Abstract
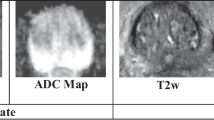
Prostate Cancer (PCa) is one among the prominent causes of mortality in men, which can only be reduced by early diagnosis. Multi-parametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging (mp-MRI) is increasingly utilized by clinicians for performing diagnostics tasks because it possesses functional and morphological competencies. Although, manual segmentation of PCa on MRI is a tedious, operator-dependent and time consuming task. Therefore, Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) of PCa using mp-MRI images is highly desirable by employing computer-assisted segmentation approaches. In this paper, a method is proposed for segmentation of PCa based on level set with Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) technique to address the limitations of existing techniques as PSO does not require any cost or objective function to be differentiable and it is easy to implement. The energy function is optimized with PSO based technique. The proposed approach is tested over three different mp-MRI modalities i.e., T2 weighted (T2w), Dynamic Contrast Enhanced (DCE) images and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) Maps derived from Diffusion Weighted Images (DWI). The accuracy achieved by PSO based methodology is 7.6% greater than without PSO integration i.e., using Gradient descent with added computational overhead of 0.03 s. The experimental outcomes reveal that the proposed methodology shows better results in terms of considered evaluation metrics when compared with the existing techniques on the I2CVB dataset. The impact of the proposed methodology is that it has the ability for precise segmentation even with intensity inhomogeneity, which validates its applications in clinical treatments. Additionally, the proposed technique reduces the manual interference, which in turn minimizes the execution time.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Algohary A, Viswanath S, Shiradkar R, Ghose S, Pahwa S, Moses D, Jambor I, Shnier R, Böhm M, Haynes AM, Brenner P (2018) Radiomic features on MRI enable risk categorization of prostate cancer patients on active surveillance: preliminary findings. J Magn Reson Imaging 22
Alkadi R, Taher F, El-Baz A, Werghi N (2019) A deep learning-based approach for the detection and localization of prostate cancer in T2 magnetic resonance images. J Digit Imaging 32(5):793–807
American Cancer Society. (2020) Facts & Figures 2020. American Cancer Society. Atlanta, Ga
Anderson D, Golden B, Wasil E, Zhang H (2015) Predicting prostate cancer risk using magnetic resonance imaging data. IseB 13(4):599–608
Cameron A, Modhafar A, Khalvati F, Lui D, Shafiee MJ, Wong A, Haider M (2014) Multiparametric MRI Prostate cancer analysis via a hybrid morphological-textural model. InEngineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC), 2014 36th annual international conference of the IEEE (pp. 3357-3360). IEEE
Cameron A, Khalvati F, Haider MA, Wong A (2016) MAPS: a quantitative radiomics approach for prostate cancer detection. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 63(6):1145–1156
Caselles V, Kimmel R, Sapiro G (1995) Geodesic active contours. IEEE Intl Conf Comput Vis:694–699
Caselles V, Kimmel R, Sapiro G (1997) Geodesic active contours. Int J Comput Vis 22(1):61–79
Chakraborty R, Sushil R, Garg ML (2019) An improved PSO-based multilevel image segmentation technique using minimum cross-entropy thresholding. Arab J Sci Eng 44(4):3005–3020
Chan TF, Vese LA (2001) Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans Image Process 10:266–277
Chan I, Wells W, Mulkern RV, Haker S, Zhang J, Zou KH, Maier SE, Tempany C (2003) Detection of prostate cancer by integration of line-scan diffusion, T2-mapping and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging; a multichannel statistical classifier. Med Phys 30(9):2390–2398
Chung AG, Khalvati F, Shafiee MJ, Haider MA, Wong A (2015) Prostate cancer detection via a quantitative radiomics-driven conditional random field framework. IEEE Access. 3:2531–2541
