
De Nooy W, Mrvar A, Batagelj V (2011) Exploratory social network analysis with Pajek, vol 27. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ding Y (2011) Scientific collaboration and endorsement: network analysis of coauthorship and citation networks. J Informetrics 5(1):187–203
Ghali N, Panda M, Hassanien AE, Abraham A, Snasel V (2012) Social networks analysis: Tools, measures and visualization. In: Computational social networks. Springer, pp 3–23
Guan J, Yan Y, Zhang JJ (2017) The impact of collaboration and knowledge networks on citations. J Inform 11(2):407–422
Horani M, Alsmadi A, Al-Ayyoub M, Jararweh Y (2018) Measuring user influence in a co-reviewer network. In: 2018 9th international conference on information and communication systems (ICICS). IEEE, pp 227–232
Hou H, Kretschmer H, Liu Z (2007) The structure of scientific collaboration networks in scientometrics. Scientometrics 75(2):189–202
Hu C, Racherla P (2008) Visual representation of knowledge networks: a social network analysis of hospitality research domain. Int J Hosp Manag 27(2):302–312
Kretschmer H (1994) Coauthorship networks of invisible colleges and institutionalized communities. Scientometrics 30(1):363–369
Kumar S, Rohani VA, Ratnavelu K (2014) International research collaborations of Asean nations in economics, 1979–2010. Scientometrics 101(1):847–867
Leskovec J, Adamic LA, Huberman BA (2007) The dynamics of viral marketing. ACM Trans Web (TWEB) 1(1):5
Liu X, Bollen J, Nelson ML, Van de Sompel H (2005) Co-authorship networks in the digital library research community. Inf Process Manag 41(6):1462–1480
Lozano S, Rodríguez XP, Arenas A (2014) Atapuerca: evolution of scientific collaboration in an emergent large-scale research infrastructure. Scientometrics 98(2):1505–1520
Luo M, Chang X, Li Z, Nie L, Hauptmann AG, Zheng Q (2017) Simple to complex cross-modal learning to rank. Comput Vis Image Underst 163:67–77
Luukkonen T, Persson O, Sivertsen G (1992) Understanding patterns of international scientific collaboration. Sci Technol Human Values 17(1):101–126
Ma Z, Chang X, Yang Y, Sebe N, Hauptmann AG (2017) The many shades of negativity. IEEE Trans Multimed 19(7):1558–1568
Newman ME (2001a) Scientific collaboration networks. i. network construction and fundamental results. Phys Rev E 64(1):016,131
Newman ME (2001b) The structure of scientific collaboration networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98(2):404–409
Newman ME (2004) Coauthorship networks and patterns of scientific collaboration. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(suppl 1):5200–5205
Rabab’Ah A, Al-Ayyoub M, Shehab MA, Jararweh Y, Jansen BJ (2016) Using the panama papers to explore the financial networks of the Middle East. In: 2016 11th international conference for internet technology and secured transactions (ICITST). IEEE, pp 92–97
Ronda-Pupo GA, Pham T (2018) The evolutions of the rich get richer and the fit get richer phenomena in scholarly networks: the case of the strategic management journal. Scientometrics 116(1):363–383
Tsvetovat M, Kouznetsov A (2011) Social network analysis for startups: finding connections on the social web. O’Reilly Media, Inc.
Uddin S, Hossain L, Rasmussen K (2013) Network effects on scientific collaborations. PloS One 8(2):e57,546
Vanni T, Mesa-Frias M, Sanchez-Garcia R, Roesler R, Schwartsmann G, Goldani MZ, Foss AM (2014) International scientific collaboration in hiv and hpv: a network analysis. PloS One 9(3):e93,376
Yan E, Ding Y (2009) Applying centrality measures to impact analysis: a coauthorship network analysis. J Assoc Inform Sci Technol 60(10):2107–2118
Ye Q, Li T, Law R (2013) A coauthorship network analysis of tourism and hospitality research collaboration. J Hosp Tour Res 37(1):51–76
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Ayyoub, M., Alawneh, E., Jararweh, Y. et al. Collaboration networks of arab biomedical researchers. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 33435–33455 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6557-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6557-5