Abstract
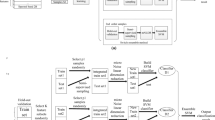
Subspace-based models have been widely applied for hyperspectral imagery applications, especially for classification. The main principle of these methods is based on the fact that the original image can approximately lie on a lower-dimensional subspace. However, due to the existence of mixed samples, the subspace projection is unstable and affected by the selection of training samples, such that may lead to poor characterization and classification performances. In order to improve the robustness and characterization ability of the subspace-based classification models, this paper proposes a novel subspace-based multitask learning framework. In particular, the original image is first projected to the multiple subspaces in different branches. Then, the support vector machine (SVM) classifier is applied in each branch to deal with the projected data sets. With a consideration of integrating the spatial information, an extended step is provided including the process of a Markov Random Field (MRF) based on the result of SVM. Finally, the classification result is obtained by a decision fusion process. Experimental results on three real hyperspectral data sets demonstrate the improvements on classification performance of the proposed methods over other related methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borel C, Gerslt S (1994) Nonlinear spectral mixing models for vegetative and soil surfaces. Remote Sens Environ 47(3):403–416
Camps-Valls G, Bruzzone L (2005) Kernel-based methods for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 43(6):1351–1362
Chang CI (2003) Hyperspectral Imaging: Techniques for Spectral Detection and Classification. Springer Science and Business Media, New York
Chang C, Zhao X, Althouse MLG, Pan JJ (1998) Least squares subspace projection approach to mixed pixel classification for hyperspectral images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 36(3):898–912
Chen C, Li W, Su H, Liu K (2014) Spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral image based on kernel extreme learning machine. Remote Sens 6(6):5795–5814
Chen C, Li W, Tramel EW, Cui M, Prasad S, Fowler JE (2014) Spectral–spatial preprocessing using multihypothesis prediction for noise-robust hyperspectral image classification. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 7(4):1047–1059
Du B, Wang S, Xu C, Wang N, Zhang L, Tao D (2018) Multi-Task learning for blind source separation. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(9):4219–4231
Du B, Wang Z, Zhang L, Zhang L, Liu W, Shen J, Tao D (2017) Exploring representativeness and informativeness for active learning. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 47(1):14–26
Du B, Zhang M, Zhang L, Hu R, Tao D (2017) PLTD: Patch-based low-rank tensor decomposition for hyperspectral images. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 19(1):67–79
Farag AA, Mohamed RM, El-Baz A (2005) A unified framework for map estimation in remote sensing image segmentation. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 43(7):1617–1634
Fauvel M, Tarabalka Y, Benediktsson JA, Chanussot J, Tilton JC (2013) Advances in spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral images. Proc IEEE 101(3):652–675
Fjortoft R, Delignon Y, Pieczynski W, Sigelle M, Tupin F (2003) Unsupervised classification of radar images using hidden Markov chains and hidden Markov random fields. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 41(3):675–686
Gao L, Li J, Khodadadzadeh M, Plaza A, Zhang B, He Z, Yan H (2015) Subspace-based support vector machines for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 12(2):349–353
Gao L, Yu H, Zhang B, Li Q (2016) Locality-preserving sparse representation-based classification in hyperspectral imagery. J Appl Remote Sens 10(4):042004
Geman S, Geman D (1984) Stochastic relaxation, Gibbs distributions, and the Bayesian restoration of images. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 6:721–741
Jia X, Richards JA (2008) Managing the spectral-spatial mix in context classification using Markov random fields. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 5(2):311–314
Jiang J, Chen C, Song X, Cai Z (2016) Hyperspectral image classification using set-to-set distance. In: Proceedings of the ICASSP: 3346–3350
Jiang J, Chen C, Yu Y, Jiang X, Ma J (2017) Spatial-aware collaborative representation for hyperspectral remote sensing image classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 14(3):404–408
Jiang J, Ma J, Chen C, Wang Z, Cai Z, Wang L (2018) SuperPCA: A superpixelwise pca approach for unsupervised feature extraction of hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(8):4581–4593
Keshava N, Mustard J (2002) Spectral unmixing. IEEE Signal Process Mag 19(1):44–57
Kirkpatrick S (1984) Optimization by simulated annealing: Quantitative studies. J Stat Phys 34(5–6):975–986
Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt CD, Vecchi MP (1983) Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 220(4598):671–680
Li J, Bioucas-Dias JM, Plaza A (2010) Semisupervised hyperspectral image segmentation using multinomial logistic regression with active learning. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 48(11):4085–4098
Li J, Bioucas-Dias JM, Plaza A (2012) Spectral–spatial hyperspectral image segmentation using subspace multinomial logistic regression and Markov random fields. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 50(3):809–823
Li W, Chen C, Su H, Du Q (2015) Local binary patterns and extreme learning machine for hyperspectral imagery classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(7):3681–3693
Melgani F, Bruzzone L (2004) Classification of hyperspectral remote sensing images with support vector machines. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 42(8):1778–1790
Platt J (1999) Probabilistic outputs for support vector machines and comparisons to regularized likelihood methods. Adv Large Margin Classif 10(3):61–74
Plaza A, Benediktsson JA, Boardman JW, Brazile J, Bruzzone L, Camps-Valls G, Chanussot J, Fauvel M, Gamba P, Gualtieri A (2009) Recent advances in techniques for hyperspectral image processing. Remote Sens Environ 113:S110–S122
Plaza A, Martinez P, Perez R, Plaza J (2004) A quantitative and comparative analysis of endmember extraction algorithms. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 42(3):650–663
Richards JA, Jia X (2006) Remote Sensing Digital Image Analysis: An Introduction. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Serpico S, Moser G (2007) Extraction of spectral channels from hyperspectral images for classification purposes. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 45(2):484–495
Vapnik V (1998) Statistical Learning Theory. Wiley, New York
Watanabe S, Lambert PF, Kulikowski CA, Buxton JL, Walker R (1967) Evaluation and selection of variables in pattern recognition. In: Computer and Information Sciences II. Academic Press: New York, NY, USA: 91–122
Xie J, Hone K, Xie W, Gao X, Shi Y, Liu X (2013) Extending twin support vector machine classifier for multi-category classification problems. Intell Data Anal 17(4):649–664
Yu H, Gao L, Li J, Li S, Zhang B, Benediktsson JA (2016) Spectral-spatial hyperspectral image classification using subspace-based support vector machines and adaptive Markov random fields. Remote Sens 8(4):355
Yu H, Gao L, Liao W, Zhang B (2018) Group sparse representation based on nonlocal spatial and local spectral similarity for hyperspectral imagery classification. Sensors 18(6):1695
Yu H, Gao L, Liao W, Zhang B, Pižurica A, Philips W (2017) Multiscale superpixel-level subspace-based support vector machines for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 14(11):2142–2146
Yu H, Gao L, Zhang B (2018) Union of random subspace-based group sparse representation for hyperspectral imagery classification. Remote Sens Lett 9(6):534–540
Zhang B, Li S, Jia X, Gao L, Peng M (2011) Adaptive Markov random field approach for classification of hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 8(5):973–977
Zhong Y, Lin X, Zhang L (2014) A support vector conditional random fields classifier with a Mahalanobis distance boundary constraint for high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 7(4):1314–1330
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 41722108, No. 91638201 and No. 61501017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Gao, L., Li, J. et al. Subspace-based multitask learning framework for hyperspectral imagery classification. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 8887–8909 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-7010-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-7010-5