Abstract
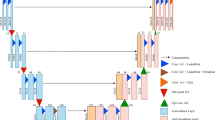
Conventional single channel speech separation has two long-standing issues. The first issue, over-smoothing, is addressed, and estimated signals are used to expand the training data set. Second, DNN generates prior knowledge to address the problem of incomplete separation and mitigate speech distortion. To overcome all current issues, we suggest employing single-channel source separation with time–frequency non-negative matrix factorization, as well as sigmoid-based normalization deep neural networks. The proposed system consists of the two steps listed below. The first is the training phase, and the second is the testing phase. The difference between these two testing and training stages is that the testing stage uses a single-channel multi-talker input signal and the training stage uses a single-channel clean input signal. Both of these testing and training stages send their input signals to Short Term Fourier Transform (STFT). STFT converts input clean signal into spectrograms then uses a feature extraction technique called TFNMF to extract features from spectrograms. After extracting the features, using the SNDNN classification algorithm, and the classified features are converted to softmax. ISTFT then applies to softmax and correctly separates speech signals. Investigational outcomes demonstrate that the proposed structure attains the best result associated with accessible practices.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, X., Qian, Y., & Yu, D. (2018). Monaural multi-talker speech recognition with attention mechanism and gated convolutional networks. In INTERSPEECH (pp. 1586-1590).
Chen et al Z., (2020) Continuous speech separation: Dataset and analysis, In: Proc. IEEE ICASSP, pp. 7284–7288.
Chen, Z., Droppo, J., Li, J., & Xiong, W. (2018). Progressive joint modeling in unsupervised single-channel overlapped speech recognition IEEE/ACM. Trans Audio, Speech, Language Process, 26(1), 184–196.
Christensen, H., Barker, J., Ma, N., et al. (2010). The chime corpus: a resource and a challenge for computational hearing in multisource environments, In Eleventh Annual Conf. of the Int. Speech Communication Association, Chiba, Japan.
Du, J., Yanhui, Tu., Dai, L.-R., & Lee, C.-H. (2016). A regression approach to single-channel speech separation via high-resolution deep neural networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 24(8), 1424–1437.
Emiya, V., Vincent, E., Harlander, N., et al. (2011). Subjective and objective quality assessment of audio source separation. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 19(7), 2046–2057.
Fascista, A., Coluccia, A., Wymeersch, H., & Seco-Granados, G. (2019). Millimeter-wave downlink positioning with a single-antenna receiver. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 18(9), 44794490.
Gogate M, Dashtipour K, Bell P, Hussain A. (2020) Deep neural network driven binaural audio visual speech separation. In 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) (pp. 1–7). IEEE.
Grais Emad M., Gerard R, Andrew JRS, and Plumbley MD. (2016) Single-channel audio source separation using deep neural network ensembles." In Audio Engineering Society Convention 140. Audio Engineering Society.
Grais, E. M., Roma, G., Simpson, A. J. R., & Plumbley, M. D. (2017). Two-stage single-channel audio source separation using deep neural networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 25(9), 1773–1783.
Hao, X., Su, X., Wang, Z., Zhang, H. (2020) UNetGAN: A robust speech enhancement approach in time domain for extremely low signal-to-noise ratio condition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.15521.
Hossain, M. I., Islam, M. S., Khatun, M. T., Ullah, R., Masood, A., & Ye, Z. (2021). Dual-transform source separation using sparse nonnegative matrix factorization. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing., 40(4), 1868–1891.
India, M., Safari, P., and Hernando, J., (2019). `Self multi-head attention for speaker recognition. arXiv:1906.09890. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1906.09890.
Jin, Y., Tang, C., Liu, Q., Wang, Y., (2020) Multi-head self-attention based deep clustering for single-channel speech separation. IEEE Access.
Jin, Y., Tang, C., Liu, Q., & Wang, Y. (2020). Multi-head self-attention based deep clustering for single-channel speech separation. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2997871
Koteswararao, Y. V., Rama, C. B., & Rao. (2021). Multichannel speech separation using hybrid GOMF and enthalpy-based deep neural networks. Multimedia Systems, 27(2), 271–286.
Le Roux, J., Wichern, G., Watanabe, S., Sarroff, A., & Hershey, J. R. (2019). Phasebook and friends: Leveraging discrete representations for source separation. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing., 13(2), 370–382.
Lee, S., Mendel, L. L., & Bidelman, G. M. (2019). Predicting speech recognition using the speech intelligibility index and other variables for cochlear implant users. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 62(5), 1517–1531.
