Abstract
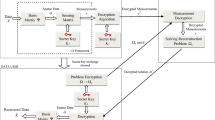
To solve the privacy image problem stored in cloud, we propose a compressive sensing (CS) based image compression, authentication, encryption algorithm in cloud, which can implement computation outsourcing to get rid of the expensive storage and computation costs. To achieve these goals, combined with the logistic-tent-sine chaotic map, a logistic-tent-sine chaotic map (LTSS) is proposed for it has larger chaotic ranges and better chaotic behaviors than simple 1D chaotic map such as a logistic chaotic map. Then, the LTSS chaotic system is employed for image protection algorithm in cloud, which contains three parts: data owner, cloud services and data user. The primary role of the data owner part is to compress and encrypt the image while embedding the owner’s Palmprint discriminative and binary features for authentication. The low-frequency part of the image is encrypted using the proposed Binary Data Cyclic Encryption algorithm (BDCE) while the owner’s palmprint features are embedded for authentication of the data owner. The high-frequency data are randomized for compression by the CS and following encrypted by the Double Random Phase Encoding (DRPE). For the cloud services, authentication services depend on the key and palmprint features and the high computational compressed sensing reconstruction is implemented in cloud can reduce the user burden. For data users, a user should provide the correct key and right palmprint, and then obtain an image available from the cloud service. The algorithm has better quality compared with the common compressive sensing based algorithms and robust to noise and occlusion for using the discrete wavelet transform. What is more, theoretical analysis and empirical evaluations show that the proposed algorithm can resist to exhaustive attack, differential attack and classical attacks.


































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez G, Li S (2006) Some basic cryptographic requirements for chaos-based cryptosystems. Int J Bifurc Chaos 16(08):2129–2151
Arroyo D, Diaz J, Rodriguez FB (2013) Cryptanalysis of a one round chaos-based substitution permutation network. Signal Process 93(5):1358–1364
Blanchard JD, Tanner J (2013) GPU accelerated greedy algorithms for compressed sensing. Math Prog Comp 5:267–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12532-013-0056-5
Candes EJ, Wakin MB (2008) An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process Mag 25(2):21–30
Chai X, Bi J et al (2020) Color image compression and encryption scheme based on compressive sensing and double random encryption strategy. Signal Process 176:107684–107701
Chai X, Zheng X, Gan Z (2018) An image encryption algorithm based on chaotic system and compressive sensing. Signal Process 148:124–144
Chen J, Zhang Y, Qi L et al (2018) Exploiting chaos-based compressed sensing and cryptographic algorithm for image encryption and compression. Opt Laser Technol 99:238–248
Darwish SM (2019) A modified image selective encryption-compression technique based on 3D chaotic maps and arithmetic coding. Multimed Tools Appl 78:19229–19252
Deepan B, Quan C, Wang Y, Tay CJ (2014) Multiple-image encryption by space multiplexing based on compressive sensing and the double-random phase-encoding technique. Appl Opt 53(20):4539–4547
Deng Q, Zeng H, Zhang J, Tian S, Cao J, Li Z, Liu A (2019) Compressed sensing for image reconstruction via back-off and rectification of greedy algorithm. Signal Process 157:280–287
Donoho DL (2006) Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 52(4):1289–1306
Fridrich J (1998) Symmetric ciphers based on two-dimensional chaotic maps. Int J Bifurcation and Chaos 8(6):1259–1284
Gan H, Xiao S, Zhao Y (2018) A novel secure data transmission scheme using chaotic compressed sensing. IEEE Access 6(99):4587–4598
Gao H, Zhang Y, Liang S, Li D (2006). A new chaotic algorithm for image encryption. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 29(2):393–399.
Guiqiang H, Xiao D, Zhang Y et al (2017) A compressive sensing based privacy preserving outsourcing of image storage and identity authentication service in cloud. Inf Sci 387:132–145
Hai X, Wu H et al (2020) An efficient visually meaningful image compression and encryption scheme based on compressive sensing and dynamic LSB embedding. Opt Lasers Eng 124:105837–105855
Islam SR, Maity SP, Ray AK (2017) Optimal combining fusion on degraded compressed sensing image reconstruction. Signal Process Image Commun 52:173–182
Itani W, Kayssi A, Chehab A (2009) Privacy as a service: privacy-aware data storage and processing in cloud computing architectures. In: 8th IEEE international conference on dependable, autonomic and secure computing, 12–14 Dec. 2009 in Chengdu, China, pp 711–716
Khan MFF, Sakamura K (2016) A discretionary delegation framework for access control systems. In: OTM 2016 conferences. LNCS 10033:865–882
Kong A, Zhang D, Kamel M (2009) A survey of palmprint recognition. Pattern Recogn 42(7):1408–1418
Li C, Li S, Asim M (2009) On the security defects of an image encryption scheme. Image Vis Comput 27(9):1371–1381
Li H, Zhang J, Wang L (2014) Robust palmprint identification based on directional representations and compressed sensing. Multimed Tools Appl 70(3):2331–2345
Liu X, Cao Y, Lu P, Lu X, Li Y (2013) Optical image encryption technique based on compressed sensing and Arnold transformation. Opt Int J Light Electron Optics 124(24):6590–6593