Clark T, Zhang J, Baig S, Wong A, Haider MA, Khalvati F (2017) Fully automated segmentation of prostate whole gland and transition zone in diffusion-weighted MRI using convolutional neural networks. J Med Imagisg 4(4):041307
Cremers D (2008) Nonlinear dynamical shape priors for level set segmentation. J Sci Comput 35(2–3):132–143
Cremers D, Osher SJ, Soatto S (2006) Kernel density estimation and intrinsic alignment for shape priors in level set segmentation. Int J Comput Vis 69(3):335–351
de Rooij M, Hamoen EH, Fütterer JJ, Barentsz JO, Rovers MM (2014) Accuracy of multiparametric MRI for prostate cancer detection: a meta-analysis. Am J Roentgenol 202(2):343–351
Duda D, Kretowski M, Mathieu R, de Crevoisier R, Bezy-Wendling J (2014) Multi-image texture analysis in classification of prostatic tissues from MRI. Preliminary results. InInformation Technologies in Biomedicine, volume 3 (pp. 139-150). Springer, Cham
Fehr D, Veeraraghavan H, Wibmer A, Gondo T, Matsumoto K, Vargas HA, Sala E, Hricak H, Deasy JO (2015) Automatic classification of prostate cancer Gleason scores from multiparametric magnetic resonance images. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112(46):E6265–E6273
Filson CP, Natarajan S, Margolis DJ, Huang J, Lieu P, Dorey FJ, Reiter RE, Marks LS (2016) Prostate cancer detection with magnetic resonance-ultrasound fusion biopsy: the role of systematic and targeted biopsies. Cancer. 122(6):884–892
Firjani A, Khalifa F, Elnakib A, Gimel’farb G, El-Ghar MA, Elmaghraby A, El-Baz A (2014) A novel image-based approach for early detection of prostate cancer using DCE-MRI. InComputational intelligence in biomedical imaging (pp. 55-82). Springer, New York, NY
Garg G, Juneja M (2018) A survey of prostate segmentation techniques in different imaging modalities. Curr Med Imag 14(1):19–46
Garg G, Juneja M (2019) A survey of denoising techniques for multi-parametric prostate MRI. Multimed Tools Appl 78(10):12689–12722
Giannini V, Vignati A, Mazzetti S, De Luca M, Bracco C, Stasi M, Russo F, Armando E, Regge D (2013) A prostate CAD system based on multiparametric analysis of DCE T1-w, and DW automatically registered images. InMedical imaging 2013: computer-aided diagnosis (Vol. 8670, p. 86703E). Intl Soc Opt Photonics.
Ginsburg SB, Algohary A, Pahwa S, Gulani V, Ponsky L, Aronen HJ, Boström PJ, Böhm M, Haynes AM, Brenner P, Delprado W (2017) Radiomic features for prostate cancer detection on MRI differ between the transition and peripheral zones: preliminary findings from a multi-institutional study. J Magn Reson Imaging 46(1):184–193
Kass M, Witkin A, Terzopoulos D (1988) Snakes: active contour models. Int J Comput Vis 1(4):321–331
Kate V, Shukla P (2020) Image segmentation of breast Cancer histopathology images using PSO-based clustering technique. InSocial networking and computational intelligence (pp. 207-216). Springer, Singapore
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle Swarm Optimization. Proceedings of IEEE international conference on neural networks. IV. Pp. 1942–1948
Khalvati F, Wong A, Haider MA (2015) Automated prostate cancer detection via comprehensive multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging texture feature models. BMC Med Imaging 15(1):27
Khalvati F, Zhang J, Wong A, Haider MA (2016) Bag of bags: nested multi instance classification for prostate Cancer detection. InMachine learning and applications (ICMLA), 2016 15th IEEE international conference on (pp. 146-151). IEEE
Lankton S, Tannenbaum A (2008) Localizing region-based active contours. IEEE Trans Image Process 17(11):2029–2039
Le MH, Chen J, Wang L, Wang Z, Liu W, Cheng KT, Yang X (2017) Automated diagnosis of prostate cancer in multi-parametric MRI based on multimodal convolutional neural networks. Phys Med Biol 62(16):6497–6514
Lemaitre G. (n.d.) Computer-aided diagnosis for prostate cancer using multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (Doctoral dissertation, Ph. D. dissertation, Universitat de Girona and Université de Bourgogne).
