Abstract
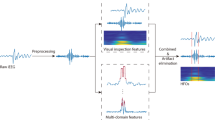
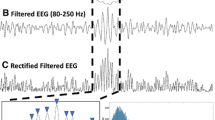
High-frequency oscillations (HFOs) in intracranial electroencephalograms of patients with epilepsy are regarded as promising biomarkers of epileptogenic zones. Their detection and classification can be achieved by visual assessment or automated approaches, although manual processing of large recordings can be laborious. As a result, an automated analysis scheme is indispensable to enable the clinical use of HFOs. In this paper, we present a two-stage strategy to detect and classify HFOs, which starts with a threshold-based approach to detect plausible HFO events followed by an event classification to discriminate different oscillations. Unlike existing approaches, the detection process in the proposed schemes starts by calculating various multi-channel features that allow interrelations among electrodes to be exploited for detection. On this basis, the detection thresholds are set epoch-by-epoch, relying on a two-component Gaussian mixture model to avoid threshold overestimation. The events deemed to be plausible HFOs are then subjected to classification. By simultaneously examining the raw data and time-frequency maps of these events, they are ultimately sorted into the following categories: HFOs, spikes, and spikes with HFOs, so that the oscillations solely caused by filtering sharp transients can be discriminated. Experimental results using simulated data and intracranial recordings from three epileptic patients demonstrate that our proposed schemes achieve promising sensitivity and precision, especially when the noise level is high.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiri, M., Lina, J.-M., Pizzo, F., & Gotman, J. (2016). High frequency oscillations and spikes: Separating real HFOs from false oscillations. Clinical Neurophysiology, 127, 187–196.
Bénar, C.-G., Chauvière, L., Bartolomei, F., & Wendling, F. (2010). Pitfalls of high-pass filtering for detecting epileptic oscillations: A technical note on false ripples. Clinical Neurophysiology, 121, 301–310.
Burnos, S., Hilfiker, P., Sürücü, O., Scholkmann, F., Krayenbühl, N., Grunwald, T., et al. (2014). Human intracranial high frequency oscillations (HFOs) detected by automatic time–frequency analysis. PLoS ONE, 9, 94381.
Chaibi, S., Lajnef, T., Sakka, Z., Samet, M., & Kachouri, A. (2013b). A comparaison of methods for detection of high frequency oscillations (HFOs) in human intacerberal EEG recordings. American Journal of Signal Processing, 3, 25–34.
Chaibi, S., Lajnef, T., Sakka, Z., Samet, M., & Kachouri, A. (2014). A reliable approach to distinguish between transient with and without HFOs using TQWT and MCA. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 232, 36–46.
Chaibi, S., Sakka, Z., Lajnef, T., Samet, M., & Kachouri, A. (2013a). Automated detection and classification of high frequency oscillations (HFOs) in human intracereberal EEG. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 8, 927–934.
Chou, C.-W., Chen, C., Kwan, S.-Y., & Wu, S.-C. (2016). Multi-channel algorithms for epileptic high-frequency oscillation detection. In Proceedings of IEEE EMBC.
Crépon, B., Navarro, V., Hasboun, D., Clemenceau, S., Martinerie, J., Baulac, M., et al. (2010). Mapping interictal oscillations greater than 200 Hz recorded with intracranial macroelectrodes in human epilepsy. Brain, 133, 33–45.
Dümpelmann, M., Jacobs, J., Kerber, K., & Schulze-Bonhage, A. (2012). Automatic 80–250 Hz ripple high frequency oscillation detection in invasive subdural grid and strip recordings in epilepsy by a radial basis function neural network. Clinical Neurophysiology, 123, 1721–1731.
Eadie, M. J. (2012). Shortcomings in the current treatment of epilepsy. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics, 12, 1419–1427.
Fedele, T., Burnos, S., Boran, E., Krayenbühl, N., Hilfiker, P., Grunwald, T., et al. (2017). Resection of high frequency oscillations predicts seizure outcome in the individual patient. Scientific Reports, 7, 13836.
Gardner, A. B., Worrell, G. A., Marsh, E., Dlugos, D., & Litt, B. (2007). Human and automated detection of high-frequency oscillations in clinical intracranial EEG recordings. Clinical Neurophysiology, 118, 1134–1143.
Gliske, S. V., Irwin, Z. T., Chestek, C., & Stacey, W. C. (2016b). Effect of sampling rate and filter settings on high frequency oscillation detections. Clinical Neurophysiology, 127, 3042–3050.
Gliske, S. V., Irwin, Z. T., Davis, K. A., Sahaya, K., Chestek, C., & Stacey, W. C. (2016a). Universal automated high frequency oscillation detector for real-time, long term EEG. Clinical Neurophysiology, 127, 1057–1066.
Jacobs, J., LeVan, P., Chander, R., Hall, J., Dubeau, F., & Gotman, J. (2008). Interictal high-frequency oscillations (80–500 Hz) are an indicator of seizure onset areas independent of spikes in the human epileptic brain. Epilepsia, 49, 1893–1907.
Jacobs, J., Staba, R., Asano, E., Otsubo, H., Wu, J., Zijlmans, M., et al. (2012). High-frequency oscillations (HFOs) in clinical epilepsy. Progress in Neurobiology, 98, 302–315.
