Abstract
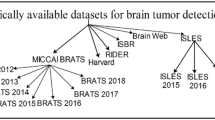
This paper presents an automatic diagnosis system for the tumor grade classification through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The diagnosis system involves a region of interest (ROI) delineation using intensity and edge magnitude based multilevel thresholding algorithm. Then the intensity and the texture attributes are extracted from the segregated ROI. Subsequently, a combined approach known as Fisher+ Parameter-Free BAT (PFreeBAT) optimization is employed to derive the optimal feature subset. Finally, a novel learning approach dubbed as PFree BAT enhanced fuzzy K-nearest neighbor (FKNN) is proposed by combining FKNN with PFree BAT for the classification of MR images into two categories: High and Low-Grade. In PFree BAT enhanced FKNN, the model parameters, i.e., neighborhood size k and the fuzzy strength parameter m are adaptively specified by the PFree BAT optimization approach. Integrating PFree BAT with FKNN enhances the classification capability of the FKNN. The diagnostic system is rigorously evaluated on four MR images datasets including images from BRATS 2012 database and the Harvard repository using classification performance metrics. The empirical results illustrate that the diagnostic system reached to ceiling level of accuracy on the test MR image dataset via 5-fold cross-validation mechanism. Additionally, the proposed PFree BAT enhanced FKNN is evaluated on the Parkinson dataset (PD) from the UCI repository having the pre-extracted feature space. The proposed PFree BAT enhanced FKNN reached to an average accuracy of 98% and 97.45%. with and without feature selection on PD dataset. Moreover, solely to contrast, the performance of the proposed PFree BAT enhanced FKNN with the existing FKNN variants the experimentations were also done on six other standard datasets from KEEL repository. The results indicate that the proposed learning strategy achieves the best value of accuracy in contrast to the existing FKNN variants.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amadasun M, King R (1989) Texural features corresponding to textural properties. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 19:1264–1274
Arif M, Akram MU, others (2010) Pruned fuzzy K-nearest neighbor classifier for beat classification. J Biomed Sci Eng 3:380.
Astrom F, Koker R (2011) A parallel neural network approach to prediction of Parkinson’s disease. Expert Syst Appl 38:12470–12474
Bahadure NB, Ray AK, Thethi HP (2018) Comparative approach of MRI-based brain tumor segmentation and classification using genetic algorithm. J Digit Imaging 31:477–489
Bakwad KM, Pattnaik SSSS, Sohi BS, et al (2009) Hybrid bacterial foraging with parameter free PSO. In: Nat. Biol. Inspired Comput. 2009. NaBIC 2009. World Congr. Ieee, pp 1077–1081
Cai Z, Gu J, Wen C et al (2018) An intelligent Parkinson’s disease diagnostic system based on a chaotic bacterial foraging optimization enhanced fuzzy KNN approach. Comput Math Methods Med 2018:1–24
Chen H-L, Yang B, Wang G et al (2011) A novel bankruptcy prediction model based on an adaptive fuzzy k-nearest neighbor method. Knowledge-Based Syst 24:1348–1359
Chen H-L, Huang C-C, Yu X-G et al (2013) An efficient diagnosis system for detection of Parkinson’s disease using fuzzy k-nearest neighbor approach. Expert Syst Appl 40:263–271
Chen H-L, Wang G, Ma C et al (2016) An efficient hybrid kernel extreme learning machine approach for early diagnosis of Parkinson′s disease. Neurocomputing 184:131–144
Cheng M, Hoang N (2014) Groutability estimation of grouting processes with microfine cements using an evolutionary instance-based learning approach. J Comput Civ Eng 28:04014014
Colominas MA, Schlotthauer G, Torres ME (2014) Improved complete ensemble EMD: a suitable tool for biomedical signal processing. Biomed Sign Proc Control 14:19–29
