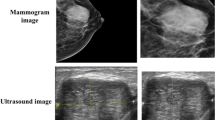
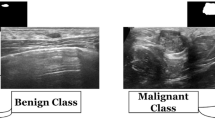
Abstract
Early detection of malignant breast cancer can significantly improve the survival chances of the involved patients. Analysis of a non-invasive and non-radioactive modality like ultrasound imaging with the help of Machine Learning(ML) and Artificial Intelligence(AI) techniques can be crucial for achieving such effective early-stage detection of the disease. A feature fusion based approach is proposed in this work, in conjunction with an ML pipeline that systematically deals with various problems like high dimensionality, class imbalance, and hyperparameter tuning, so that efficient benign vs. malignant classification can be performed. Experimental evaluation on two publicly available datasets reveals that the proposed approach is able to outperform state-of-the-art techniques on the classification task with an overall performance of above 95% for all the evaluation metrics under consideration and an AUC of \(\sim \)0.99. More specifically, an overall improvement of (1-4)%, (2-10)% and (2-7)% over the current state-of-the-art approaches could be obtained for the Accuracy, AUC and Sensitivity metrics respectively, on both the datasets. Such an efficient approach can provide the necessary real-time decision support to the involved radiologists, making better cancer patient care possible.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Code Availability
All the code corresponding to the experimental evaluation of the proposed approach will be made available at https://github.com/arnkmish.
References
Abadi M, Barham P, Chen J, Chen Z, Davis A, Dean J, Devin M, Ghemawat S, Irving G, Isard M, et al. (2016) Tensorflow: a system for large-scale machine learning. In: 12Th {USENIX} symposium on operating systems design and implementation ({OSDI} 16), pp 265–283
Al-Dhabyani W, Gomaa M, Khaled H, Fahmy A (2020) Dataset of breast ultrasound images. Data Brief 28:104863
Asraf A, Islam MZ, Haque MR, Islam MM (2020) Deep learning applications to combat novel coronavirus (covid-19) pandemic. SN Comput Sci 1(6):1–7
Ayon SI, Islam M, et al. (2019) Diabetes prediction: a deep learning approach. Int J Inf Eng Electr Bus 11(2)
Ayon SI, Islam MM, Hossain MR (2020) Coronary artery heart disease prediction: a comparative study of computational intelligence techniques. IETE J Res :1–20
Bradski G, Kaehler A (2000) Opencv. Dr. Dobb’s. J Softw Tools 3
Byra M, Galperin M, Ojeda-Fournier H, Olson L, O’Boyle M, Comstock C, Andre M (2019) Breast mass classification in sonography with transfer learning using a deep convolutional neural network and color conversion. Med Phys 46(2):746–755
Cai L, Wang X, Wang Y, Guo Y, Yu J, Wang Y (2015) Robust phase-based texture descriptor for classification of breast ultrasound images. Biomed Eng Online 14(1):26
Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP (2002) Smote: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J Artif Intell Res 16:321–357
Coelho LP (2012) Mahotas: Open source software for scriptable computer vision. arXiv:1211.4907
Dalal N, Triggs B (2005) Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: 2005 IEEE Computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR’05), vol 1. IEEE, pp 886–893
Daoud MI, Abdel-Rahman S, Bdair TM, Al-Najar MS, Al-Hawari FH, Alazrai R (2020) Breast tumor classification in ultrasound images using combined deep and handcrafted features. Sensors 20(23):6838
Das A, Rana S (2021) Exploring residual networks for breast cancer detection from ultrasound images. In: 2021 12Th international conference on computing communication and networking technologies (ICCCNT), IEEE, pp 1–6
Das S, Mishra A, Roy P (2018) Automatic diabetes prediction using tree based ensemble learners. In: Proceedings of international conference on computational intelligence and IoT (ICCIIoT)
