Abstract
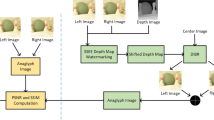
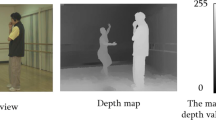
Depth Image Based Rendering (DIBR) for 3D-TV, or free-view TV, is one of the most promising techniques in multimedia world, whereby a monoscopic image and the depth image of the same view are utilized to generate stereoscopic left and right images. Therefore, the protection of valuable content generated for 3D TV is an important concern in the world of digital media. In this paper, we exploit an interpolation errors expansion scheme by employing Genetic Programming based smart reversible watermarking technique that is viable for 3D-TV. The proposed technique exploits directional weights using hidden dependencies pertaining to the imperceptibility and capacity of the watermark in a previously established interpolation scheme. It then embeds the watermark in the 3D content using interpolation error expansion based reversible watermarking scheme. Previously presented empirical techniques are not much effective as they use hit and trial strategies for selecting optimal weights for watermark embedding. The proposed technique achieves significant watermark capacity as well as imperceptibility, and is reversible when compared to existing state of the art techniques.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
(Online) Available: http://www.historytimelines.org.uk/eventstimelines/08,televisioninvention timeline.htm. Accessed 10 Dec 2018
Abdeldaim AM, Sahlol AT, Elhoseny M, Hassanien AE (2018) Computer-aided acute lymphoblastic leukemia diagnosis system based on image analysis. In: Hassanien A, Oliva D (eds) Advances in soft computing and machine learning in image processing studies in computational intelligence. Springer, Cham, p 730. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63754-9
Alattar AM (2003) Reversible watermark using difference expansion of triplets. International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP) 1:501–504
Alattar AM (2004) Reversible watermark using the difference expansion of a generalized integer transform. IEEE Trans Image Process 13:1147–1156
Alattar AM (2004) Reversible watermark using difference expansion of quads. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP) 3:377–380
Baird JL BAIRD TELEVISION (Online) Available: http://www.bairdtelevision.com. Accessed 10 Dec 2018
Barton JM (1997) Method and apparatus for embedding authentication information within digital data. ed: Google Patents
Celik MU, Sharma G, Tekalp AM, Saber E (2005) Lossless generalized-LSB data embedding. IEEE Trans Image Process 14:253–266
Chang CC, Lin CC, Tseng CS, Tai WL (2007) Reversible hiding in DCT-based compressed images. 141:123–138
Chen X, Sun X, Sun H, Zhou Z, Zhang J (2013) Reversible watermarking method based on asymmetric-histogram shifting of prediction errors. J Syst Softw 86:2620–2626
Christoph F (2003) A 3D-TV approach using Depth Image Based Rendering (DIBR). Visualization, Imaging, and Image Processing (VIIP), Benalmadena, Spain 482-487
Christoph F (2004) Depth-image-based rendering (dibr), compression, and transmission for a new approach on 3d-tv. SPIE Stereoscopic Displays Virtual Reality System XI 5291:93–104
Coltuc D (2011) Improved embedding for prediction-based reversible watermarking. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Security 6:873–882
Coltuc D (2012) Low distortion transform for reversible watermarking. IEEE Trans Image Process 21:412–417
Coltuc D, Chassery JM (2007) Very fast watermarking by reversible contrast mapping. IEEE Signal Process Lett 14:255–258
Hee DK, Ji WL, Tae WO, Heung KL (2012) Robust DT-CWT watermarking for DIBR 3D images. IEEE Trans on Broadcasting 58(4):533–543
Hong WCJ, Chen TS (2009) Blockwise reversible data hiding by contrast mapping. Inf Technol J 8:1287–1291
Honsinger CW, Jones PW, Rabbani M, Stoffel JC (2001) Lossless recovery of an original image containing embedded data. ed: Google Patents
Hyoung JK, Sachnev V, Qing SY, Jeho N, Hyon GC (2008) A novel difference expansion transform for reversible data embedding. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Security 3:456–465
Jun T (2003) Reversible data embedding using a difference expansion. IEEE Trans on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 13:890–896
Kamstra L, Heijmans HJAM (2005) Reversible data embedding into images using wavelet techniques and sorting. IEEE Trans Image Process 14:2082–2090
Kim HD, Lee JW, Oh TW, Lee HK (2012) Robust DT-CWT watermarking for DIBR 3D images. IEEE Trans Broadcast 58(4):533–543
Ko LT, Chen JE, Shieh YS, Hsin HC, Sung TY (2011) Nested quantization index modulation for reversible watermarking and its application to healthcare information management systems. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2012
