Abstract
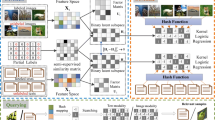
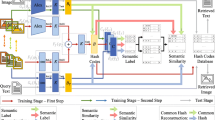
Due to the fast query speed and low storage cost, multimodal hashing methods have been attracting increasing attention in large-scale cross-media retrieval tasks. Most existing multimodal hashing methods can only handle fully-paired settings, where all data samples with different modalities are well paired. However, in practical applications, such fully-paired multimodal data may not be available. To this end, semi-paired multimodal hashing methods have been proposed by exploiting correlations between unpaired samples. Nevertheless, currently existing semi-paired hashing methods are unsupervised methods. When little supervised information is available, these methods cannot utilize supervised information to enhance the retrieval performance. To effectively utilize the limited supervised information, this paper proposed a novel hashing framework, named semi-paired and semi-supervised multimodal hashing (SSMH), to deal with the scenario where partial pairwise correspondences and labels are provided in advance for cross-media retrieval task. The proposed SSMH propagates the semantic labels from labeled multimodal samples to unlabeled multimodal samples, so that the label information of the entire multimodal training set is available. Then, most existing similarity graph based supervised multimodal hashing methods can be used to learn hashing codes. Therefore, the proposed framework can fully utilize the limited label information and pairwise correspondences to keep the semantic similarity for hashing codes. Thorough experiments on standard datasets show the superior performance of the proposed framework.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang X, Yang Y (2017) Semisupervised feature analysis by mining correlations among multiple tasks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(10):2294–2305
Ding G, Guo Y, Zhou J (2014) Collective matrix factorization hashing for multimodal data. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2083–2090
Gionis A, Indyk P, Motwani R (1999) Similarity search in high dimensions via hashing. In: Proceedings of the international conference on very large data bases, pp 518–529
Gong Y, Lazebnik S, Gordo A (2013) Iterative quantization: a Procrustean approach to learning binary codes for large-scale image retrieval. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(12):2916–2929
Jin Z, Li C, Lin Y et al (2017) Density sensitive hashing. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(8):1362–1371
Kim S, Kang Y, Choi S (2012) Sequential spectral learning to hash with multiple representations. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision, vol 7576, pp 538–551
Kulis B, Grauman K (2012) Kernelized locality-sensitive hashing. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(6):1092
Kumar S, Udupa R (2011) Learning hash functions for cross-view similarity search. In: Proceedings of the international joint conferences on artificial intelligence, pp 1360–1365
Lei Z, Zi H, Li Z et al (2018) Exploring auxiliary context: discrete semantic transfer hashing for scalable image retrieval. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst pp(99):1–13
Lin C, Dong X, Tsang WH (2014) Spectral embedded hashing for scalable image retrieval. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(7):1180–1190
Lin Z, Ding G, Hu M et al (2015) Semantics-preserving hashing for cross-view retrieval. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3864–3872
Liu W, Wang J, Kumar S (2011) Hashing with graphs. In: International conference on machine learning, pp 1–8
Liu X, He J, Liu D et al (2012) Compact kernel hashing with multiple features. In: Proceedings of the ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 881–884
Liu W, Kumar S, Kumar S (2014) Discrete graph hashing. In: Proceedings of the advances in neural information processing systems, vol 4, pp 3419–3427
Liu L, Yu M, Shao L (2015) Multiview alignment hashing for efficient image search. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(3):956
Luo M, Chang X, Li Z et al (2017) Simple to complex cross-modal learning to rank. Comput Vis Image Underst 163:67–77
Luo X, Nie L, He X et al (2018) Fast scalable supervised hashing. In: The international ACM SIGIR conference, pp 735–744
Nie L, Zhang L, Yang Y et al (2015) Beyond doctors: future health prediction from multimedia and multimodal observations, pp 591–600
Nie L, Zhang L, Yan Y et al (2017) Multiview physician-specific attributes fusion for health seeking. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(11):3680–3691
Shen F, Shen C, Liu W et al (2015) Supervised discrete hashing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 37–45
Shen X, Shen F, Sun QS et al (2015) Multi-view latent hashing for efficient multimedia search. In: Proceedings of the ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 831–834
Shen X, Sun QS, Yuan YH (2016) Semi-paired hashing for cross-view retrieval. Neurocomputing 213:14–23
Shen X, Shen F, Sun QS et al (2017) Semi-paired discrete hashing: learning latent hash codes for semi-paired cross-view retrieval. IEEE Trans Cybern 47 (12):4275–4288
Song J, Yang Y, Huang Z et al (2011) Multiple feature hashing for real-time large scale near-duplicate video retrieval. In: Proceedings of the AACM international conference on multimedia, pp 423–432
Song J, Yang Y, Yang Y et al (2013) Inter-media hashing for large-scale retrieval from heterogeneous data sources. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data, pp 785–796
Wang J, Shen HT, Song J et al (2014) Hashing for similarity search: arXiv:1408.2927
Wang D, Gao X, Wang X et al (2015) Semantic topic multimodal hashing for cross-media retrieval. In: IJCAI, pp 3890–3896
Wang Q, Si L, Shen B (2015) Learning to hash on partial multi-modal data. In: Proceedings of the international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 3904–3910
Wang D, Gao X, Wang X et al (2016) Multimodal discriminative binary embedding for large-scale cross-modal retrieval. IEEE Trans Image Process 25 (10):4540–4554
Wang S, Chang X, Li X et al (2016) Diagnosis code assignment using sparsity-based disease correlation embedding. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 28 (12):3191–3202
Weiss Y, Torralba A, Fergus R (2008) Spectral hashing. In: Proceedings of the advances in neural information processing systems, vol 282, pp 1753–1760
Wu B, Yang Q, Zheng WS et al (2015) Quantized correlation hashing for fast cross-modal search, Proceedings of the international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 3946–3952
Xie L, Shen J, Zhu L (2016) Online cross-modal hashing for web image retrieval. In: AAAI
Xie L, Shen J, Han J et al (2017) Dynamic multi-view hashing for online image retrieval. In: Twenty-sixth international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 3133–3139
Zhang D, Li WJ (2014) Large-scale supervised multimodal hashing with semantic correlation maximization. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 2177–2183
Zhen Y, Yeung DY (2012) A probabilistic model for multimodal hash function learning. In: ACM SIGKDD, pp 940–948
Zhou D, Bousquet O, Lal T N et al (2003) Learning with local and global consistency. International conference on neural information processing systems 16(4):321–328
Zhou J, Ding G, Guo Y (2014) Latent semantic sparse hashing for cross-modal similarity search. In: ACM, pp 415–424
Zhu L, Huang Z, Chang X et al (2017) Exploring consistent preferences: discrete hashing with pair-exemplar for scalable landmark search. In: ACM, pp 726–734
Zhu L, Huang Z, Liu X et al (2017) Discrete multimodal hashing with canonical views for robust mobile landmark search. IEEE Trans Multimedia 19(9):2066–2079
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61702394, Grant 61572385 and Grant 61711530248, in part by the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China under Grant 2018T111021 and Grant 2017M613082, in part by the Aeronautical Science Foundation of China under Grant 20171981008, in part by the Shaanxi Key Research and Development Program under Grant 2017ZDXM-GY-002, and in part by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant JBX170313 and Grant XJS17063.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Shang, B., Wang, Q. et al. Semi-paired and semi-supervised multimodal hashing via cross-modality label propagation. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 24167–24185 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6858-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6858-8