Liu, Y., Delfarah, M., & Wang, D. (2020). Deep CASA for talker-independent monaural speech separation. In ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 6354-6358). IEEE.
Luo, Y., Chen, Z., & Mesgarani, N. (2018). “Speaker-independent speech separation with deep attractor network,” IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio, Speech, Language Process, 26(4), 787796.
Luo, Yi., & Mesgarani, N. (2019). Conv-tasnet: Surpassing ideal time–frequency magnitude masking for speech separation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 27(8), 1256–1266.
Mayer, F., Williamson, D. S., Mowlaee, P., & Wang, DeLiang. (2017). Impact of phase estimation on single-channel speech separation based on time-frequency masking. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 141(6), 4668–4679.
Ni, Z., Mandel, M.I. (2019). Mask-dependent phase estimation for monaural speaker separation’, arXiv preprint arXiv:191102746
Qian, Y., Chang, X., & Yu, D. (2018). Single-channel multi-talker speech recognition with permutation invariant training. Speech Communication, 104, 1–11.
Rath, M., Kulmer, J., Leitinger, E., & Witrisal, K. (2020). Single-anchor positioning: multipath processing with non-coherent directional measurements. IEEE Access, 8, 88115–88132.
Ratnam, V. V., Molisch, A. F., Bursalioglu, O. Y., & Papadopoulos, H. C. (2018). Hybrid beamforming with selection for multiuser massive MIMO systems. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 66(15), 41054120.
Rhebergen, K. S., & Versfeld, N. J. (2005). A speech intelligibility index-based approach to predict the speech reception threshold for sentences in fluctuating noise for normal-hearing listeners. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 117(4), 2181–2192.
Rix, A., Beerends, J., Hollier, M., et al. (2001). Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ), an objective method for end-to-end speech quality assessment of narrowband telephone networks and speech codecs. ITU-T Recommendation, 862.
Santos, J. F., Senoussaoui, M., & Falk, T. H. (2014). An improved non-intrusive intelligibility metric for noisy and reverberant speech. In 2014 14th International Workshop on Acoustic Signal Enhancement (IWAENC) (pp. 55-59). IEEE.
Stein Ioushua, S., & Eldar, Y. C. (2019). A family of hybrid analogdigital beamforming methods for massive MIMO systems. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 67(12), 32433257.
Sun, L., Zhu, G., & Li, P. (2020). Joint constraint algorithm based on deep neural network with dual outputs for single-channel speech separation. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 14, 1–9.
Taal, C. H., Hendriks, R. C., Heusdens, R., et al. (2011). An algorithm for intelligibility prediction of time–frequency weighted noisy speech. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 19(7), 2125–2136.
Wang, DeLiang, & Chen, J. (2018). Supervised speech separation based on deep learning: An overview. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 26(10), 1702–1726.
Wang, Y., Jun, Du., Dai, L.-R., & Lee, C.-H. (2017). A gender mixture detection approach to unsupervised single-channel speech separation based on deep neural networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 25(7), 1535–1546.
Watanabe S et al., (2018) ESPnet: End-to-end speech processing toolkit, In Proc. ISCA Interspeech, pp. 2207–2211.
Weng, C., Dong, Yu., Seltzer, M. L., & Droppo, J. (2015). Deep neural networks for single-channel multi-talker speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 23(10), 1670–1679.
Wichern, G., Antognini, J., Flynn, M., Zhu, L. R., McQuinn, E., Crow, D., & Roux, J. L. (2019). WHAM!: Extending speech separation to noisy environments. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.01160.
Wiem, B., Anouar, B. M., & Aïcha, B. (2020). Phase-aware subspace decomposition for single channel speech separation. IET Signal Processing., 14(4), 214–222.
Wiem, B., Anouar, B. M. M., Mowlaee, P., et al. (2018). Unsupervised single channel speech separation based on optimized subspace separation. Speech Communication, 96, 93–101.
Xiang, Y., Shi, L., Højvang, J. L., Rasmussen, M. H., & Christensen, M. G. (2020). An NMF-HMM Speech Enhancement Method based on Kullback-Leibler Divergence. Ininterspeech, 22, 2667–2671.
Zhang, W., Chang, X., Qian, Y., & Watanabe, S. (2020). Improving end-to-end single-channel multi-talker speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing., 28, 1385–1394.
Funding
In this research article has not been funded by anyone.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koteswararao, Y.V., Rama Rao, C.B. Single channel source separation using time–frequency non-negative matrix factorization and sigmoid base normalization deep neural networks. Multidim Syst Sign Process 33, 1023–1043 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-022-00830-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-022-00830-2