Lemaitre G, Massich J, Martí R, Freixenet J, Vilanova JC, Walker PM, Sidibé D, Mériaudeau F (2015) A boosting approach for prostate cancer detection using multi-parametric MRI. InTwelfth international conference on quality control by artificial vision 2015 Apr 30 (Vol. 9534, p. 95340A). Intl Soc Opt Photonics
Lemaître G, Martí R, Freixenet J, Vilanova JC, Walker PM, Meriaudeau F (2015) ComputerAided detection and diagnosis for prostate cancer based on mono and multi-parametric MRI: a review. Comput Biol Med 60:8–31
Li C, Xu C, Gui C, Fox MD (2005) Level set evolution without re-initialization: A new variational formulation,” in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogn, pp. 430–436
Li C, Kao C-Y, Gore JC, Ding Z (2008) Minimization of region-scalable fitting energy for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 17(10):1940–1949
Li C, Xu C, Member S, Gui C, Fox MD (2010) Distance regularized level set evolution and its application to image segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(12):3243–3254
Litjens GJ, Vos PC, Barentsz JO, Karssemeijer N, Huisman HJ (2011) Automatic computer aided detection of abnormalities in multi-parametric prostate MRI. InMedical imaging 2011: computer-aided diagnosis (Vol. 7963, p. 79630T). Intl Soc Opt Photonics
Litjens GJ, Barentsz JO, Karssemeijer N, Huisman HJ (2012) Automated computer-aided detection of prostate cancer in MR images: from a whole-organ to a zone-based approach. InMedical imaging 2012: computer-aided diagnosis (Vol. 8315, p. 83150G). Intl Soc Opt Photonics.
Litjens GJ, Elliott R, Shih N, Feldman M, Barentsz JO, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa CA, Kovacs I, Huisman HJ, Madabhushi A (2014) Distinguishing prostate cancer from benign confounders via a cascaded classifier on multi-parametric MRI. InMedical imaging 2014: computer-aided diagnosis (Vol. 9035, p. 903512). Intl Soc Opt Photonics
Liu S, Peng Y (2012) A local region-based chan-vese model for image segmentation. Pattern Recogn 45(7):2769–2779
Liu P, Wang S, Turkbey B, Grant K, Pinto P, Choyke P, Wood BJ, Summers RM (2013) A prostate cancer computer-aided diagnosis system using multimodal magnetic resonance imaging and targeted biopsy labels. InMedical imaging 2013: computer-aided diagnosis (Vol. 8670, p. 86701G). Intl Soc Opt Photonics.
Liu Z, Jiang W, Lee KH, Lo YL, Ng YL, Dou Q, Vardhanabhuti V, Kwok KW (2019) A two-stage approach for automated prostate lesion detection and classification with mask R-CNN and weakly supervised deep neural network. InWorkshop on artificial intelligence in radiation therapy (pp. 43-51). Springer, Cham
Lopes R, Ayache A, Makni N, Puech P, Villers A, Mordon S, Betrouni N (2011) Prostate cancer characterization on MR images using fractal features. Med Phys 38(1):83–95
Matulewicz L, Jansen JF, Bokacheva L, Vargas HA, Akin O, Fine SW, Shukla-Dave A, Eastham JA, Hricak H, Koutcher JA, Zakian KL (2014) Anatomic segmentation improves prostate cancer detection with artificial neural networks analysis of 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 40(6):1414–1421
Mazzetti S, De Luca M, Bracco C, Vignati A, Giannini V, Stasi M, Russo F, Armando E, Agliozzo S, Regge D (2011) A CAD system based on multi-parametric analysis for cancer prostate detection on DCE-MRI. InMedical imaging 2011: computer-aided diagnosis (Vol. 7963, p. 79633Q). Intl Soc Opt Photonics
Mohammed ZF, Abdulla AA (2020) Thresholding-based white blood cells segmentation from microscopic blood images. UHD J Sci Technol 4(1):9–17
Niaf E, Rouvière O, Lartizien C (2011) Computer-aided diagnosis for prostate cancer detection in the peripheral zone via multisequence MRI. InMedical imaging 2011: computer-aided diagnosis (Vol. 7963, p. 79633P). Intl Soc Opt Photonics
