Abstract
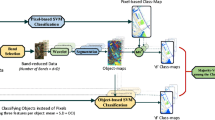
Classification of Hyperspectral images is mostly based on the spectral-spatial features in existing classification techniques. The captured Hyperspectral images from satellites may contain some noisy bands due to water absorption. The process of radiometric and atmospheric corrections leads to the removal of useful bands present in the acquired HSI. In this paper, a novel framework is proposed in which interpolation is used to accommodate the loss of noisy bands. Further, the extraction of hybrid features is performed using PCA and LPP to preserve spatial information, and these features are passed as input to the machine learning models. The proposed framework is compared with the existing spectral-spatial and spectral based frameworks by using the standard datasets-Indian Pines, Salinas, Pavia University, and Kennedy Space Centre. The accuracy of the classification is increased significantly when the proposed framework is blended with state-of-art classifiers.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aziz R, Verma CK, Srivastava N (2017) Dimension reduction methods for microarray data: a review. AIMS Bioeng 4(1):179–197
Benediktsson JA, Palmason JA, Sveinsson JR (2005) Classification of hyperspectral data from urban areas based on extended morphological profiles. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 43(3):480–491
Burger JE, Gowen AA (2011) The interplay of chemometrics and hyperspectral chemical imaging. In: 2011 3rd Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS). pp 1–4. IEEE
Camps-Valls G, Tuia D, Bruzzone L, Benediktsson JA (2014) Advances in hyperspectral image classification: Earth monitoring with statistical learning methods. IEEE Signal Process Magazine 31(1):45–54
Chen Y, Lin Z, Zhao X, Wang G, Gu Y (2014) Deep learning-based classification of hyperspectral data. IEEE J Selected Topics Appl Earth Observ Remote Sensing 7(6):2094–2107
Dell’Acqua F, Gamba P, Ferrari A, Palmason JA, Benediktsson JA, Árnason K (2004) Exploiting spectral and spatial information in hyperspectral urban data with high resolution. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 1(4):322–326
Ding C, Li T (2007) Adaptive dimension reduction using discriminant analysis and k-means clustering. In: proceedings of the 24th international conference on Machine learning, pp 521–528
Fagan M, DeFries R, Sesnie S, Arroyo-Mora J, Soto C, Singh A, Townsend P, Chazdon R (2015) Mapping species composition of forests and tree plantations in northeastern Costa Rica with an integration of hyperspectral and multitemporal landsat imagery. Remote Sens 7(5):5660–5696
Fauvel M, Tarabalka Y, Benediktsson JA, Chanussot J, Tilton JC (2013) Advances in spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral images. Proc IEEE 101(3):652–675
Ganesan VSK, Vasuki S (2018) Maximin distance based band selection for endmember extraction in hyperspectral images using simplex growing algorithm. Multimed Tools Appl 77(6):7221–7237
He X, Cai D, Min W (2005) Statistical and computational analysis of locality preserving projection. In: proceedings of the 22nd international conference on Machine learning, ACM. pp 281–288
He X, Niyogi P (2004) Locality preserving projections. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 153–160
Keshava N (2003) A survey of spectral unmixing algorithms. Lincoln Lab J 14(1):55–78
Kruse FA, Boardman JW, Huntington JF (2003) Comparison of airborne hyperspectral data and EO-1 Hyperion for mineral mapping. IEEE Trans Geoscience Remote Sens 41(6):1388–1400
Li W, Prasad S, Fowler JE, Bruce LM (April 2012) Locality-preserving dimensionality reduction and classification for hyperspectral image analysis. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 50(4):1185–1198
Lin Z, Chen Y, Zhao X, Wang G (2013) Spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral image using autoencoders. In: 2013 9th International Conference on Information, Communications & Signal Processing, IEEE. pp 1–5
Manian V, Velez-Reyes M (2008) Support vector classification of land cover and benthic habitat from hyperspectral images. Int J High Speed Electr Syst 18(02):337–348
Mou L, Ghamisi P, Zhu XX (2017) Deep recurrent neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55 (7):3639–3655
Plaza A, Martinez P, Perez R, Plaza J (2004) A new approach to mixed pixel classification of hyperspectral imagery based on extended morphological profiles. Pattern Recogn 37(6):1097–1116
Plaza A, Martinez P, Plaza J, Perez R (2005) Dimensionality reduction and classification of hyperspectral image data using sequences of extended morphological transformations. IEEE Trans Geoscience Remote Sens 43(3):466–479
Rodarmel C, Shan J (2002) Principal component analysis for hyperspectral image classification. Surv Land Inf Sci 62(2):115–122
Shalizi CR (2009) The truth about principal components and factor analysis
Singh S, Kasana SS (2018) Efficient classification of the hyperspectral images using deep learning. Multimed Tools Appl 77(20):27061–27074
Tong L, Yu J, Xiao C, Qian B (2017) Hyperspectral unmixing via deep matrix factorization. Int J Wavelets, Multiresol Inf Process 15(06):1750058
Vasuki S, et al. (2017) Clustering based band selection for endmember extraction using simplex growing algorithm in hyperspectral images. Multimed Tools Appl 76(6):8355–8371
Wang XD, Chen RC, Yan F, Zeng ZQ, Hong CQ (2019) Fast adaptive k-means subspace clustering for high-dimensional data. IEEE Access 7:42639–42651
Wang X, Luo G, Tian L (2017) Application of hyperspectral image anomaly detection algorithm for internet of things. Multimed Tools Appl, pp 1–13
Wang Y, Tang YY, Li L (2017) Spectral-spatial destriping of hyperspectral image via correntropy based sparse representation and unidirectional huber–Markov random fields. Int J Wavelets, Multiresol Inf Process 15(06):1750056
Yang C, Everitt JH, Bradford JM (2008) Yield estimation from hyperspectral imagery using Spectral Angle mapper(SAM). Trans ASABE 51(2):729–737
Yue J, Mao S, Li M (2016) A deep learning framework for hyperspectral image classification using spatial pyramid pooling. Remote Sens Lett 7 (9):875–884
Zhao K (2016) Classification for tree ages using hyperspectral images in british columbia, canada. In: Material Science and Environmental Engineering: The Proceedings of 2016 International Workshop on Material Science and Environmental Engineering (IWMSEE2016), World Scientific. pp 567–577
Zhou F, Hang R, Liu Q, Yuan X (2019) Hyperspectral image classification using spectral-spatial LSTMs. Neurocomputing 328:39–47
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Kasana, S.S. A Pre-processing framework for spectral classification of hyperspectral images. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 243–261 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09180-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09180-2