Costa AF, Humpire-mamani G, Juci A, et al (2012) An Efficient Algorithm for Fractal Analysis of Textures. In: 25th SIBGRAPI Conf. Graph. Patterns Images. IEEE, Ouro Preto, Brazil, pp 39–46
Cover T, Hart P (1967) Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 13:21–27
Das R (2010) A comparison of multiple classification methods for diagnosis of Parkinson disease. Expert Syst Appl 37:1568–1572
Denoeux T (1995) A k-nearest neighbor classification rule based on Dempster-Shafer theory. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 25:804–813
Derrac J, Chiclana F, García S, Herrera F (2016) Evolutionary fuzzy k -nearest neighbors algorithm using interval-valued fuzzy sets. Inf Sci (Ny) 329:144–163
Emblem KE, Nedregaard B, Hald JK et al (2009) Automatic glioma characterization from dynamic susceptibility contrast imaging: brain tumor segmentation using knowledge-based fuzzy clustering. J Magn Reson Imaging 30:1–10
Fawcett T (2004) ROC graphs: notes and practical considerations for researchers. Mach Learn 31:1–38
Georgiadis P, Cavouras D, Kalatzis I et al (2008) Improving brain tumor characterization on MRI by probabilistic neural networks and non-linear transformation of textural features. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 89:24–32
Gibbs P, Turnbull LW (2003) Textural analysis of contrast-enhanced MR images of the breast. Magn Reson Med 50:92–98
Guo P-F, Bhattacharya P, Kharma N (2010) Advances in detecting Parkinson’s disease. In: Int. Conf. Med. Biometrics. pp 306–314
Gupta N, Bhatele P, Khanna P (2019) Glioma detection on brain MRIs using texture and morphological features with ensemble learning. Biomed Sign Proc Control 47:115–125
Guyon I, Weston J, Barnhill S, Vapnik V (2002) Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Mach Learn 46:389–422
Haralick RM, Shanmugam K, Dinstein I (1973) Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern SMC-3:610–621
Harvard Medical School. http://med.harvard.edu/AANLIB/. Accessed 2 Apr 2016
Hemanth JD, Anitha J (2019) Modified genetic algorithm approaches for classification. Appl Soft Comput J 75:21–28
Hemanth DJ, Vijila CKS, Selvakumar AI, Anitha J (2011) Performance Enhanced Hybrid Kohonen-Hopfield Neural Network for Abnormal Brain Image Classification. In: Signal Process. Image Process. Pattern Recognit. Springer, pp 356–365
Herlidou-Meme S, Constans J, Carsin B et al (2003) MRI texture analysis on texture test objects, normal brain and intracranial tumors. Magn Reson Imaging 21:989–993
Hong L, Wan Y, Jain A (1998) Fingerprint image enhancement: algorithm and performance evaluation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20:777–789
Hu X, Xie C (2005) Improving fuzzy k-NN by using genetic algorithm. J Comput Inf Syst 1:203–213
Hui LY, Muftah M, Das T et al (2012) Classification of MR tumor images based on Gabor wavelet analysis. J Med Biol Eng 32:22–28
Iftekharuddin KM, Zheng J, Islam MA, Ogg RJ (2009) Fractal-based brain tumor detection in multimodal MRI. Appl Math Comput 207:23–41
Kaur T, Saini B, Gupta S (2017) Quantitative metric for MR brain tumor grade classification using sample space density measure of analytic intrinsic mode function representation. IET Image Process 11:620–632
Kaur T, Saini BS, Gupta S (2018) A joint intensity and edge magnitude-based multilevel thresholding algorithm for the automatic segmentation of pathological MR brain images. Neural Comput Appl 30:1317–1340
Kaur T, Saini BS, Gupta S (2018) A novel feature selection method for brain tumor MR image classification based on the fisher criterion and parameter-free bat optimization. Neural Comput Appl 29:193–206
Keller JM, Gray MR (1985) A fuzzy K-nearest neighbor algorithm. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern SMC-15:580–585
Kucnehva LI (1995) An intuitionistic fuzzy k-nearest neighbors rule.
