Abstract
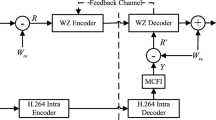
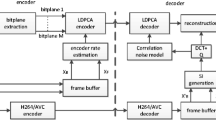
In distributed video coding, generation of high-quality side information is required for reliable soft-input information for decoding each DCT band of a Wyner-Ziv (WZ) frame in the decoder, which in turn leads to a more efficient decoding. Consequently, less error-correcting bits need to be transmitted from the encoder to the decoder to decode the bitplanes of each DCT band, leading to a better compression efficiency and rate-distortion performance. In this paper, we investigate the problem of successive improvements in the quality of side information frames in distributed video coding in order to improve the rate-distortion performance. A new algorithm for the successive refinement of the side information is proposed to refine the initial side information frame using the additional information obtained after decoding the previous DCT bands of a WZ frame. As more information about the WZ frame becomes available after the decoding of each DCT band of the WZ frame, the corresponding side information frame is refined and then employed to decode the next DCT band of the WZ frame. Simulations are carried out demonstrating that the proposed algorithm for refinement of side information frame results in a considerable improvement in the RD performance of distributed video coding.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaron A, Girod B (2002) Compression with side information using turbo codes. In: Proceedings of IEEE data compression conference, pp 252–261
Aaron A, Girod B (2002) Compression with side information using turbo codes. In: Proceedings IEEE data compression conference, pp 252–261
Aaron A, Rane S, Girod B (2004) Wyner-Ziv video coding with hash-based motion compensation at the receiver. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on image processing, ICIP’04, vol 5, pp 3097–3100
Argyropoulos S, Thomos N, Boulgouris NV, Strintzis MG (2007) Adaptive frame interpolation for Wyner-Ziv video coding. In: Proceedings of IEEE 9th workshop on multimedia signal processing, 2007. MMSP 2007, pp 159–162
Artigas X, Ascenso J, Dalai M, Klomp S, Kubasov D, Ouaret M (2007) The DISCOVER codec: architecture, techniques and evaluation. In: Proceedings of Picture Coding Symposium (PCS), pp 1-4, Lisbon, Portugal
Ascenso J, Brites C, Pereira F (2005) Improving frame interpolation with spatial motion smoothing for pixel domain distributed video coding. In: 5th EURASIP conference on speech and image processing, multimedia communications and services, pp 1–6
Ascenso J, Pereira F (2007) Adaptive hash-based side information exploitation for efficient Wyner-Ziv video coding. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on image processing, (ICIP 2007), vol 3, pp III–29
Ascenso J, Pereira F (2008) Advanced side information creation techniques and framework for Wyner–Ziv video coding. J Vis Commun Image Represent 19(1):600–613
Avaro O, Eleftheriadis A, Herpel C, Rajan G, Ward L (2000) MPEG-4 Systems: overview. Signal Process Image Commun 15(4):281–298
Bjøntegaard G (2001) Calculation of average PSNR differences between RD curves, Tech. Rep., 13th VCEGM33 Meeting. Austin
Dinh TN, Lee G, Chang JY, Cho HJ (2007) A novel motion compensated frame interpolation method for improving side information in distributed video coding. In: Proceedings of International Symposium on Information Technology Convergence, ISITC 2007, pp 179–183
Dinh TN, Lee G, Chang JY, Cho HJ (2007) A novel motion compensated frame interpolation method for improving side information in distributed video coding. In: Proceedings of international symposium on information technology convergence, ISITC 2007, pp 179–183
Dufaux F, Gao W, Tubaro S, Vetro A (2010) Distributed video coding: trends and perspectives. EURASIP J Image Video Process (1):508167
Esmaili GR, Cosman PC (2011) Wyner–ziv video coding with classified correlation noise estimation and key frame coding mode selection. IEEE Trans Image Process 20 (9):2463–2474
Fan X, Au OC, Cheung NM (2009) Adaptive correlation estimation for general Wyner-Ziv video coding. In: Proceedings of 16th IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), pp 1409– 1412
Huang X, Forchhammer S (2008) Improved side information generation for distributed video coding. In: IEEE international workshop multimedia signal process, pp 223–228
Huang X, Forchhammer S (2012) Cross-band noise model refinement for transform domain Wyner–Ziv video coding. Signal Process Image Commun 27(1):16–30
Joint Video Team (JVT) reference software. [Online]. Available at: http://iphome.hhi.de/suehring/tml/index.htm
Liu R, Yue Z, Chen C (2009) Side information generation based on hierarchical motion estimation in distributed video coding. Chin J Aeronautics 22(2):167–173
Liveris AD, Xiong Z, Georghiades CN (2002) Compression of binary sources with side information using low-density parity-check codes. In: Proceedings of global telecommunications conference, vol 2, pp 1300–1304
Louw DJ, Kaneko H (2012) A system combining extrapolated and interpolated side information for single view multi-hypothesis distributed video coding. In: 2012 international symposium on IEEE information theory and its applications (ISITA)
Luong HV, Raket LL, Huang X, Forchhammer S (2012) Side information and noise learning for distributed video coding using optical flow and clustering. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(12):4782– 4796
Martins R, Brites C, Ascenso J, Pereira F (2009) Refining side information for improved transform domain Wyner-Ziv video coding. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 19(9):1327–1341
Puri R, Ramchandran K (2002) PRISM: A new robust video coding architecture based on distributed compression principles. In: Proceedings of the annual allerton conference on communication , control and computing, vol 40, pp 586–595
Slepian D, Wolf J (1973) Noiseless coding of correlated information sources. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 19(4):471–480
Taheri YM, Ahmad MO, Swamy MNS (2014) Side information generation using optical flow and block matching in Wyner-Ziv video coding. In: Proceedings of 21st IEEE international conference on electronics, circuits and systems (ICECS), pp 722–725
Taheri YM, Ahmad MO, Swamy MNS (2018) A joint correlation noise estimation and decoding algorithm for distributed video coding. Springer Multimedia Tools and Applications 77(6):7327–7355
Van Luong H, Huang X (2011) Parallel iterative decoding of transform domain Wyner-Ziv video using cross bitplane correlation. In: Proceedings of 18th IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP2011), pp 2633–2636
Varodayan D, Chen D, Flierl M, Girod B (2008) Wyner–ziv coding of video with unsupervised motion vector learning. Signal Process Image Commun 23(5):369–378
Wang S, Cui L, Stankovic L, Stankovic V, Cheng S (2012) Adaptive correlation estimation with particle filtering for distributed video coding. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 22(5):649–658
Wiegand T, Sullivan GJ, Bjontegaard G, Luthra A (2003) Overview of the h. 264/AVC video coding standard. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 13 (7):560–576
Wyner A, Ziv J (1976) The rate-distortion function for source coding with side information at the decoder. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 22(1):1–10
Yaacoub C, Farah J, Pesquet-Popescu B (2009) Improving hash-based Wyner-Ziv video coding using genetic algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 5th international ICST mobile multimedia communications conference, p 30
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada and in part by the Regroupement Stratégique en Microélectronique du Québec (ReSMiQ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammad Taheri, Y., Ahmad, M.O. & Swamy, M.N.S. Successive refinement of side information frames in distributed video coding. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 20697–20722 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7249-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7249-5