Abstract
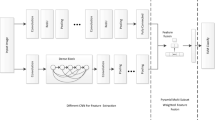
To address the problem of redundant learning in remote sensing scene classification, a method of multi-space-scale frequency covariance pooling (MSFCP) is proposed in this study. Specifically, a Gabor filter is introduced to the network which reduced redundant learning in ordinary convolution filters and enhanced the robustness of the network to external interference. Secondly, reducing redundant information in low-frequency components via dividing the feature map output by the first layer into high and low-frequencies and performing average pooling for low-frequency information. Next, the introduction of the Octave Convolution (OctConv) operation realized self-update and information interaction of high and low-frequency characteristics. Finally, the global covariance pooling is performed on the output feature map to enhance the representation ability of the entire network and boost the classification effect. Our method performed an accuracy value of 99.35 ± 0.28 (%) on the UC Merced Land Use dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed MSFCP method achieves better classification performance and lower network model complexity than other methods, which significantly reduces the demand for computing power. Hence, a good trade-off is achieved between experimental accuracy and computational resource consumption.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaib S, Gu Y, Yao H (2015) An informative feature selection method based on sparse PCA for VHR scene classification[J]. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 13(2):147–151. https://doi.org/10.1109/lgrs.2015.2501383
Chan TH, Jia K, Gao S (2015) PCANet: a simple deep learning baseline for image classification?[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5017–5032. https://doi.org/10.1109/tip.2015.2475625
Chen Y, Fang H, Xu B (2019) Drop an octave: reducing spatial redundancy in convolutional neural networks with octave convolution[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.05049. arXiv:1904.05049v3
Cheng G, Guo L, Zhao T (2013) Automatic landslide detection from remote-sensing imagery using a scene classification method based on BoVW and pLSA[J]. Int J Remote Sens 34(1):45–59. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2012.705443
Cheng G, Han J, Zhou P (2014) Multi-class geospatial object detection and geographic image classification based on collection of part detectors[J]. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 98:119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.10.002
Cheng G, Zhou P, Han J (2015) Auto-encoder-based shared mid-level visual dictionary learning for scene classification using very high resolution remote sensing images[J]. IET Comput Vis 9(5):639–647. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-cvi.2014.0270
Cheng G, Han J, Guo L (2015) Effective and efficient midlevel visual elements-oriented land-use classification using VHR remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(8):4238–4249. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2015.2393857
Cheng G, Ma C, Zhou P (2016) Scene classification of high resolution remote sensing images using convolutional neural networks[C]//2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). IEEE, 767–770. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/igarss.2016.7729193
Cheng G, Han J, Lu X (2017) Remote sensing image scene classification: benchmark and state of the art[J]. Proc IEEE 105(10):1865–1883. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2017.2709802
Cheriyadat AM (2013) Unsupervised feature learning for aerial scene classification[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 52(1):439–451. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2013.2241444
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R (2009) Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database[C]//2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE:248–255. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvprw.2009.5206848
dos Santos JA, Penatti OAB, da Silva Torres R (2010) Evaluating the potential of texture and color descriptors for remote sensing image retrieval and classification[C]//VISAPP (2),203–208. doi:https://doi.org/10.5220/0002843402030208
Fang Z, Li W, Zou J (2016) Using CNN-based high-level features for remote sensing scene classification[C]//2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). IEEE, 2610–2613. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/igarss.2016.7729674
He K, Zhang X, Ren S (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 770–778. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2016.90
He N, Fang L, Li S, Plaza J, Plaza A (2020) Skip-connected covariance network for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learn Syst 31(5):1461–1474
Jain AK, Ratha NK, Lakshmanan S (1997) Object detection using Gabor filters[J]. Pattern Recogn 30(2):295–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-3203(96)00068-4
Jiang B., Li X., Sun T. (2018). A decision-level fusion method based on convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification[C]//2018 IEEE 3rd advanced information technology, electronic and automation control conference (IAEAC). IEEE, 128-132. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/iaeac.2018.8577603.