Ko LT, Chen JE, Shieh YS, Scalia M, Sung TY (2012) A novel fractional-discrete-cosine-transform-based reversible watermarking for healthcare information management systems. Math Probl Eng
Lin CC, Shiu PF (2010) DCT-based reversible data hiding scheme. J Softw 5(2):214–224
Lin YH, Wu JL (2011) A digital blind watermarking for depth-image-based rendering 3D images. IEEE Trans Broadcast 57(2):602–611
Luo L, Zhenyong C, Ming C, Xiao Z, Zhang X (2010) Reversible image watermarking using interpolation technique. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Security 5:187–193
Luo TL, Gangyi J, Mei Y, Haiyong X, Feng S (2016) Inter-view local texture analysis based stereo image reversible data hiding. Digital Signal Processing 48:116–129
Memon NA, Khan A, Gilani S, Muhammad A (2011) Reversible watermarking method based on adaptive thresholding and companding technique. Int J Comput Math 88:1573–1594
Ming C, Zhenyong C, Xiao Z, Zhang X (2009) Reversible image watermarking based on full context prediction. 16th IEEE International Cnference on Image Processing, p 4253–4256
Mohamed E, Gustavo RG, Osama MAE, Shihab AS, Arunkumar N, Ahmed F (2018) Secure medical data transmission model for IoT-based healthcare systems. IEEE Access 6:20596–20608
Mohamed E, Diego O, Valentín OE, Aboul EH, Gunasekaran M (2018) Parameter identification of two dimensional digital filters using electro-magnetism optimization. Multimed Tools Appl In Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6095-1
Naheed T, Usman I, Khan TM, Dar AH, Shafique MF (2014) Intelligent reversible watermarking technique in medical images using GA and PSO. Optik 125:2515–2525
Ni Z, Shi YQ, Ansari N, Su W (2006) Reversible data hiding. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 16:354–362
Redert A, de Beeck MO, Fehn C, Ijsselsteijn W, Pollefeys M, Van GL (2002) Advanced three-dimensional television system technologies (2002) Proceedings First International Symposium on 3D Data Processing Visualization and Transmission, p 313–319
Saberian MJ, Akhaee M, Marvasti F (2008) An invertible quantization based watermarking approach. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP, p 1677–1680
Sara SA Genetic Programming Toolbox for MATLAB. http://gplab.sourceforge.net/. Accessed 10 Dec 2018
Scharstein D, Szelisk R The Middlebury Computer Vision Page (Online). Available: http://vision.middlebury.edu/. Accessed 10 Dec 2018
Seung WJ (2016) Lossless embedding of depth hints in JPEG compressed color images. Signal Process 122:39–51
Seung HN, Seung MM, Heung KL, Wook HK, Jong UH, Sunghee C (2018) A SIFT features based blind watermarking for DIBR 3D images. Multimed Tools Appl 77:7811–7850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4678-x
Sriti T, Amit KS, Satya PG, Mohamed E (2018) Multi-layer security of medical data through watermarking and chaotic encryption for tele-health applications. Multimed Tools Appl First Online. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6263-3
Tian J (2003) Reversible data embedding using a difference expansion. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 13:890–896
Tseng HW, Hsieh V (2009) Prediction-based reversible data hiding. Inf Sci 179:2460–2469
Tzu CL, Ying HH (2008) The distortion control method of reversible contrast mapping hiding scheme. International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, p 1133–1136
Usman I, Khan A (2010) BCH coding and intelligent watermark embedding: employing both frequency and strength selection. Appl Soft Comput 10(1):332–343
Vleeschouwer CD, Delaigle JF, Macq B (2001) Circular interpretation of histogram for reversible watermarking. IEEE Fourth Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, p 345–350
Vleeschouwer CD, Delaigle JF, Macq B (2003) Circular interpretation of bijective transformations in lossless watermarking for media asset management. IEEE Trans on Multimedia 5:97–105
Wen CY (2015) Ling HC (2015) reversible DCT-based data hiding in stereo images. Multimed Tools Appl 74(17):7181–7193
Xuan G, Yao Q, Yang C, Gao J, Chai P, Shi YQ (2006) Lossless data hiding using histogram shifting method based on integer wavelets. Digital Watermarking, Springer, p 323–332
Yang B, Schmucker M, Funk W, Busch C, Sun S (2004) Integer DCT-based reversible watermarking for images using companding technique. Electronic Imaging 405-415
Yiu MC, Hao TW (2007) A sequential quantization strategy for data embedding and integrity verification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 17:1007–1016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bashir, T., Usman, I., Albesher, A. et al. GP based smart reversible watermarking of depth image based rendering for stereoscopic images. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 21943–21962 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7399-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7399-5