Abstract
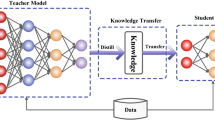
Domain adaptation is widely-used in deep neural networks to address the problem of data distribution shift. Most of the deep CNN models use the Maximum Mean Discrepancy(MMD) to measure the distribution difference between the source and task domains, which have achieved great success on transfer learning tasks. However, these conventional domain adaptation methods have limited use in dynamic knowledge adaptation due to the constant transfer coefficient for all adaptation layers. In this paper, we propose an efficient dynamic domain adaptation method on deep CNN models, which transfers knowledge dynamically according to different layers and training extent. Specifically, we first present a deep understanding of how transferable each layer in various deep CNN models is, including the different VGG and AlexNet architectures. Then, a dynamic transfer coefficient is proposed based on the deep understanding. By doing this, our paper gives guidance on how to choose transferring layers and adaptation coefficients aptly instead of using empirical constant transfer parameters in conventional methods. Extensive experiments conducted on standard benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed method achieves the state-of-the-art results by using dynamic domain adaptation parameters compared with conventional methods.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen C, Chen Z, Jiang B, et al (2018) Joint domain alignment and discriminative feature learning for unsupervised deep domain adaptation[J]
Dai W, Yang Q, Xue GR, et al (2007) Boosting for transfer learning[C]. International Conference on Machine Learning
Ding H, Zhou H, Zhou SK, et al (2017) A deep cascade network for unaligned face attribute classification[J]
Ding Z, Shao M, Fu Y (2018) Incomplete multisource transfer learning[J]. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learning Sys 29(2):310–323
Donahue J, Jia Y, Vinyals O, et al. (2013) DeCAF: a deep convolutional activation feature for generic visual recognition[J]
Fernando B, Habrard A, Sebban M, et al (2013) Unsupervised visual domain adaptation using subspace alignment[C]. International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE
Gong B, Shi Y, Sha F, et al (2012) Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation[C]. In: 2012 IEEE conference on IEEE computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE
Gopalan R, Li R, Chellappa R (2011) Domain adaptation for object recognition: an unsupervised approach[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision
Guo Y, Shi H, et al (2018) SpotTune: transfer learning through adaptive fine-tuning[J]
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al (2015) Deep residual learning for image recognition[J]
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G (2012) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. NIPS Curran Associates Inc
Li J, Lu K, Huang Z, et al (2018) Heterogeneous domain adaptation through progressive alignment[J]. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Sys 30(5):1381–1391
Li J, Lu K, Huang Z, et al (2018) Transfer independently together: a generalized framework for domain adaptation[J]. IEEE Trans Cybern 49(6):2144–2155
Li S, Song S, Wu C (2018) Layer-wise domain correction for unsupervised domain adaptation[J]. Frontiers Inform Technol Electron Eng 19(1):91–103
Liu G, Qiu Z, Qu H, et al (2015) Computing k shortest paths using modified pulse-coupled neural network[J]. Neurocomputing 149:1162–1176
Long M, Cao Y, Wang J, et al (2015) Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks[J]
Long M, Cao Z, Wang J, et al (2017) Conditional adversarial domain adaptation[J]
Long M, Wang J, Ding G, et al (2014) Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision
Long M, Zhu H, Wang J, et al (2016) Deep transfer learning with joint adaptation networks[J]
Lu H, Li Y, Uemura T, et al (2018) Low illumination underwater light field images reconstruction using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Futur Gener Comput Syst 82:142–148
Najafabadi MM, Villanustre F, Khoshgoftaar TM, et al (2015) Deep learning applications and challenges in big data analytics[J]. J Big Data 2(1):1
Pan SJ, Yang Q (2010) A survey on transfer learning[J]. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 22(10):1345–1359
Pan SJ, Tsang IW, Kwok JT, et al (2010) Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis[J]. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(2):199–210
Qiu S, Deng W (2018) Deep local descriptors with domain adaptation[J]
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, et al (2014) ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. Int J Comput Vis 115(3):211–252
Saenko K, Kulis B, Fritz M, et al (2010) Adapting visual category models to new domains[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision
Saenko K, Kulis B, Fritz M, et al (2010) Adapting visual category models to new domains[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision
Scholkopf B, Platt J, Hofmann T (2006) Correcting sample selection bias by unlabeled data[C]. International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems
Sun B, Saenko K (2016) Deep CORAL: correlation alignment for deep domain adaptation[M]. Computer Vision - ECCV 2016 Workshops
Tzeng E, Hoffman J, Darrell T, et al (2015) Simultaneous deep transfer across domains and tasks[J]
Tzeng E, Hoffman J, Zhang N, et al (2014) Deep domain confusion: maximizing for domain invariance[J]. Comput Sci
Wen J, Xu Y, Liu H (2018) Incomplete multiview spectral clustering with adaptive graph learning[J]. IEEE transactions on cybernetics, 2018
Xie X, Liu G, Cai Q, et al (2019) The maximum points-based supervised learning rule for spiking neural networks[J]. Soft Computing 23(20):10187–10198
Xie X, Qu H, Liu G, et al (2017) Efficient training of supervised spiking neural networks via the normalized perceptron based learning rule[J]. Neurocomputing 241:152–163
Xie X, Qu H, Yi Z, et al (2017) Efficient training of supervised spiking neural network via accurate synaptic-efficiency adjustment method[J]. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learning Sys 28(6):1411–1424
Yosinski J, Clune J, Bengio Y, et al (2014) How transferable are features in deep neural networks?[J]. Eprint Arxiv 27:3320–3328
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Yang Q (2018) Parameter transfer unit for deep neural networks[J]
Zhang Z, Liu L, Shen F et al (2018) Binary multi-view clustering[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell PP(99):1–1
Zhu L, Huang Z, Li Z, et al (2018) Exploring auxiliary context: discrete semantic transfer hashing for scalable image retrieval[J]. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems 29(11):5264–5276
Zhu L, Huang Z, Liu X, et al (2017) Discrete multi-modal hashing with canonical views for robust mobile landmark search[J]. IEEE Trans Multimed 19(9):2066–2079
Zhu L, Shen J, Xie L, et al (2017) Unsupervised visual hashing with semantic assistant for content-based image retrieval[J]. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 29(2):472–486
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 61806040, 61771098 and 61573081), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No: 2018M633348), and the fund from the Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Grant No: 2017GFW0128, 18ZDYF2268, 2018JY0578 and 2017JY0007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Liu, G., Xie, X. et al. Efficient dynamic domain adaptation on deep CNN. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 33853–33873 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08584-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08584-z