Niaf E, Rouvière O, Mège-Lechevallier F, Bratan F, Lartizien C (2012) Computer-aided diagnosis of prostate cancer in the peripheral zone using multiparametric MRI. Phys Med Biol 57(12):3833–3851
Nikolova M, Esedoglu S, Chan TF (2006) Algorithms for finding global minimizers of image segmentation and denoising models. SIAM J Appl Math 66(5):1632–1648
Paragios N, Deriche R (2000) Geodesic active contours and level sets for the detection and tracking of moving objects. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22(3):266–280
Paragios N, Deriche R (2002) Geodesic active regions and level set methods for supervised texture segmentation. Int J Comput Vis 46:223–247
Parfait S, Walker PM, Créhange G, Tizon X, Miteran J (2012 Sep 1) Classification of prostate magnetic resonance spectra using support vector machine. Biomed Signal Process Control 7(5):499–508
Parra NA, Pollack A, Chinea FM, Abramowitz MC, Marples B, Munera F, Castillo R, Kryvenko ON, Punnen S, Stoyanova R (2017) automatic Detection and Quantitative Dce-Mri scoring of Prostate cancer aggressiveness. Frontiers in oncology. 7
Peng Y, Jiang Y, Antic T, Giger ML, Eggener S, Oto A (2013) A study of T 2-weighted MR image texture features and diffusion-weighted MR image features for computer-aided diagnosis of prostate cancer. InMedical imaging 2013: computer-aided diagnosis (Vol. 8670, p. 86701H). Intl Soc Opt Photonics.
Peng Y, Jiang Y, Yang C, Brown JB, Antic T, Sethi I, Schmid-Tannwald C, Giger ML, Eggener SE, Oto A (2013) Quantitative analysis of multiparametric prostate MR images: differentiation between prostate cancer and normal tissue and correlation with Gleason score—a computer-aided diagnosis development study. Radiology. 267(3):787–796
Ramudu K, Babu TR (2018) Segmentation of tissues from MRI biomedical images using kernel fuzzy PSO clustering based level set approach. Curr Med Imag 14(3):389–400
Rundo L, Militello C, Russo G, Garufi A, Vitabile S, Gilardi MC, Mauri G (2017) Automated prostate gland segmentation based on an unsupervised fuzzy C-means clustering technique using multispectral T1w and T2w MR imaging. Information. 8(2):49
Rundo L, Han C, Zhang J, Hataya R, Nagano Y, Militello C, Ferretti C, Nobile MS, Tangherloni A, Gilardi MC, Vitabile S (2020) CNN-based prostate zonal segmentation on T2-weighted MR images: a cross-dataset study. InNeural approaches to dynamics of signal exchanges (pp. 269-280). Springer, Singapore
Schröder FH, Hugosson J, Roobol MJ, Tammela TL, Ciatto S, Nelen V, Kwiatkowski M, Lujan M, Lilja H, Zappa M, Denis LJ (2009) Screening and prostate-cancer mortality in a randomized European study. N Engl J Med 360(13):1320–1328
Sharif M, Amin J, Raza M, Yasmin M, Satapathy SC (2020) An integrated design of particle swarm optimization (PSO) with fusion of features for detection of brain tumor. Pattern Recogn Lett 129:150–157
Song X, Li H (2020) Segmentation based on particle swarm optimization. InInternational conference on applications and techniques in cyber security and intelligence (pp. 731-736). Springer, Cham
Steiger P, Thoeny HC (2016) Prostate MRI based on PI-RADS version 2: how we review and report. Cancer Imaging 16(1):9
Sung YS, Kwon HJ, Park BW, Cho G, Lee CK, Cho KS, Kim JK (2011) Prostate cancer detection on dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI: computer-aided diagnosis versus single perfusion parameter maps. Am J Roentgenol 197(5):1122–1129
Thamaraichelvi B (2020) PSO optimized pulse coupled neural network for segmenting MR brain image. In2020 international conference on communication and signal processing (ICCSP) (pp. 0731-0733). IEEE
