Abstract
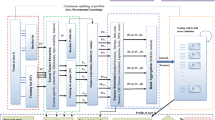
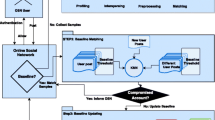
Social media networks usage is spreading but accompanied by a new shape of the social engineering attacks in which users’ accounts are compromised by attackers to spread malicious messages for different purposes. To overcome these attacks, authorship verification, a classification problem for classifying a text, whether it belongs to a user or not, is needed. Moreover, the verification must be accurate and fast. Herein, an authorship verification model proposed. The model uses XGBoost, as a preprocessor, to discover functional features of the text message, which ranked using MCDM methods to build a classification model. Twitter messages are used to test the model; however, any social media’s data might be used. The suggested model was evaluated against a crawled dataset from Twitter composed of 16124 tweets with 280 characters. The proposed method achieved F-score over 0.94.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
16 February 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10617-5
References
Al-Khatib MA, Al-qaoud JK (2020) Authorship verification of opinion articles in online newspapers using the idiolect of author: a comparative study. Inf Commun Soc:1–19
Alazab M, Huda S, Abawajy J, Islam R, Yearwood J, Venkatraman S, Broadhurst R (2014) A hybrid wrapper-filter approach for malware detection. J Netw 9(11):2878–2891
Barbon S, Igawa RA, Zarpelão B. B. (2017) Authorship verification applied to detection of compromised accounts on online social networks. Multimed Tools Appl 76(3):3213–3233
Benevenuto F, Magno G, Rodrigues T, Almeida V (2010) Detecting spammers on twitter. In: Collaboration, electronic messaging, anti-abuse and spam conference (CEAS), vol 6, pp 12
Bhattacharya S, Kaluri R, Singh S, Alazab M, Tariq U, et al. (2020) A novel pca-firefly based xgboost classification model for intrusion detection in networks using gpu. Electronics 9(2):219
Boenninghoff B, Rupp J, Nickel RM, Kolossa D (2020) Deep bayes factor scoring for authorship verification. arXiv:2008.10105
borison R (2014) Presenting: The 100 most influential tech people on twitter. https://www.businessinsider.com/100-influential-tech-people-on-twitter-2014-4
Brestovac G, Grgurinam R (2013) Applying multi-criteria decision analysis methods in embedded systems design
Calabresi M (2017) Inside russia’s social media war on america. Time Magazine
Castro A, Lindauer B (2012) Author identification on twitter
Chen T, Guestrin C (2016) Xgboost: a scalable tree boosting system. In: Proceedings of the 22nd acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. ACM, pp 785–794
Egele M, Stringhini G, Kruegel C, Vigna G (2013) Compa: Detecting compromised accounts on social networks. In: NDSS
Fülöp J (2005) Introduction to decision making methods. In; BDEI-3 Workshop, washington. Citeseer, pp 1–15
Gong NZ, Frank M, Mittal P (2014) Sybilbelief: a semi-supervised learning approach for structure-based sybil detection. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 9(6):976–987
Hall MA (1999) Correlation-based feature selection for machine learning
Jahan A, Edwards KL, Bahraminasab M (2016) Multi-criteria decision analysis for supporting the selection of engineering materials in product design. Butterworth-Heinemann
Juola P et al (2008) Authorship attribution. Found Trends®; Inf Retr 1(3):233–334
Kaur R, Singh S, Kumar H (2018) Authcom: Authorship verification and compromised account detection in online social networks using ahp-topsis embedded profiling based technique. Expert Syst Appl 113:397–414
Kotsiantis S, Kanellopoulos D, Pintelas P (2006) Data preprocessing for supervised leaning. Int J Comput Sci 1(2):111–117
Kumar GD, Kumar GD (2018) Machine learning techniques for improved business analytics. IGI global
Lagerholm F (2017) Using artificial intelligence to verify authorship of anonymous social media posts
Lee E (2013) Associated press twitter account hacked in marketmoving attack. Bloomberg Technology
Li JS, Monaco JV, Chen LC, Tappert CC (2014) Authorship authentication using short messages from social networking sites. In: 2014 IEEE 11Th international conference on e-business engineering. IEEE, pp 314–319
