Abstract
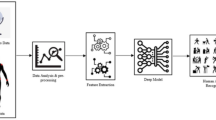
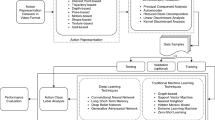
Human activity recognition has become one of the most active areas of research in computer vision, due to its increasing demand in many automated monitoring applications such as visual surveillance, human-computer interaction, health care, security systems, and many more. This work aims to introduce an integrated feature descriptor which combines texture feature and shape feature, at multiple orientations, to construct the efficient and robust feature vector for activity recognition in realistic scenarios. This feature descriptor is an integration of Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), multiscale Local Binary Pattern, and Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG). HOG descriptor extracts local-oriented histograms of the frame sequences, multiscale LBP gives the complex structural information of the frames and DWT gives the directional information at multiple scales. By exploiting these properties, we have constructed an integrated feature descriptor to construct the feature vector and achieves promising results of activity recognition in realistic videos. Multiclass Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier with one-vs-one architecture has been used for activity recognition. The experiments are performed on five benchmark publicly available video datasets, namely Weizmann, IXMAS, UT Interaction, HMDB51, and UCF101. The experimental results are compared with the results of other state-of-art methods based on conventional machine learning and deep learning-based methods to show the effectiveness and usefulness of the proposed work. The experimental results have demonstrated that the proposed method performs better than the other state-of-art methods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahad MA, Islam MN, Jahan I (2016) Action recognition based on binary patterns of action-history and histogram of oriented gradient. Journal on Multimodal User Interfaces 10(4):335–344
Ahmad M, Lee SW (2008) Human action recognition using shape and CLG-motion flow from multi-view image sequences. Pattern Recogn 41(7):2237–2252
Ahonen T, Matas J, He C, Pietikäinen M (2009) Rotation invariant image description with local binary pattern histogram fourier features. InScandinavian conference on image analysis 2009 Jun 15, pp 61-70. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Akula A, Shah AK, Ghosh R (2018) Deep learning approach for human action recognition in infrared images. Cogn Syst Res 50:146–154
Almaadeed N, Elharrouss O, Al-Maadeed S, Bouridane A, Beghdadi A (2019) A novel approach for robust multi human action detection and recognition based on 3-dimentional convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11272. 2019 Jul 25
Althloothi S, Mahoor MH, Zhang X, Voyles RM (2014) Human activity recognition using multi-features and multiple kernel learning. Pattern Recogn 47(5):1800–1812
Aly S, Sayed A (2019 Sep 15) Human action recognition using bag of global and local Zernike moment features. Multimed Tools Appl 78(17):24923–24953
Avola D, Bernardi M, Foresti GL (2019) Fusing depth and colour information for human action recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 78(5):5919–5939
Ballan L, Bertini M, Del Bimbo A, Serra G (2010) Video event classification using string kernels. Multimed Tools Appl 48(1):69–87
Ben-Arie J, Wang Z, Pandit P, Rajaram S (2002) Human activity recognition using multidimensional indexing. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell Arch 24(8):1091–1104
Bhatti N, Hanbury A, Stottinger J (2018) Contextual local primitives for binary patent image retrieval. Multimed Tools Appl 77(7):9111–9151
Bi F, Fu X, Chen W, Fang W, Miao X, Assefa B (2020) Fire detection method based on improved fruit fly optimization-based SVM. CMC-Computers Materials & Continua 62(1):199–216
Blank M, Gorelick L, Shechtman E, Irani M, Basri R (2005) Actions as space-time shapes. InTenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV'05) Volume 1 2005 Oct 17, vol 2, pp 1395–1402
Bobick AF, Davis JW (2001) The recognition of human movement using temporal templates. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(3):257–267
Boser BE, Guyon IM, Vapnik VN (1992) A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. InProceedings of the fifth annual workshop on Computational learning theory 1992 Jul 1, pp 144–152
Carlsson S, Sullivan J (2001) Action recognition by shape matching to key frames. InWorkshop on models versus exemplars in computer vision 2001 Dec, vol 1, no 18
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2011) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST) 2(3):27
Cohen I, Li H (2003) Inference of human postures by classification of 3D human body shape. In: 2003 IEEE international SOI conference. Proceedings (cat. No. 03CH37443) 2003 Oct 17 pp 74-81. IEEE