Tiwari P, Kurhanewicz J, Madabhushi A (2013) Multi-kernel graph embedding for detection, Gleason grading of prostate cancer via MRI/MRS. Med Image Anal 17(2):219–235
Turkbey B, Choyke PL (2012) Multiparametric MRI and prostate cancer diagnosis and risk stratification. Curr Opin Urol 22(4):310–315
Valerio M, Donaldson I, Emberton M, Ehdaie B, Hadaschik BA, Marks LS, Mozer P, Rastinehad AR, Ahmed HU (2015) Detection of clinically significant prostate cancer using magnetic resonance imaging–ultrasound fusion targeted biopsy: a systematic review. Eur Urol 68(1):8–19
Vese LA, Chan TF (2002) A multiphase level set framework for image segmentation using the Mumford and shah model. Int J Comput Vis 50:271–293
Viswanath S, Bloch BN, Chappelow J, Patel P, Rofsky N, Lenkinski R, Genega E, Madabhushi A (2011) Enhanced multi-protocol analysis via intelligent supervised embedding (EMPrAvISE): detecting prostate cancer on multi-parametric MRI. InMedical imaging 2011: computer-aided diagnosis (Vol. 7963, p. 79630U). Intl Soc Opt Photonics.
Viswanath SE, Bloch NB, Chappelow JC, Toth R, Rofsky NM, Genega EM, Lenkinski RE, Madabhushi A (2012) Central gland and peripheral zone prostate tumors have significantly different quantitative imaging signatures on 3 tesla endorectal, in vivo T2-weighted MR imagery. J Magn Reson Imaging 36(1):213–224
Vos PC, Barentsz JO, Karssemeijer N, Huisman HJ (2012) Automatic computer-aided detection of prostate cancer based on multiparametric magnetic resonance image analysis. Phys Med Biol 57(6):1527–1542
Wang L, Pan C (2015) Explicit order model for region-based level set segmentation. InAcoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), 2015 IEEE international conference on Apr 19 (pp. 927-931). IEEE.
Wang L, Zwiggelaar R (2017) 3d texton based prostate cancer detection using multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging. InAnnual conference on medical image understanding and analysis (pp. 309-319). Springer, Cham
Wang LF, Yu Z, Pan C (2012) A unified level set framework utilizing parameter priors for medical image segmentation. Sci China Inf Sci 55:1–14
Wang LF, Wu H-Y, Pan C (2013) Region based image segmentation with local signed difference energy. Pattern Recogn Lett 34(6):637–645
Xu C, Prince JL (1998) Snakes, shapes, and gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans Image Process 7(3):359–369
Yang X, Liu C, Wang Z, Yang J, Le Min H, Wang L, Cheng KT (2017) Co-trained convolutional neural networks for automated detection of prostate cancer in multi-parametric MRI. Med Image Anal 42:212–227
Zhang L, Lim CP (2020) Intelligent optic disc segmentation using improved particle swarm optimization and evolving ensemble models. Appl Soft Comput 20:106328
Zhang KH, Song HH, Zhang L (2010) Active contours driven by local image fitting energy. Pattern Recogn 43(4):1199–1206
Zhao F, Chen Y, Liu H, Fan J (2019) Alternate PSO-based adaptive interval type-2 intuitionistic fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for color image segmentation. IEEE Access 7:64028–64039
Zhao J, Wang X, Li M (2020) A novel Neutrosophic image segmentation based on improved fuzzy C-means algorithm (NIS-IFCM). Int J Pattern Recognit Artif Intell 34(05):2055011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
The dataset used in this research article is openly available and provided by [34].
Conflict of interest
There are no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garg, G., Juneja, M. Particle swarm optimization based segmentation of Cancer in multi-parametric prostate MRI. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 30557–30580 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11133-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11133-2