Abstract
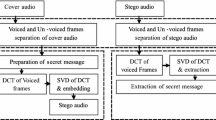
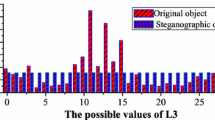
Speech is one of the essential ways of communication. The study of speech steganography provides great value in information security. To improve imperceptibility and robustness of speech steganography, the characteristics of speech signals should be fully taken into account. In this paper, a robust speech steganographic scheme based on Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Modified Discrete Cosine Transform (MDCT) is proposed. Firstly, Voice Activity Detector (VAD) is used to detect voiced frames from speech signals, along with MDCT with Kaiser Bessel Derived (KBD) window being performed on each frame. Then the MDCT coefficients are selected from a certain frequency range and divided into a pair of segments. The two largest singular values of the paired segments are modified respectively according to their value difference to embed secret message. The thresholds are adaptively adjusted according to the largest singular values. Extensive experiments are carried out to compare the proposed method with three other methods from imperceptibility, robustness, capacity, and security. The experimental results show that under the simulation parameters β = 320, Nk = 58, fl = 100 Hz, fh = 3 kHz, and α = 0.61, the proposed method has striking advantages to resist common robust attacks and the state-of-the-art steganalysis attacks while maintaining good imperceptibility.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahani S, Ghaemmaghami S, Wang ZJ, sparse representation based wavelet domain speech steganography method. A IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang pp 1–1 (2015)
Al-Nuaimy W, et al. (2011) An svd audio watermarking approach using chaotic encrypted images. Digital Signal Process 21(6):764–779
Banik BG, Bandyopadhyay SK (2018) Blind key based attack resistant audio steganography using cocktail party effect. Secur Commun Netw 2018:1–21
Bhat KV, Sengupta I, Das A (2010) An adaptive audio watermarking based on the singular value decomposition in the wavelet domain. Digital Signal Process 20(6):1547–1558
Biglieri E, Yao K (1989) Some properties of singular value decomposition and their applications to digital signal processing. Signal Process 18(3):277–289
Dhar PK, Shimamura T (2015) Blind SVD-based audio watermarking using entropy and log-polar transformation. Journal of Information Security and Applications 20:74
Dhas MDK, Sheeba PM (2017) Analysis of audio signal using integer MDCT with Kaiser Bessel Derived window. In: 2017 IEEE International conference on advanced computing and communication systems (ICACCS-2017), pp 1–6
Ghasemzadeh H, Arjmandi MK (2017) Universal audio steganalysis based on calibration and reversed frequency resolution of human auditory system. IET Signal Process 11(8):916–922
Hu HT, Chang JR (2017) Efficient and robust frame-synchronized blind audio watermarking by featuring multilevel dwt and dct. Cluster Comput 20 (1):805–816
Hu HT, Lee TT (2019) Frame-synchronized blind speech watermarking via improved adaptive mean modulation and perceptual-based additive modulation in DWT domain. Digit Signal Process 87:75–85
Hua G, Huang JW, Shi YQ, Goh J, Thing VLL (2016) Twenty years of digital audio watermarking-a comprehensive review. Signal Process 128 (2016):222–242
Huang Y, Liu C, Tang S, Bai S (2012) Steganography integration into a low-bit rate speech codec. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 7(6):1865–1875
Hwang MJ, Lee J, Lee M, Kang HG, SVD-based adaptive QIM (2018) Watermarking on stereo audio signals. IEEE Trans Multimedia 20(1):45–54
Ito A, Abe S, Suzuki Y (2009) Information hiding for g.711 speech based on substitution of least significant bits and estimation of tolerable distortion. In: 2009 IEEE International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, pp 1409–1412