Das SK, Roy P, Mishra AK (2021) Deep learning techniques dealing with diabetes mellitus: a comprehensive study. In: Health informatics: a computational perspective in healthcare, Springer, pp 295–323
Das SK, Roy P, Mishra AK (2021) Dfu_spnet: a stacked parallel convolution layers based cnn to improve diabetic foot ulcer classification ICT Express
Das SK, Roy P, Mishra AK (2021) Fusion of handcrafted and deep convolutional neural network features for effective identification of diabetic foot ulcer. Concurr Comput Pract Experience :e6690
Das SK, Roy P, Mishra AK (2021) Oversample-select-tune: a machine learning pipeline for improving diabetes identification. Concurr Comput Pract Experience :e6741
Das SK, Roy P, Mishra AK (2022) Recognition of ischaemia and infection in diabetic foot ulcer: a deep convolutional neural network based approach. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 32(1):192–208
Elreedy D, Atiya AF (2019) Acomprehensiveanalysisofsyntheticminorityoversamplingtechnique(smote)forhandlingclassimbalance. InfSci 505:32–64
Feurer M, Hutter F (2019) Hyperparameteroptimization. In: Automatedmachinelearning. Springer, Cham, pp 3–33
Goodfellow IJ, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Courville A, Bengio Y (2014) Generativeadversarialnetworks.arXiv:1406.2661
Haque MR, Islam MM, Iqbal H, Reza MS, Hasan MK (2018) Performanceevaluationofrandomforestsandartificialneuralnetworksfortheclassificationofliverdisorder. In: 2018Internationalconferenceoncomputer,communication,chemical,materialandelectronicengineering(IC4ME2),IEEE,pp 1–5
Haralick RM, Shanmugam K, Dinstein IH (1973) Texturalfeaturesforimageclassification.IEEETransSystManCybern(6):610–621
Harris CR, Millman KJ, vanderWalt SJ, Gommers R, Virtanen P, Cournapeau D, Wieser E, Taylor J, Berg S, Smith NJ, etal. (2020) Arrayprogrammingwithnumpy. Nature 585(7825):357–362
Hasan MK, Islam MM, Hashem M (2016) Mathematicalmodeldevelopmenttodetectbreastcancerusingmultigenegeneticprogramming. In: 20165Thinternationalconferenceoninformatics,electronicsandvision(ICIEV),IEEE,pp 574–579
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deepresiduallearningforimagerecognition. In: ProceedingsoftheIEEEconferenceoncomputervisionandpatternrecognition,pp 770–778
Huang G, Liu Z, VanDerMaaten L, Weinberger KQ (2017) Denselyconnectedconvolutionalnetworks. In: ProceedingsoftheIEEEconferenceoncomputervisionandpatternrecognition,pp 4700–4708
Islam MM, Haque MR, Iqbal H, Hasan MM, Hasan M, Kabir MN (2020) Breastcancerprediction:acomparativestudyusingmachinelearningtechniques. SNComputSci 1(5):1–14
Islam MM, Iqbal H, Haque MR, Hasan MK (2017) Predictionofbreastcancerusingsupportvectormachineandk-nearestneighbors. In: 2017IEEERegion10humanitariantechnologyconference(r10-HTC),IEEE,pp 226–229
Islam MM, Karray F, Alhajj R, Zeng J (2021) Areviewondeeplearningtechniquesforthediagnosisofnovelcoronavirus(covid-19). IEEEAccess 9:30551–30572
Islam MZ, Islam MM, Asraf A (2020) Acombineddeepcnn-lstmnetworkforthedetectionofnovelcoronavirus(covid-19)usingx-rayimages. InfMedUnlocked 20:100412
Jain D, Borah MD, Biswas A (2020) Fine-tuningtextrankforlegaldocumentsummarization:abayesianoptimizationbasedapproach. In: Forumforinformationretrievalevaluation,pp 41–48
Jain D, Mishra AK, Das SK (2021) Machinelearningbasedautomaticpredictionofparkinson’sdiseaseusingspeechfeatures. In: Proceedingsofinternationalconferenceonartificialintelligenceandapplications,Springer,pp 351–362
Kim SH, Kang BJ, Choi BG, Choi JJ, Lee JH, Song BJ, Choe BJ, Park S, Kim H (2013) Radiologists’performancefordetectinglesionsandtheinterobservervariabilityofautomatedwholebreastultrasound. KoreanJRadiol 14(2):154–163