Dalal N, Triggs B (2005) Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol. 1, pp 886–893
Fernández A, Ghita O, González E, Bianconi F, Whelan PF (2011) Evaluation of robustness against rotation of LBP, CCR and ILBP features in granite texture classification. Mach Vis Appl 22(6):913–926
Gadekallu TR, Khare N, Bhattacharya S, Singh S, Reddy Maddikunta PK, Ra IH, Alazab M (2020) Early detection of diabetic retinopathy using PCA-firefly based deep learning model. Electronics. 9(2):274
Gonzalez RC, Woods RE (2002) Digital Image Processing. 2nd edn Prentice Hall. New Jersey, 793
Gumaei A, Al-Rakhami M, AlSalman H, Rahman SM, Alamri A (2020) DL-HAR: deep learning-based human activity recognition framework for edge computing. CMC-Computers Materials & Continua. 65(2):1033–1057
Hsu CW, Lin CJ (2002) A comparison of methods for multiclass support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 13(2):415–425
Jamel AA, Akay B (2020) Human activity recognition based on parallel approximation kernel k-means algorithm. Comput Syst Sci Eng 35(6):441–456
Jhuang H, Garrote H, Poggio E, Serre T, Hmdb T (2011) A large video database for human motion recognition. In: Proc of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision 2011 Vol 4, No 5, p. 6
Kabir MH, Thapa K, Yang JY, Yang SH (2019) State-space based linear modeling for human activity recognition in smart space. Intell Autom Soft Comput 25(4):673–681
Ke S-R, Thuc H, Lee Y-J, Hwang J-N, Yoo J-H, Choi K-H (2013) A review on video-based human activity recognition. Computers 2(2):88–131
Kellokumpu V, Zhao G, Pietikäinen M (2010) Dynamic textures for human movement recognition. In: Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Image and Video Retrieval 2010 Jul 5, pp 470–476
Kellokumpu V, Zhao G, Pietikäinen M (2011) Recognition of human actions using texture descriptors. Mach Vis Appl 22(5):767–780
Khan MA, Zhang YD, Khan SA, Attique M, Rehman A, Seo S (2020) A resource conscious human action recognition framework using 26-layered deep convolutional neural network. Multimed Tools Appl 1:1–23
Khan MA, Javed K, Khan SA, Saba T, Habib U, Khan JA, Abbasi AA (2020) Human action recognition using fusion of multiview and deep features: an application to video surveillance. Multimed Tools Appl 14:1–27
Khare M, Srivastava RK, Khare A (2017) Object tracking using combination of daubechies complex wavelet transform and Zernike moment. Multimed Tools Appl 76(1):1247–1290
Kim SJ, Kim SW, Sandhan T, Choi JY (2014) View invariant action recognition using generalized 4D features. Pattern Recogn Lett 49:40–47
Kumaran N, Vadivel A, Kumar SS (2018) Recognition of human actions using CNN-GWO: a novel modeling of CNN for enhancement of classification performance. Multimed Tools Appl 77(18):23115–23147
Laptev I (2005) On space-time interest points. Int J Comput Vis 64(2–3):107–123
Liu Y, Nie L, Han L, Zhang L, Rosenblum DS (2015) Action2Activity: recognizing complex activities from sensor data. In: Twenty-fourth international joint conference on artificial intelligence 2015 Jun 24
Liu Y, Nie L, Liu L, Rosenblum DS (2016) From action to activity: sensor-based activity recognition. Neurocomputing. 181:108–115
Liu L, Cheng L, Liu Y, Jia Y, Rosenblum DS (2016) Recognizing complex activities by a probabilistic interval-based model. InAAAI 2016 Feb 12 (Vol. 30, pp. 1266–1272)
Liu C, Li Z, Shi X, Du C (2018) Learning a mid-level representation for Multiview action recognition. Adv Multimed 1:2018
Moussa MM, Hamayed E, Fayek MB, El Nemr HA (2015) An enhanced method for human action recognition. J Adv Res 6(2):163–169
Murtaza F, Yousaf MH, Velastin SA (2016) Multi-view human action recognition using 2D motion templates based on MHIs and their HOG description. IET Comput Vis 10(7):758–767
Nguyen DT, Ogunbona PO, Li W (2013) A novel shape-based non-redundant local binary pattern descriptor for object detection. Pattern Recogn 46(5):1485–1500
Nigam S, Khare A (2015) Multiresolution approach for multiple human detection using moments and local binary patterns. Multimed Tools Appl 74(17):7037–7062
Nigam S, Khare A (2016) Integration of moment invariants and uniform local binary patterns for human activity recognition in video sequences. Multimed Tools Appl 75(24):17303–17332
Ojala T, Pietikäinen M, Harwood D (1996) A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on featured distributions. Pattern Recogn 29(1):51–59
Ojala T, Pietikainen M, Maenpaa T (2002) Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(7):971–987
Pietikäinen M, Hadid A, Zhao G, Ahonen T (2011) Local binary patterns for still images. InComputer vision using local binary patterns 2011, pp 13-47. Springer, London
Ryoo MS, Aggarwal JK (2009) Spatio-temporal relationship match: video structure comparison for recognition of complex human activities. In2009 IEEE 12th international conference on computer vision 2009 Sep 29, pp 1593-1600. IEEE.