Kanhe A, Aghila G (2018) A dct–svd-based speech steganography in voiced frames. Circuits Syst, Signal Process, pp 1–20
Kazemi R, Rezaei R, Akhaee MA, Behnia F (2016) Covert communications through mobile voice channels. IET Inf Secur 10(3):156–164
Kumar PM, Srinivas K (2019) Real time implementation of speech steganography. In: 2019 International conference on smart systems and inventive technology (ICSSIT), pp 369–369
Lei B, et al. (2012) A robust audio watermarking scheme based on lifting wavelet transform and singular value decomposition. Signal Process 92(9):1985–2001
Lei BY, Soon IY, Li Z (2011) Blind and robust audio watermarking scheme based on SVD-DCT. Signal Process 91(8):1973–1984
Lei BY, Song IS, Rahman SA (2013) Robust and secure watermarking scheme for breath sound. J Syst Softw 86(6):1638–1649
Li JF, Wu T (2015) Robust audio watermarking scheme via QIM of correlation coefficients using LWT and QR decomposition 2015 IEEE International conference on informative and cybernetics for computational social systems (ICCSS), 1–6
Liu P, Li S, Wang H, Shen L (2017) Steganography integrated into linear predictive coding for low bit-rate speech codec. Multimed Tools Appl 76 (2):2837–2859
Liu Q, Sung AH, Qiao M (2009) Temporal derivative-based spectrum and mel-cepstrum audio steganalysis. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 4 (3):359–368
Liu J, Zhou K, Tian H (2012) Least-significant-digit steganography in low bitrate speech. In: 2012 Proc IEEE int conf Commun (ICC), pp 1133–1137
Nematollahi MA, Al-Haddad SAR, Zarafshan F (2015) Blind Digital Speech Watermarking based on Eigen-Value Quantization in DWT. Journal of King Saud University-computer and Information Sciences 27(1):58–67
Nematollahi MA, Vorakulpipat C, Gamboa-Rosales H (2017) Digital speech watermarking based on linear predictive analysis and singular value decomposition. Proc Nat Acad Sci India A 87(3): 433–446
Piotrowski Z, Gajewski P (2012) Fidelity estimation of watermarked audio signals according to the itu-r bs.1116-1 standard. Acta Phys 121(1):A82–A85
Tabara B, Wojtun J, Piotrowski Z (2017) Data hiding method in speech using echo embedding and voicing correction. In: 2017 Signal processing symposium (SPSympo), pp 1–6
Tian H, Zhou K, Jiang H, Liu J, Huang Y, Feng D (2009) An m-sequence based steganography model for voice over ip. In: IEEE international conference on communications, 2009. ICC’09, pp 1–5
Tsai SE, Yang SM (2018) An effective watermarking method based on energy averaging in audio signals. Math Probl Eng 2018:1–8
Wu ZJ, Li R, Li CL (2020) Adaptive speech information hiding method based on K-Means. IEEE Access, pp 23308–23316
Xiang Y, Natgunanathan I, Peng DZ, Zhou WL, Yu S (2012) A dual-channel time-spread echo method for audio watermarking. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Security 7(2):383–392
Xiang S, Yang L, Wang Y (2017) Robust and reversible audio watermarking by modifying statistical features in time domain. Advances in Multimedia 2017:1–10
Xiao B, Huang Y, Tang S (2008) An approach to information hiding in low bit-rate speech stream. In: IEEE GLOBECOM 2008 - 2008 IEEE Global telecommunications conference, pp 1–5
Xin G, Liu Y, Yang T, Cao Y (2018) An adaptive audio steganography for covert wireless communication. Secur Commun Netw 2018:1–10
Xue YM, Mu K, Wang YZ, Chen Y, Zhong P, Wen J (2019) Robust speech steganography using differential SVD. IEEE Access 7:153724–153733
Yan S, Tang G, Sun Y, Gao Z, Shen L (2015) A triple-layer steganography scheme for low bit-rate speech streams. Multimed Tools Appl 74(24):11763–11782
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Grant No. 61872368 and No.61802410
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, J., Zeng, H., Wang, Y. et al. An SVD-based adaptive robust speech steganography using MDCT coefficient. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 2517–2536 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09725-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09725-5