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam:amethodforstochasticoptimization.arXiv:1412.6980
Lazarus E, Mainiero MB, Schepps B, Koelliker SL, Livingston LS (2006) Bi-radslexiconforusandmammography:interobservervariabilityandpositivepredictivevalue. Radiology 239(2):385–391
Li H, Xu Z, Taylor G, Studer C, Goldstein T (2017) Visualizingthelosslandscapeofneuralnets.arXiv:1712.09913
Lo CM, Chang R, Huang C, Moon W (2015) Computer-aideddiagnosisofbreasttumorsusingtexturesfromintensitytransformedsonographicimages. In: 1Stglobalconferenceonbiomedicalengineering&9thasian-pacificconferenceonmedicalandbiologicalengineering,Springer,pp 124–127
Löfstedt T, Brynolfsson P, Asklund T, Nyholm T, Garpebring A (2019) Gray-levelinvariantharalicktexturefeatures. PloSONE 14(2):e0212110
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fullyconvolutionalnetworksforsemanticsegmentation. In: ProceedingsoftheIEEEconferenceoncomputervisionandpatternrecognition,pp 3431–3440
Mishra AK, Das SK, Roy P, Bandyopadhyay S (2020) Identifyingcovid19fromchestctimages:adeepconvolutionalneuralnetworksbasedapproach.JHealthcEng:2020
Mishra AK, Roy P, Bandyopadhyay S (2019) Geneticalgorithmbasedselectionofappropriatebiomarkersforimprovedbreastcancerprediction. In: ProceedingsofSAIintelligentsystemsconference,Springer,pp 724–732
Mishra AK, Roy P, Bandyopadhyay S (2021) Binaryparticleswarmoptimizationbasedfeatureselection(bpso-fs)forimprovingbreastcancerprediction. In: Proceedingsofinternationalconferenceonartificialintelligenceandapplications,Springer,pp 373–384
Mishra AK, Roy P, Bandyopadhyay S, Das SK (2021) Breastultrasoundtumourclassification:amachinelearning—radiomicsbasedapproach.ExpertSyst:e12713
Mockus J (2012) Bayesianapproachtoglobaloptimization:theoryandapplications.SpringerSciBusMedia37
Moon WK, Lee YW, Ke HH, Lee SH, Huang CS, Chang RF (2020) Computer-aideddiagnosisofbreastultrasoundimagesusingensemblelearningfromconvolutionalneuralnetworks. ComputMethodsProgBiomed 190:105361
Moura DC, López MAG (2013) Anevaluationofimagedescriptorscombinedwithclinicaldataforbreastcancerdiagnosis. IntJComputAssistRadiolSurg 8(4):561–574
Muhammad L, Islam MM, Usman SS, Ayon SI (2020) Predictivedataminingmodelsfornovelcoronavirus(covid-19)infectedpatients’recovery. SNComputSci 1(4):1–7
Park CS, Kim SH, Jung NY, Choi JJ, Kang BJ, Jung HS (2015) Interobservervariabilityofultrasoundelastographyandtheultrasoundbi-radslexiconofbreastlesions. BreastCancer 22(2):153–160
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, Blondel M, Prettenhofer P, Weiss R, Dubourg V, Vanderplas J, Passos A, Cournapeau D, Brucher M, Perrot M, Duchesnay E (2011) Scikit-learn:machinelearninginPython. JMachLearnRes 12:2825–2830
Rahman MM, Islam M, Manik M, Hossen M, Al-Rakhami MS, etal. (2021) Machinelearningapproachesfortacklingnovelcoronavirus(covid-19)pandemic. SnComputSci 2(5):1–10
Rodriguez-Cristerna A, Guerrero-Cedillo C, Donati-Olvera G, Gómez-Flores W, Pereira W (2017) Studyoftheimpactofimagepreprocessingapproachesonthesegmentationandclassificationofbreastlesionsonultrasound. In: 201714Thinternationalconferenceonelectricalengineering,computingscienceandautomaticcontrol(CCE),IEEE,pp 1–4
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net:convolutionalnetworksforbiomedicalimagesegmentation. In: Internationalconferenceonmedicalimagecomputingandcomputer-assistedintervention,Springer,pp 234–241
Sadad T, Hussain A, Munir A, Habib M, AliKhan S, Hussain S, Yang S, Alawairdhi M (2020) Identificationofbreastmalignancybymarker-controlledwatershedtransformationandhybridfeaturesetforhealthcare. ApplSci 10(6):1900
Sadoughi F, Kazemy Z, Hamedan F, Owji L, Rahmanikatigari M, Azadboni TT (2018) Artificialintelligencemethodsforthediagnosisofbreastcancerbyimageprocessing:areview. BreastCancerTargetsTher 10:219
