Abstract
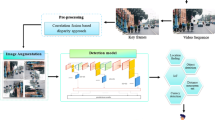
Nowadays, more and more people choose to upload their data and information to cloud. The cloud saves users’ data and information and starts providing computing services and artificial intelligence analysis. However, the privacy of users’ information and data will be completely exposed to the cloud without any protection. In this paper, we propose two methods of the blind (privacy-preserving) background extraction from video surveillance for both scenarios with the single-party cloud server (SCS) and multi-party cloud servers (MCS). We combine 1D logistics chaotic encryption with background subtraction based on a mixed Gaussian model, and propose a blind background subtraction method for a single server (SCS) . We combine the Chinese Remainder Theorem (CRT) and the ViBE background subtraction method and propose a multi-server blind background subtraction method (MCS). The test set for the experiment is CDW-2014, the experimental results show that our method has satisfactory results in recognition accuracy, recognition speed, and security analysis.
The proposed methods have several advantages: (1) Based on our encryption method, the background extraction method in the original video does not need to be changed; (2) The server does not recognize any valid information for the calculation results; (3) Single cloud server (SCS) uses the chaotic mapping can ensure high-level security and resistance to several attacks; (4) Multiple cloud servers (MCS) can improve data security and improve processing efficiency. This method can accurately extract the background like the original ViBE algorithm while protecting the privacy of client video data.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnich O, Van Droogenbroeck M (2011) Vibe: A universal background subtraction algorithm for video sequences. IEEE Trans Image Process 20 (6):1709–1724
Bouwmans T, Javed S, Sultana M, Jung SK (2019) Deep neural network concepts for background subtraction: A systematic review and comparative evaluation. Neural Netw
Chen Y, Hao C, Liu AX, Wu E (2019) Multi-level model for video object segmentation based on supervision optimization. IEEE Trans Multimed 1–1
Chu K-Y, Kuo Y-H, Hsu WH (2013) Real-time privacy-preserving moving object detection in the cloud. In: Proceedings of the 21st ACM International Conference on Multimedia. MM ’13. ACM, New York, pp 597–600
Jin X, Guo K, Song C, Li X, Zhao G, Luo J, Li Y, Chen Y, Liu Y, Wang H (2016) Private video foreground extraction through chaotic mapping based encryption in the cloud. In: Tian Q, Sebe N, Qi G-J, Huet B, Hong R, Liu X (eds) MultiMedia Modeling. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 562–573
Jin X, Wu Y, Li X, Li Y, Zhao G, Guo K (2016) Ppvibe: Privacy preserving background extractor via secret sharing in multiple cloud servers. In: 8th International Conference on Wireless Communications & Signal Processing, WCSP 2016, Yangzhou, China, October 13-15, 2016, pp 1–5
Stauffer C, Grimson WEL (1999) Adaptive background mixture models for real-time tracking. In: Cvpr, IEEE, p 2246
Stauffer C, Grimson WEL (2000) Learning patterns of activity using real-time tracking. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell 22(8):747–757
Upmanyu M, Namboodiri AM, Srinathan K, Jawahar CV (2009) Efficient privacy preserving video surveillance. In: 2009 IEEE 12th international conference on computer vision, pp 1639–1646
Wang Y, Jodoin P-M, Porikli F, Konrad J, Benezeth Y, Ishwar P (2014) Cdnet 2014: An expanded change detection benchmark dataset. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 387–394
Zhen P, Zhao G, Min L, Jin X (2016) Chaos-based image encryption scheme combining dna coding and entropy. Multimed Tools Appl 75:6303–6319
Acknowledgments
This work is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 61701008, 61772047), the Open Project Program of State Key Laboratory of Cryptology (grant number MMKFKT201804), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (grant number 19L2040), the Open Project Program of State Key Laboratory of Virtual Reality Technology and Systems, Beihang University (grant number VRLAB2019C03) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant number 328201907).
Parts of this paper have previously appeared in our previous work [5, 6]. This is the extended journal version of the conference papers. The main differences between this journal version and the conference version are: We have expanded our previous work in more details and experimental results. We performed complete efficiency tests on single-party cloud server (SCS) method and multi-party cloud servers (MCS) method, including two methods for testing the processing speed of single-frame images at different resolutions, two methods for testing the accuracy of the complete segment video, and more comprehensive and reliable security analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, X., Yu, H., Zhang, H. et al. Blind background extraction from videos in the cloud. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 28755–28771 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09386-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09386-4