Liu A, Wang W (2018) A privacy-preserving framework for trust-oriented point-ofinterest recommendation. IEEE Access 6:393–404
Liu H, Xiao D, Liu Y, Zhang Y (2015) Securely compressive sensing using double random phase encoding. Opt Int J Light Electron Optics 126(20):2663–2670
Lorenz EN (1963) Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J Atmos Sci 20(2):130–141
Lu P, Xu Z, Lu X, Liu X (2013) Digital image information encryption based on compressive sensing and double random-phase encoding technique. Opt Int J Light Electron Optics 124(16):2514–2518
Muhammad B, Kalam Azad MA, Athanasios V (2017) Security and privacy challenges in mobile cloud computing: survey and way ahead. J Netw Comput 84:38–54
Needell D, Tropp JA (2009) CoSaMP: iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples. Appl Comput Harmon Anal 26:301–321
Panah AS, Van SR, Sellis T (2016) On the properties of non-media digital watermarking: a review of state of the art techniques. IEEE Access 4:2670–2704
Psannis K, Stergiou C et al (2019) Advanced media-based smart big data on intelligent cloud systems. IEEE Trans Sustain Comput 4:77–87
Rajput SK, Nishchal NK (2017) Optical double image security using random phase fractional Fourier domain encoding and phase-retrieval algorithm. Opt Commun 388:38–46
Rawat N, Kim B, Muniraj I et al (2015) Compressive sensing based robust multispectral double-image encryption. Appl Opt 54(7):1782–1793
Stergiou C, Plageras A et al (2019) Secure machine learning scenario from big data in cloud computing via internet of things network, springer. Handbook of Computer Networks and Cyber Security, Principles and Paradigms, Multimedia Systems and Applications, pp 525–554
Stergiou C, Psannis K (2017) Efficient and secure big data delivery in cloud computing Springer, Multimedia Tools and Applications 76:22803–22822
Stergiou C, Psannis K et al (2018) Algorithms for efficient digital media transmission over IoT and cloud networking. J Multimed Inf Syst 5(1):1–10
Stergiou C, Psannis K et al (2018) Secure integration of IoT and cloud computing. Futur Gener Comput Syst 78(3):964–975
Sui L, Xu M, Tian A (2017) Optical noise-free image encryption based on quick response code and high dimension chaotic system in gyrator transform domain. Opt Lasers Eng 91:106–114
Sun P (2020) Security and privacy protection in cloud computing: discussions and challenges. J Netw Comput Appl 160:102642–102663
Tong A, Zhang M, Wang Z, Ma J (2016) A joint color image encryption and compression scheme based on hyper-chaotic system. J Nonlinear Dyn 84(4):2333–2356
Wang S, Wang X (2019) A secure cloud storage framework with access control based on blockchain. IEEE Access 7:112713–112725
Wang C, Zhang B, Ren K, Roveda JM (2013) Privacy-assured outsourcing of image reconstruction service in cloud. IEEE Trans Emerg Top Comput 1(1):166–177
Wu Y, Noonan JP, Agaian S (2011) NPCR and UACI randomness tests for image encryption, cyber journals: multidisciplinary journals in science and technology. J Select Areas Telecommunications (JSAT) 1(2):31–38
Wu X, Tang S, Yang P, Xiang C, Zheng X (2018) Cloud is safe when compressive: efficient image privacy protection via shuffling enabled compressive sensing. Comput Commun 117:36–45
Xiao D, Li M et al (2020) Low-cost and high-efficiency privacy-protection scheme for distributed compressive video sensing in wireless multimedia sensor networks. J Netw Comput Appl 1611:102654–102675
Xiong L, Xu Z, Shi YQ (2018) An integer wavelet transform based scheme for reversible data hiding in encrypted images. Multidim Syst Sign Process 29(3):1191–1202
Xu Y, Fei L, Wen J, Zhang D (2018) Discriminative and robust competitive code for Palmprint recognition. IEEE trans. Syst Man Cybern Syst Hum Syst 48(2):232–241
Yang J, Li J (2015) A hybrid solution for privacy preserving medical data sharing in cloud environment. Futur Gener Comput Syst 43–44:74–86
Ye R (2011) An image encryption scheme with efficient permutation and diffusion processes. Commun Comput Inf Sci 202:32–39
Yu C, Li H, Zhao Z (2017) A high and efficient sparse and compressed sensing-based security approach for biometric protection. In: International conference on intelligent computing pp 666–677
Zhang Y, Zhang LY, Zhou J (2016) A review of compressive sensing in information security field. IEEE Access 4:2507–2519
Zhou Y, Bao L, Chen CLP (2014) A new 1d chaotic system for image encryption. Signal Process 97:172–182
Zhou N, Li H, Wang D, Pan S, Zhou Z (2015) Image compression and encryption scheme based on 2D compressive sensing and fractional Mellin transform. Opt Commun 343:10–21
Zhou N, Zhang A, Zheng F (2014) Novel image compression–encryption hybrid algorithm based on key-controlled measurement matrix in compressive sensing. Opt Laser Technol 62(10):152–160
Zhu S, Zhu C (2019) A new image compression-encryption scheme based on compressive sensing and cyclic shift. Multimed Tools Appl 78:20855–20875
Zhu L, Zhang C, Xu C et al (2018) An efficient and privacy-preserving biometric identification scheme in cloud computing. IEEE Access 6:19025–19033
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Yu, C. & Wang, X. A novel 1D chaotic system for image encryption, authentication and compression in cloud. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 8721–8758 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10117-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10117-y