Jacobs, J., Zijlmans, M., Zelmann, R., Chatillon, C. É., Hall, J., Olivier, A., et al. (2010). High-frequency electroencephalographic oscillations correlate with outcome of epilepsy surgery. Annals of Neurology, 67, 209–220.
Jirsch, J., Urrestarazu, E., LeVan, P., Olivier, A., Dubeau, F., & Gotman, J. (2006). High-frequency oscillations during human focal seizures. Brain, 129, 1593–1608.
Jmail, N., Gavaret, M., Bartolomei, F., & Bénar, C.-G. (2017). Despiking SEEG signals reveals dynamics of gamma band preictal activity. Physiological Measurement, 38, 42.
Jmail, N., Gavaret, M., Wendling, F., Kachouri, A., Hamadi, G., Badier, J.-M., et al. (2011). A comparison of methods for separation of transient and oscillatory signals in EEG. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 199, 273–289.
Kerber, K., Dümpelmann, M., Schelter, B., Le Van, P., Korinthenberg, R., Schulze-Bonhage, A., et al. (2014). Differentiation of specific ripple patterns helps to identify epileptogenic areas for surgical procedures. Clinical Neurophysiology, 125, 1339–1345.
Lilly, J. M., & Olhede, S. C. (2009). Higher-order properties of analytic wavelets. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 57, 146–160.
Liu, S., Sha, Z., Sencer, A., Aydoseli, A., Bebek, N., Abosch, A., et al. (2016). Exploring the time–frequency content of high frequency oscillations for automated identification of seizure onset zone in epilepsy. Journal of Neural Engineering, 13, 026026.
McLachlan, G., & Krishnan, T. (2008). The EM algorithm and extensions (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Mukhopadhyay, S., & Ray, G. (1998). A new interpretation of nonlinear energy operator and its efficacy in spike detection. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 45, 180–187.
Navarrete, M., Pyrzowski, J., Corlier, J., Valderrama, M., & Le Van Quyen, M. (2017). Automated detection of high-frequency oscillations in electrophysiological signals: Methodological advances. Journal of Physiology-Paris, 110(4), 316–326.
Otsu, N. (1979). A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 9, 62–66.
Pail, M., Halámek, J., Daniel, P., Kuba, R., Tyrlíková, I., Chrastina, J., et al. (2013). Intracerebrally recorded high frequency oscillations: Simple visual assessment versus automated detection. Clinical Neurophysiology, 124, 1935–1942.
Roehri, N., Lina, J.-M., Mosher, J. C., Bartolomei, F., & Bénar, C.-G. (2016). Time–frequency strategies for increasing high-frequency oscillation detectability in intracerebral EEG. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 63, 2595–2606.
Roehri, N., Pizzo, F., Bartolomei, F., Wendling, F., & Bénar, C.-G. (2017). What are the assets and weaknesses of HFO detectors? A benchmark framework based on realistic simulations. PLoS ONE, 12, 0174702.
Rosner, B. (1995). Fundamentals of biostatistics (4th ed.). London: Duxbury Press.
Sokolova, M., & Lapalme, G. (2009). A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks. Information Processing & Management, 45, 427–437.
Staba, R. J., Wilson, C. L., Bragin, A., Fried, I., & Engel, J. (2002). Quantitative analysis of high-frequency oscillations (80–500 Hz) recorded in human epileptic hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 88, 1743–1752.
von Ellenrieder, N., Dubeau, F., Gotman, J., & Frauscher, B. (2017). Physiological and pathological high-frequency oscillations have distinct sleep-homeostatic properties. NeuroImage: Clinical, 14, 566–573.
Wang, S., Wang, I. Z., Bulacio, J. C., Mosher, J. C., Gonzalez-Martinez, J., Alexopoulos, A. V., et al. (2013). Ripple classification helps to localize the seizure-onset zone in neocortical epilepsy. Epilepsia, 54, 370–376.
Worrell, G. A., Jerbi, K., Kobayashi, K., Lina, J.-M., Zelmann, R., & Le Van Quyen, M. (2012). Recording and analysis techniques for high-frequency oscillations. Progress in Neurobiology, 98, 265–278.
Wu, J., Sankar, R., Lerner, J., Matsumoto, J., Vinters, H., & Mathern, G. (2010). Removing interictal fast ripples on electrocorticography linked with seizure freedom in children. Neurology, 75, 1686–1694.
Yao, D. (2000). Electric potential produced by a dipole in a homogeneous conducting sphere. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 47, 964–966.
Zelmann, R., Mari, F., Jacobs, J., Zijlmans, M., Dubeau, F., & Gotman, J. (2012). A comparison between detectors of high frequency oscillations. Clinical Neurophysiology, 123, 106–116.
Zijlmans, M., Jacobs, J., Kahn, Y. U., Zelmann, R., Dubeau, F., & Gotman, J. (2011). Ictal and interictal high frequency oscillations in patients with focal epilepsy. Clinical Neurophysiology, 122, 664–671.
Zijlmans, M., Jacobs, J., Zelmann, R., Dubeau, F., & Gotman, J. (2009). High-frequency oscillations mirror disease activity in patients with epilepsy. Neurology, 72, 979–986.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan, R.O.C. for the projects under Contract Nos. MOST 104-2221-E-007-145 and MOST 105-2221-E-007-090.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, SC., Chou, CW., Chen, C. et al. Epileptic high-frequency oscillations: detection and classification. Multidim Syst Sign Process 31, 965–988 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-019-00693-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-019-00693-0