Saha P, Sadi MS, Islam MM (2021) Emcnet:automatedcovid-19diagnosisfromx-rayimagesusingconvolutionalneuralnetworkandensembleofmachinelearningclassifiers. InfMedUnlocked 22:100505
Shi X, Cheng HD, Hu L, Ju W, Tian J (2010) Detectionandclassificationofmassesinbreastultrasoundimages. DigitSignalProcess 20(3):824–836
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Verydeepconvolutionalnetworksforlarge-scaleimagerecognition.arXiv:1409.1556
Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z (2016) Rethinkingtheinceptionarchitectureforcomputervision. In: ProceedingsoftheIEEEconferenceoncomputervisionandpatternrecognition,pp 2818–2826
Verma K, Singh BK, Tripathi P, Thoke A (2015) Reviewoffeatureselectionalgorithmsforbreastcancerultrasoundimage. In: Newtrendsinintelligentinformationanddatabasesystems,Springer,pp 23–32
Victoria AH, Maragatham G (2021) Automatictuningofhyperparametersusingbayesianoptimization. EvolvingSyst 12:217–223
WCRF (2020) Breastcancerstatistics2018. https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/cancer-trends/breast-cancer-statistics
Wu J, Chen XY, Zhang H, Xiong LD, Lei H, Deng SH (2019) Hyperparameteroptimizationformachinelearningmodelsbasedonbayesianoptimization. JElectrSciTechnol 17(1):26–40. https://doi.org/10.11989/JEST.1674-862X.80904120.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1674862X19300047
Wu T, Sultan LR, Tian J, Cary TW, Sehgal CM (2019) Machinelearningfordiagnosticultrasoundoftriple-negativebreastcancer. BreastCancerResTreat 173(2):365–373
Xiao T, Liu L, Li K, Qin W, Yu S, Li Z (2018) Comparisonoftransferreddeepneuralnetworksinultrasonicbreastmassesdiscrimination.BioMedResInt:2018
Xie J, Song X, Zhang W, Dong Q, Wang Y, Li F, Wan C (2020) Anovelapproachwithdual-samplingconvolutionalneuralnetworkforultrasoundimageclassificationofbreasttumors. PhysMedBiol 65(24):245001
Yang MC, Moon WK, Wang YCF, Bae MS, Huang CS, Chen JH, Chang RF (2013) Robusttextureanalysisusingmulti-resolutiongray-scaleinvariantfeaturesforbreastsonographictumordiagnosis. IEEETransMedImaging 32(12):2262–2273
Yap MH, Pons G, Martí J, Ganau S, Sentís M, Zwiggelaar R, Davison AK, Marti R (2017) Automatedbreastultrasoundlesionsdetectionusingconvolutionalneuralnetworks. IEEEJBiomedHealthInf 22(4):1218–1226
Zhang E, Seiler S, Chen M, Lu W, Gu X (2019) Boundary-awaresemi-superviseddeeplearningforbreastultrasoundcomputer-aideddiagnosis. In: 201941StannualinternationalconferenceoftheIEEEengineeringinmedicineandbiologysociety(EMBC),IEEE,pp 947–950
Zhou Z, Siddiquee MMR, Tajbakhsh N, Liang J (2018) Unet++:anestedu-netarchitectureformedicalimagesegmentation. In: Deeplearninginmedicalimageanalysisandmultimodallearningforclinicaldecisionsupport,Springer,pp 3–11
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Moi Hoon Yap, Reader in Computer Vision, Manchester Metropolitan University, Department of Computing, Mathematics and Digital Technology, John Dalton Building, Chester Street, Manchester M1 5GD, one of the PIs of the Breast Ultrasound Lesions Dataset(Dataset B) [69] for granting access to the UDIAT dataset to carry out academic research.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Data availability
The BUSI dataset utilized in this work for experimental evaluation purpose is a publicly available dataset introduced by [2]. The UDIAT dataset is another publicly available dataset utilized in this work which can be accessed by following official request procedure as suggested by the authors in [69].
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, A.K., Roy, P., Bandyopadhyay, S. et al. Feature fusion based machine learning pipeline to improve breast cancer prediction. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 37627–37655 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13498-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13498-4