Abstract
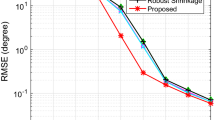
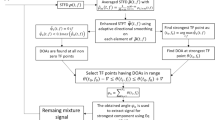
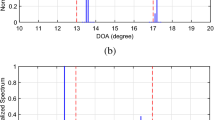
We focus on the design of the measurement schemes in the compressed sensing (CS) method for direction-of-arrival estimation, and three stochastic measurement schemes are considered. In the perspectives of average apertures and incoherences, we give a detailed mathematical analysis for these schemes. The superiorities in incoherences for these schemes are illustrated, compared with the popularly used random Gaussian measurement scheme. Then we demonstrate that the newly used Poisson disk sampling scheme and uniform jittered sampling scheme can obtain relatively large average apertures by using a proposed computational method. Finally, several simulations are implemented to evaluate the performances of the CS methods with these stochastic measurement schemes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barabell, A. J. (1983). Improving the resolution performance of eigenstructure-based direction-finding algorithms. In Proceedings of IEEE ICASSP’83, Boston, USA (pp. 336–339).
Bartlett, M. S. (1948). Smoothing periodograms from time series with continuous spectra. Nature, 161, 686–687.
Bridson, R. (2007). Fast poisson disk sampling in arbitrary dimensions. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 sketches (p. 22). New York: USA.
Candès, E. J. (2006). Compressive sampling. In Proceedings of international congress of mathematicians, Madrid, Spain (Vol. 3, pp. 1433–1452).
Candès, E. J., & Wakin, M. B. (2008). An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 25(2), 21–30.
Candès, E. J., Romberg, J. K., & Tao, T. (2006). Robust uncertanity principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Transation on Information Theory, 52(2), 489–509.
Candès, E. J., Eldar, Y. C., Needell, D., & Randall, P. (2011). Compressed sensing with coherent and redundant dictionaries. Applied and Computational Harmonical Analysis, 31(1), 489–509.
Capon, J. (1969). High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis. Proceedings of the IEEE, 57(8), 1408–1418.
Chen, J., & Huo, X. M. (2006). Theoretical results on sparse representations of multiple-measurment vectors. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 54(12), 4634–4643.
Cook, R. (1986). Stochastic sampling in computer graphics. ACM Transaction on Graphics, 5(1), 51–72.
Cotter, S. F., Rao, B., Engan, K., & Kreutz-Delgado, K. (2005). Sparse solution to linear inverse problems with multiple measurement vectors. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 53(7), 2477–2488.
Dippé, M., & Wold, E. H. (1985). Antialiasing through stochastic sampling. ACM Siggraph Computer Graphics, 19(3), 69–78.
Donoho, D. L. (2006). Compressed sensing. IEEE Transaction on Information Theory, 52(4), 1289–1306.
Gu, J. F., Zhu, W. P., & Swamy, M. (2011). Compressed sensing for DOA estimation with fewer receivers than sensors. In Proceedings of IEEE ISCAS, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (pp. 1752–1755).
Gurbuz, A. C., McClellan, J. H., & Cevher, V. (2008). A compressive beamforming method. In Proceedings of IEEE ICASSP’08, Las Vegas, USA (pp. 2617–2620).
Gurbuz, A. C., Cevher, V., & McClellan, J. (2012). Bearing estimation via spatial sparsity using compressive sensing. IEEE Transaction on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 48(2), 1358–1369.
Johnson, D. H., & Dudgeon, D. E. (1993). Array signal processing: Concepts and techniques. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Krim, H., & Viberg, M. (1996). Two decades of array signal processing research: The parametric approach. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 13(4), 67–94.
Lagae, A., & Dutré, P. (2008). A comparison of methods for generating poisson disk distributions. Computer Graphics Forum, 27(1), 114–129.
Liu, Z., Ruan, X., & He, J. (2013). Efficient 2-D DOA estimation for coherent sources with a sparse acoustic vector-sensor array. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 24(1), 105–120.
Malioutov, D., Cetin, M., & Willsky, A. S. (2005). A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays. IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing, 53(8), 3010–3022.
Mallat, S. G., & Zhang, Z. F. (1993). Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries. IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing, 41(12), 3397–3415.
Shirley, P. (1991). Discrepancy as a quality measure for sampling distribution. In Proceedings of eurographics’91 (pp. 183–194).
Stoica, P., & Nehorai, A. (1989). Music, maximum likelihood, and Cramer-Rao bound. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing, 37(5), 720–741.
Swindlehurst, A. L., & Kailath, T. (1992). A performance analysis of subspace based methods in the presence of model errors-part I: The music algorithm. IEEE Transation on Signal Processing, 40(7), 1758–1774.
Tang, Z. J., Gerrit, B., & Leus, G. (2011). Aliasing-free wideband beamforming using sparse signal representation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 59(7), 3464–3469.
Tropp, J. A., & Gilbert, A. C. (2007). Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Transaction on Information Theory, 53(12), 4655–4666.
Tropp, J. A., & Wright, S. J. (2010). Computational methods for sparse solution of linear inverse problems. Proceedings of the IEEE, 98(6), 948–958.
Tzagkarakis, G., Milioris, D., & Tsakalides, P. (2010). Multiple-measurement Bayesian compreesed sensing using GSM prior for DOA estimation. In Proceedings of IEEE ICASSP’10, Dallas, USA (pp. 2610–2613).
Van Trees, H. L. (2002). Optimum array processing. New York: Wiley.
Van Veen, B. D., & Buckley, K. M. (1988). Beamforming: A versatile approach to spatial filtering. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 5, 4–24.
Wang, Y., Leus, G., & Pandharipand, A. (2009). Direction estimation using compressive sampling array processing. In IEEE/SP 15th workshop on SSP, Cardiff, United Kingdom (pp. 626–629).
Yamada, I., & Oguchi, K. (2011). High-resolution estimation of the directions-of-arrival distribution by algebraic phase unwrapping algorithms. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 22(1–3), 191–211.
Zhang, X., Chen, C., Li, J., & Xu, D. (2012). Blind DOA and polarization estimation for polarization-sensitive array using dimension reduction music. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing. doi:10.1007/s11045-012-0186-3.
Acknowledgments
We are appreciative for the anonymous reviewers’ constructive comments, with which great improvements have been made in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61271014 and 61072118, and the ATR National Defense Technology Key Laboratory Foundation under Grant 11ZS93.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, X., Cheng, L. Three stochastic measurement schemes for direction-of-arrival estimation using compressed sensing method. Multidim Syst Sign Process 25, 621–636 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-012-0220-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-012-0220-5