Seemanthini K, Manjunath SS (2018) Human detection and tracking using HOG for action recognition. Proc Comput Sci 132:1317–1326
Sharif A, Khan MA, Javed K, Gulfam H, Iqbal T, Saba T, Ali H, Nisar W (2019) Intelligent human action recognition: a framework of optimal features selection based on Euclidean distance and strong correlation. J Control Eng Appl Inform 21(3):3–11
Sharif M, Khan MA, Zahid F, Shah JH, Akram T (2020) Human action recognition: a framework of statistical weighted segmentation and rank correlation-based selection. Pattern Anal Applic 23(1):281–294
Sharma CM, Kushwaha AKS, Nigam S, Khare A (2011) Automatic human activity recognition in video using background modeling and spatio-temporal template matching based technique. In: Proc. of international conference on advances in computing and artificial intelligence (ACAI –2011), pp 97–101
Shen J, Yang W, Sun C (2013) Real-time human detection based on gentle MILBoost with variable granularity HOG-CSLBP. Neural Comput & Applic 23(7–8):1937–1948
Shen J, Deng RH, Cheng Z, Nie L, Yan S (2015) On robust image spam filtering via comprehensive visual modeling. Pattern Recogn 48(10):3227–3238
Singh D, Singh B (2019) Investigating the impact of data normalization on classification performance. Appl Soft Comput 23:105524
Singh R, Kushwaha AK, Srivastava R (2019) Multi-view recognition system for human activity based on multiple features for video surveillance system. Multimed Tools Appl 78(12):17165–17196
Singh R, Dhillon JK, Kushwaha AK, Srivastava R (2019) Depth based enlarged temporal dimension of 3D deep convolutional network for activity recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 78(21):30599–30614
Soomro K, Zamir AR, Shah M (2012) UCF101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. arXiv preprint arXiv:1212.0402. 2012 Dec 3
Srivastava P, Khare A (2017) Integration of wavelet transform, local binary patterns and moments for content-based image retrieval. J Vis Commun Image Represent 42:78–103
Srivastava P, Khare A (2018) Utilizing multiscale LLocal binary pattern for content-based image retrieval. Multimed Tools Appl 77(10):12377–12403
Tan X, Triggs B (2010) Enhanced local texture feature sets for face recognition under difficult lighting conditions. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(6):1635–1650
Uddin MA, Lee YK (2019) Feature fusion of deep spatial features and handcrafted spatiotemporal features for human action recognition. Sensors. 19(7):1599
Veeraraghavan A, Chellappa R, Roy-Chowdhury AK (2006) The function space of an activity. In: 2006 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR'06) 2006 Jun 17, vol 1, pp 959-968. IEEE
Vili K, Guoying Z, Matti P (2008) Texture based description of movements for activity analysis. InInt. Conf. on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP 2008) 2008 Jan 22, vol 1, pp 206–213
Vishwakarma DK (2020) A two-fold transformation model for human action recognition using decisive pose. Cogn Syst Res 61:1–3
Wang L, Qian X, Zhang Y, Shen J, Cao X (2019) Enhancing sketch-based image retrieval by cnn semantic re-ranking. IEEE Trans Cybern 15
Yeffet L, Wolf L (2009) Local trinary patterns for human action recognition. In2009 IEEE 12th international conference on computer vision 2009 Sep 27, pp 492–497
Zare A, Moghaddam HA, Sharifi A (2020) Video spatiotemporal mapping for human action recognition by convolutional neural network. Pattern Anal Applic 23(1):265–279
Zhang HB, Zhang YX, Zhong B, Lei Q, Yang L, Du JX, Chen DS (2019) A comprehensive survey of vision-based human action recognition methods. Sensors. 19(5):1005
Zhu L, Shen J, Jin H, Zheng R, Xie L (2015) Content-based visual landmark search via multimodal hypergraph learning. IEEE Trans Cybern 45(12):2756–2769
Zhu L, Shen J, Xie L, Cheng Z (2016) Unsupervised visual hashing with semantic assistant for content-based image retrieval. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 29(2):472–486
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kushwaha, A., Khare, A. & Srivastava, P. On integration of multiple features for human activity recognition in video sequences. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 32511–32538 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11207-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11207-1