Lahmiri S (2017) Glioma detection based on multi-fractal features of segmented brain MRI by particle swarm optimization techniques. Biomed Sign Proc Control 31:148–155
Lee S-H (2015) Feature selection based on the center of gravity of BSWFMs using NEWFM. Eng Appl Artif Intell 45:482–487
Lee MC, Nelson SJ (2008) Supervised pattern recognition for the prediction of contrast-enhancement appearance in brain tumors from multivariate magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. Artif Intell Med 43:61–74
Leng L, Zhang J, Xu J, et al (2010) Dynamic weighted discrimination power analysis in DCT domain for face and palmprint recognition. In: Inf. Commun. Technol. Converg. (ICTC), 2010 Int. Conf. pp 467–471
Leng L, Zhang J, Xu J, et al (2010) Dynamic weighted discrimination power analysis: A novel approach for face and palmprint recognition in DCT domain. In: Int. J. Phys. Sci. pp 467–471
Leng L, Zhang J, Chen G, et al (2011) Two-directional two-dimensional random projection and its variations for face and palmprint recognition. In: Int. Conf. Comput. Sci. Its Appl. pp 458–470
Leng L, Zhang S, Bi X, Khan MK (2012) Two-dimensional cancelable biometric scheme. In: 2012 Int. Conf. Wavelet Anal. Pattern Recognit. pp 164–169
Leng L, Li M, Teoh ABJ 2013) Conjugate 2D palmhash code for secure palm-print-vein verification. In: Image Signal Process. (CISP), 2013 6th Int. Congr. pp 1705–1710
Leng L, Li M, Kim C, Bi X (2017) Dual-source discrimination power analysis for multi-instance contactless palmprint recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 76:333–354
Li Z, Tang J (2015) Unsupervised feature selection via nonnegative spectral analysis and redundancy control. IEEE Trans Image Process 24:5343–5355
Li D-C, Liu C-W, Hu SC (2011) A fuzzy-based data transformation for feature extraction to increase classification performance with small medical data sets. Artif Intell Med 52:45–52
Little MA, McSharry PE, Hunter EJ et al (2009) Suitability of dysphonia measurements for telemonitoring of Parkinson’s disease. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 56:1015–1022
Liu DY, Chen HL, Yang B et al (2012) Design of an enhanced fuzzy k-nearest neighbor classifier based computer aided diagnostic system for thyroid disease. J Med Syst 36:3243–3254
Liu Y, Nie L, Han L, et al (2015) Action2Activity: Recognizing Complex Activities from Sensor Data. In: IJCAI. pp 1617–1623
Lu S, Qiu X, Shi J et al (2017) A pathological brain detection system based on extreme learning machine optimized by bat algorithm. CNS Neurol Disord Targets (Formerly Curr Drug Targets-CNS Neurol Disord) 16:23–29
Luukka P (2011) Feature selection using fuzzy entropy measures with similarity classifier. Expert Syst Appl 38:4600–4607
Mahdavi M, Fesanghary M, Damangir E (2007) An improved harmony search algorithm for solving optimization problems. Appl Math Comput 188:1567–1579
Mahmoud-Ghoneim D, Toussaint G, Constans J-M, de Certaines JD (2003) Three dimensional texture analysis in MRI: a preliminary evaluation in gliomas. Magn Reson Imaging 21:983–987
Materka A, Strzelecki M (1998) Texture analysis methods--a review. Tech. Univ. lodz, Inst. Electron. COST B11 report, Brussels
Meng X-B, Gao XZ, Liu Y, Zhang H (2015) A novel bat algorithm with habitat selection and Doppler effect in echoes for optimization. Expert Syst Appl 42:6350–6364
Menze BH, Jakab A, Bauer S et al (2014) The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34:1993–2024
Nayak DR, Dash R, Majhi B et al (2016) Brain MR image classification using two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform and AdaBoost with random forests. Neurocomputing 177:188–197
Nayak DR, Dash R, Majhi B (2018) Discrete ripplet-II transform and modified PSO based improved evolutionary extreme learning machine for pathological brain detection. Neurocomputing 282:232–247
Ozcift A, Gulten A (2011) Classifier ensemble construction with rotation forest to improve medical diagnosis performance of machine learning algorithms. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 104:443–451
Psorakis I, Damoulas T, Girolami MA (2010) Multiclass relevance vector machines: sparsity and accuracy. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 21:1588–1598
Rakotomamonjy A (2003) Variable selection using SVM-based criteria. J Mach Learn Res 3:1357–1370
Ramana Murthy G, Senthil Arumugam M, Loo CK (2009) Hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm with fine tuning operators. Int J Bio-Inspired Comput 1:14–31
Rhee F-H, Hwang C (2003) An interval type-2 fuzzy K-nearest neighbor. In: fuzzy Syst. 2003. FUZZ’03. 12th IEEE Int. Conf. Pp 802–807
Sachdeva J, Kumar V, Gupta I et al (2012) A novel content-based active contour model for brain tumor segmentation. Magn Reson Imaging 30:694–715
Sachdeva J, Kumar V, Gupta I et al (2013) Segmentation, feature extraction, and multiclass brain tumor classification. J Digit Imaging 26:1141–1150