Kapoor R, Gupta R, Kumar R (2019) Fog removal in images using improved dark channel prior and contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization[J]. Multimed Tools Appl 78(16):23281–23307. https://doi.org/10.1109/cisp.2009.5301485
Li P, Xie J, Wang Q (2017) Is second-order information helpful for large-scale visual recognition?[C]//proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2070–2078. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2017.228
Li P, Xie J, Wang Q (2018) Towards faster training of global covariance pooling networks by iterative matrix square root normalization[C]//proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 947–955. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2018.00105
Li X, Jiang B, Wang S (2019) A review and comparison of optical remote sensing scene classification[J]. Radio. Engineering 49(4):265–271. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2019.04.01
Lin M, Chen Q, Yan S (2013) Network in network[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.4400. arXiv:1312.4400v3
Liu Q, Hang R, Song H (2017) Learning multiscale deep features for high-resolution satellite image scene classification[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(1):117–126. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2017.2743243
Meshgini S, Aghagolzadeh A, Seyedarabi H (2012) Face recognition using gabor filter bank, kernel principle component analysis and support vector machine[J]. Int J Comput Theory Eng 4(5):767–771. https://doi.org/10.7763/ijcte.2012.v4.574
Nanjun H, Leyuan F, Shutao L (2018) Remote Sensing Scene Classification Using Multilayer Stacked Covariance Pooling[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. 1–12. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2018.2845668
Nogueira K, Penatti OAB, dos Santos JA (2017) Towards better exploiting convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification[J]. Pattern Recognit 61:539–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.07.001
Ojala T, Pietikäinen M, Mäenpää T (2002) Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Analys Machine Intell 7:971–987. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2002.1017623
Othman E, Bazi Y, Alajlan N (2016) Using convolutional features and a sparse autoencoder for land-use scene classification[J]. Int J Remote Sens 37(10):2149–2167. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2016.1171928
Penatti OAB, Nogueira K, Dos Santos JA (2015) Do deep features generalize from everyday objects to remote sensing and aerial scenes domains?[C]//proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, 4451. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/cvprw.2015.7301382
Ren W, Ma L, Zhang J, et al. (2018) Gated fusion network for single image dehazing[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 3253–3261
Ren W., Pan J., Zhang H., Cao X., Yang M.H. Single Image Dehazing via Multi-scale Convolutional Neural Networks with Holistic Edges[J]. Int J Comput Vis, 2020, 128(8), 128, 259.
Sheng G, Yang W, Xu T (2012) High-resolution satellite scene classification using a sparse coding based multiple feature combination[J]. Int J Remote Sens 33(8):2395–2412. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2011.608740
Swain MJ, Ballard DH (1991) Color indexing[J]. Int J Comput Vis 7(1):11–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00130487
Wang EK, Li Y, Nie Z, Yu J, Liang Z, Zhang X, Yiu SM (2019) Deep fusion feature based object detection method for high resolutionoptical remote sensing images. Appl Sci 9(6):1130
Wang S, Guan Y, Shao L (2020) Multi-granularity canonical appearance pooling for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:5396–5407
Wu H, Liu B, Su W (2016) Hierarchical coding vectors for scene level land-use classification[J]. Remote Sens 8(5):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8050436
Xu SH, Mu XD, Zhao P (2016) Scene classification of remote sensing image based on multi-scale feature and deep neural network[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica. China 45(7):834–840. https://doi.org/10.11947/j.AGCS.2016.20150623
Yang Y, Newsam S (2010) Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification[C]//Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL international conference on advances in geographic information systems. ACM, 270–279. doi:https://doi.org/10.1145/1869790.1869829
Yao W, Loffeld O, Datcu M (2016) Application and evaluation of a hierarchical patch clustering method for remote sensing images[J]. IEEE J Select Topics Appl Earth Observ Remote Sens 9(6):2279–2289. https://doi.org/10.1109/jstars.2016.2536143
Zhang, Hua, et al (2016) Sketchnet: Sketch classification with web images." Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Zhao B, Zhong Y, Zhang L (2016) A spectral–structural bag-of-features scene classifier for very high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery[J]. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 116:73–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2016.03.004
Zheng X, Sun X, Fu K (2012) Automatic annotation of satellite images via multifeature joint sparse coding with spatial relation constraint[J]. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 10(4):652–656. https://doi.org/10.1109/lgrs.2012.2216499
Zhong Y, Zhu Q, Zhang L (2015) Scene classification based on the multifeature fusion probabilistic topic model for high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(11):6207–6222. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2015.2435801
Zhu Q, Zhong Y, Zhao B (2016) Bag-of-visual-words scene classifier with local and global features for high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 13(6):747–751. https://doi.org/10.1109/lgrs.2015.2513443
Zhu Q, Hong Y, Zhang L (2017) Scene classification based on the fully sparse semantic topic model[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55(10):5525–5538. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2017.2709802
Acknowledgements
Firstly, the author would like to thank the provider of UC Merced Land Use dataset and the support of experimental equipment provided by the Institute of Artificial Intelligence Application of Central South University of Forestry and Technology. Meanwhile, the author would also like to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions, which significantly improved this paper.
I hereby express gratitude to my dear partner Yuan Gao, without his effort, this paper cannot be accomplished. In the process of compilation, he made great contribution on data collecting and analyze. Besides, he completed the Section 4 and 5 by himself.
This work was supported by the National 948 Project of China: Forest Fire Prediction and Fire Fighting Resource Dispatching Technology under Grant 2014-4-09, National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 61602528), the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 2017JJ3527), and Graduate Innovation Fund of Central South University of Forestry and Technology (20183033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Yuan G is the Joint first author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Gao, Y., Chen, A. et al. Remote sensing scene classification with multi-spatial scale frequency covariance pooling. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 30413–30435 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12603-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12603-x