Abstract
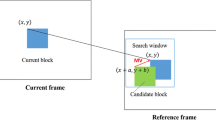
Many useful DSP algorithms have high dimensions and complex logic. Consequently, an efficient implementation of these algorithms on parallel processor arrays must involve a structured design methodology. Full-search block-matching motion estimation is one of those algorithms that can be developed using parallel processor arrays. In this paper, we present a hierarchical design methodology for the full-search block matching motion estimation. Our proposed methodology reduces the complexity of the algorithm into simpler steps and then explores the different possible design options at each step. Input data timing restrictions are taken into consideration as well as buffering requirements. A designer is able to modify system performance by selecting some of the algorithm variables for pipelining or broadcasting. Our proposed design strategy also allows the designer to study time and hardware complexities of computations at each level of the hierarchy. The resultant architecture allows easy modifications to the organization of data buffers and processing elements-their number, datapath pipelining, and complexity-to produce a system whose performance matches the video data sample rate requirements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Raheem, E. M. M. (1995). Design and VLSI implementation of multirate filter banks. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada.
Abdel-Raheem E., Elguibaly F., Antoniou A. (1994). Systolic implementation of FIR decimators and interpolators. IEE Proceedings on Circuits Device System, 141(6): 489
Bhaskaran V., Konstantinides K. (1995). Image and video compression standards, algorithms and architectures. Boston MA, Kluwer Academic Publishers
Elgamel, M. A., Nallamilli, B. R., Bayoumi, M. A., & Mashaly, S. (2002). Systolic array architectures for full-search block matching motion estimation. In Proceedings of the third international workshop on digital and computational video, (pp. 108–115). Clearwater, FL.
Elguibaly F., Tawfik A. (1996). Mapping 3-D IIR digital filters onto systolic arrays. Multidimensional Signal Processing, 7(1): 7–26
Ghanbari M. (1990). The cross-search algorithm for motion estimation. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 38(7): 950–953
Hsu M.-Y., Chang H.-C., Wang Y.-C., Chen L.-G. (2001). Scalable module-based for MPEG-4 BMA motion estimation. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems. Vol. 2, (pp. 245–248). Phoenix-Scottsdale, AZ.
International Organization for Standardization (1992). Coding of moving pictures and associated audio for digital storage media at up to about 1.5 M bits/s, ISO/IEC 11172.
Jain J.R., Jain A.K. (1981). Displacement measurement and its application in interframe image coding. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 29(12): 1799
Karp R.M., Miller E.E., Winograd S. (1967). The organization of computations for uniform recurrence equations. Journal of the ACM, 14(3): 563–590
Kung S.Y. (1988). VLSI array processors. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs NJ
Kung H.T., Leiserson C.E. (1978). Systolic arrays for VLSI. Sparse Matrix Proceedings, SIAM, 245–282.
Le Gall D. (1992). The MPEG video compression algorithm. Image Communication, 4(2): 129–140
Lou J.-H., Wang C.-N., Chiang T. (2002). A novel all-binary motion estimation (ABME) with optimized hardware architecture. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 12(8): 700–712
MacInnis A.G. (1992). MPEG systems coding specification. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 4(2): 153–159
Mohammadzadah, M., Eshghi, M., & Azdfar, M. (2005). An optimized systolic array architecture for full-search block matching algorithm and its implementation on FPGA Chips. In Proceedings of the third international IEEE-NEWCAS conference, (pp. 174–177). Quebec City, Quebec, Canada.
Paul, B. B., & Viscito, E. (1994). Hierarchical motion estimation with 2-scale tilings. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference image processing (ICIP-94), (pp. 260–264). Austin, TX.
Rao S.K., Kailath T. (1988). Regular iterative algorithms and their implementation on processor arrays. Proceedings of the IEEE, 76(3): 259–269
Ryszko, A., & Wiatr, K. (2001). Motion estimation operation implemented in FPGA chips for real-time image compression. In Proceedings of the second international symposium on image and signal processing and analysis (ISPA), (pp. 399–404). Pula, Croatia.
Wujian, Z., Rundle, Z., & Kasai, R. (2001). A high-throughput systolic array for motion estimation using adaptive bit resolution. In Proceedings of the 2001 fourth international conference on ASIC (pp. 378–381). Shanghai, China.
Yeo H., Hu Y.H. (1995). A novel modular systolic array architecture for full-search block matching motion estimation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 5(5): 407–416
Zafar S., Zhang Y., BarasJ.S. (1991a). Predictive block matching motion estimation for T.V. coding– Part I: Inter-block prediction. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 37(3): 97–101
Zafar S., Zhang Y., Baras J.S. (1991b). Predictive block matching motion estimation for T.V. coding– Part II: Inter-frame prediction. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 37(3): 102–105
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rehan, M., El-Kharashi, M.W. & Gebali, F. A hierarchical design methodology for full-search block matching motion estimation. Multidim Syst Sign Process 17, 327–341 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-006-0003-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-006-0003-y