Sachdeva J, Kumar V, Gupta I et al (2016) A package-SFERCB-“segmentation, feature extraction, reduction and classification analysis by both SVM and ANN for brain tumors”. Appl Soft Comput 47:151–167
Sakar CO, Kursun O (2010) Telediagnosis of Parkinson’s disease using measurements of dysphonia. J Med Syst 34:591–599
Shahbaba B, Neal R (2009) Nonlinear models using Dirichlet process mixtures. J Mach Learn Res 10:1829–1850
Shrivastava P, Shukla A, Vepakomma P et al (2017) A survey of nature-inspired algorithms for feature selection to identify Parkinson’s disease. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 139:171–179
Skogen K, Schulz A, Dormagen JB et al (2016) Diagnostic performance of texture analysis on MRI in grading cerebral gliomas. Eur J Radiol 85:824–829
Spadoto AA, Guido RC, Carnevali FL, et al (2011) Improving Parkinson’s disease identification through evolutionary-based feature selection. In: 2011 Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. pp 7857–7860
Subashini MM, Sahoo SK, Sunil V, Easwaran S (2016) A non-invasive methodology for the grade identification of astrocytoma using image processing and artificial intelligence techniques. Expert Syst Appl 43:186–196
Subashini MM, Sahoo SK, Sunil V, Easwaran S (2016) A non-invasive methodology for the grade identification of astrocytoma using image processing and artificial intelligence techniques. Expert Syst Appl 43:186–196
Tang X (1998) Texture information in run-length matrices. IEEE Trans Image Process 7:1602–1609
Tencer L, Reznakova M, Cheriet M (2012) A new framework for online sketch-based image retrieval in web environment. In: Inf. Sci. Signal Process. their Appl. Spec. Sess. IEEE, Montreal, QC, pp 1430–1431
Tien Bui D, Nguyen QP, Hoang ND, Klempe H (2016) A novel fuzzy K-nearest neighbor inference model with differential evolution for spatial prediction of rainfall-induced shallow landslides in a tropical hilly area using GIS. Landslides 14:1–17
Vidya KS, Ng EY, Acharya UR et al (2015) Computer-aided diagnosis of myocardial infarction using ultrasound images with DWT, GLCM and HOS methods: a comparative study. Comput Biol Med 62:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2015.03.033
Wagner F, Gryanik A, Schulz-Wendtland R et al (2012) 3D characterization of texture: evaluation for the potential application in mammographic mass diagnosis. Biomed Eng (NY) 57:490–493
Wang S, Kim S, Chawla S et al (2010) Differentiation between glioblastomas and solitary brain metastases using diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroimage 44:653–660
Wang S, Zhang Y, Dong Z et al (2015) Feed-forward neural network optimized by hybridization of PSO and ABC for abnormal brain detection. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 25:153–164
Xu Y, van Beek EJR, Hwanjo Y et al (2006) Computer-aided classification of interstitial lung diseases via MDCT: 3D adaptive multiple feature method (3D AMFM). Acad Radiol 13:969–978
Yang X-S (2010) A new metaheuristic bat-inspired algorithm. In: Nat. inspired Coop. Strateg. Optim. (NICSO 2010). Springer, pp 65–74
Yang M-S, Chen C-H (1998) On the edited fuzzy K-nearest neighbor rule. IEEE Trans Syst Man, Cybern Part B 28:461–466
Yang X-S, Deb S (2009) Cuckoo search via Levy flights. In: Nat. Biol. Inspired Comput. 2009. NaBIC 2009. World Congr. pp 210–214
Yang X-S, Deb S (2010) Engineering optimisation by cuckoo search. Int J Math Model Numer Optim 1:330–343
Yang G, Zhang Y, Yang J et al (2016) Automated classification of brain images using wavelet-energy and biogeography-based optimization. Multimed Tools Appl 75:15601–15617
Yilmaz S, Kucuksille EU (2015) A new modification approach on bat algorithm for solving optimization problems. Appl Soft Comput 28:259–275
Zacharaki EI, Wang S, Chawla S, Soo D (2009) Classification of brain tumor type and grade using MRI texture and shape in a machine learning scheme. Magn Reson Med 62:1609–1618
Zhang Y, Wang S, Ji G, Dong Z (2013) An MR brain images classifier system via particle swarm optimization and kernel support vector machine. Sci World J 2013
Zhang Y-D, Jiang Y, Zhu W et al (2018) Exploring a smart pathological brain detection method on pseudo Zernike moment. Multimed Tools Appl 77:22589–22604
Zollner FG, Emblem KE, Schad LR (2012) SVM-based glioma grading: optimization by feature reduction analysis. J Med Phys 22:205–214
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
‘None Declared’.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, T., Saini, B.S. & Gupta, S. An adaptive fuzzy K-nearest neighbor approach for MR brain tumor image classification using parameter free bat optimization algorithm. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 21853–21890 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7498-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7498-3