Maria KA (2016) Authorship Attribution Forensics: Feature selection methods in authorship identification using a small e-mail dataset. Master’s thesis, Technoglossia University, Greec
Mikolov T, Sutskever I, Chen K, Corrado GS, Dean J (2013) Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 3111–3119
Nauta M (2016) Detecting hacked twitter accounts by examining behavioural change using twtter metadata. In: Proceedings of the 25th Twente Student Conference on IT
Okereafor K, Adelaiye O Randomized cyber attack simulation model: A cybersecurity mitigation proposal for post covid-19 digital era
Parmigiani G (2001) Decision theory. Bayesian
phys.org: Twitter to double tweet limit to 280 characters (update) (2017). https://phys.org/news/2017-11-twitter-character-limit.html
Press CU (2009) Tokenization. https://nlp.stanford.edu/IR-book/html/htmledition/tokenization-1.html
Ramos J, et al. (2003) Using tf-idf to determine word relevance in document queries. In: Proceedings of the first instructional conference on machine learning, vol 242, Piscataway, pp 133–142
Rocha A, Scheirer WJ, Forstall CW, Cavalcante T, Theophilo A, Shen B, Carvalho AR, Stamatatos E (2016) Authorship attribution for social media forensics. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 12(1):5–33
Roszkowska E (2013) Rank ordering criteria weighting methods–a comparative overview
Saaty TL (2001) Decision making with the analytic network process (anp) and its super decisions software: the national missile defense (nmd) example. ISAHP 2001 proceedings, pp 2–4
Saaty TL (2005) Theory and applications of the analytic network process: decision making with benefits, opportunities, costs, and risks. RWS publications
Saaty TL (2008) Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int J Serv Sci 1(1):83–98
Savyan P, Bhanu SMS (2020) Ubcadet: detection of compromised accounts in twitter based on user behavioural profiling. Multimed Tools Appl:1–37
Schoenfeld B, Giraud-Carrier C, Poggemann M, Christensen J, Seppi K (2018) Preprocessor selection for machine learning pipelines. arXiv:1810.09942
Seyler D, Li L, Zhai C (2018) Identifying compromised accounts on social media using statistical text analysis. arXiv:1804.07247
Sivic J, Zisserman A (2008) Efficient visual search of videos cast as text retrieval. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31(4):591–606
Stamatatos E (2009) A survey of modern authorship attribution methods. J Amer Soc Inf Sci Technol 60(3):538–556
Statista: Number of social network users worldwide from 2017 to 2025 (2020). https://www.statista.com/statistics/278414/number-of-worldwide-social-network-users/
live stats, I.: Twitter usage statistics (2020). https://www.internetlivestats.com/twitter-statistics/
Steinert-Threlkeld ZC (2018) Twitter as data. Cambridge University Press
Suman C, Saha S, Bhattacharyya P, Chaudhari RS (2020) Emoji helps! a multi-modal siamese architecture for tweet user verification. Cogn Comput:1–16
Trång D, Johansson F, Rosell M (2015) Evaluating algorithms for detection of compromised social media user accounts. In: 2015 Second european network intelligence conference. IEEE, pp 75–82
Usha A, Thampi SM (2017) Authorship analysis of social media contents using tone and personality features. In: International conference on security, privacy and anonymity in computation, communication and storage. Springer, pp 212–228
Worldometers: World population projections (2020). https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/world-population-projections/
Zangerle E, Specht G (2014) Sorry, i was hacked: a classification of compromised twitter accounts. In: Proceedings of the 29th annual acm symposium on applied computing. ACM, pp 587–593
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: The author name “Suleyman Alterkavı” was incorrectly presented.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alterkavı, S., Erbay, H. Novel authorship verification model for social media accounts compromised by a human. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 13575–13591 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10361-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10361-2