Abstract
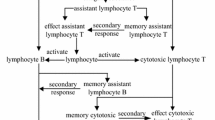
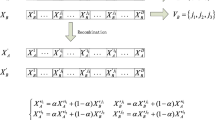
In this paper, a new evolutionary algorithm, called immune clonal coevolutionary algorithm (ICCoA) for dynamic multiobjective optimization (DMO) is proposed. On the basis of the basic principles of artificial immune system, the proposed algorithm adopts the immune clonal selection to solve DMO problems. In addition, the theory of coevolution is incorporated in ICCoA in global operation to preserve the diversity of Pareto-fronts. Moreover, coevolutionary competitive and cooperative operation is designed to enhance the uniformity and the diversity of the solutions. In comparison with NSGA-II, immune clonal algorithm for DMO and direction-based method, the simulation results obtained on 5 difficult test problems and on related performance metrics suggest that ICCoA can achieve better distributed solutions and be very effective in maintaining the uniformity of Pareto-fronts.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abido MA (2010) Multiobjective particle swarm optimization with nondominated local and global sets. Nat Comput 9(1):747–766. doi:10.1007/s11047-009-9171-7
Cámara M, Ortega J, de Toro F (2009) Performance measures for dynamic multi-objective optimization. Bio-inspired systems: computational and ambient intelligence. Springer, Berlin, pp 760–767
Chambers M, Cleveland WS, Kleiner B et al (1983) Graphical methods for data analysis. Wadsworth Brooks/Cole, Pacific Grover
Chen WS, Jiao LC (2010) Adaptive tracking for periodically time-varying and nonlinearly parameterized systems using multilayer neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 21(2):345–351
Coello Coello AC, Cortes NC (2002) An approach to solve multiobjective optimization problems based on an artificial immune system. in: Proceedings of 1st international conference artificial immune system, Int. Center Adv. Res. Identif. Sci. (ICARIS), pp 212-221
de Castro LN, Timmis J (2002a) Artificial immune systems: a new computational intelligence approach. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–357
de Castro LN, Timmis J (2002b) Learning and optimization using the clonal selection principle. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 6(3):239–251
de Castro LN, Timmis J, Knidel H, Von Zuben F (2010) Artificial immune systems: structure, function, diversity and an application to biclustering. Nat Comput 9(3):575–577. doi:10.1007/s11047-009-9145-9
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 6(2):182–197
Farina M, Deb K, Amato P (2004) Dynamic multiobjective optimization problems: test cases, approximations, and applications. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 8(5):425–442
Forrest S, Perelson AS, Allen L, Cherukuri R (1994) Self–nonself discrimination in a computer. In: Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE symposium on research in security and privacy, IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos, 1994, pp 202–212
Gibbons JD (1985) Nonparametric statistical inference, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York
Goh CK, Tan KC (2007) An investigation on noisy environments in evolutionary multiobjective optimization. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 11(3):354–381
Goh CK, Tan KC (2009) A competitive-cooperative coevolutionary paradigm for dynamic multiobjective optimization. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 13(1):103–127
Gong MG, Du HF, Jiao LC (2006) Optimal approximation of linear systems by artificial immune response. Sci China Ser F 49(1):63–79
Gong MG, Jiao LC, Du HF, Bo LF (2008) Multiobjective immune algorithm with nondominated neighbor-based selection. Evolutionary computation. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 225–255. doi:10.1162/evco.2008.16.2.225
Helbig M, Engelbrecht AP et al (2013) Dynamic multi-objective optimization using PSO. Metaheuristics for Dynamic Optimization Studies in Computational Intelligence 433:147–188
Huang L, Suh IH, Abraham A (2011) Dynamic multi-objective optimization based on membrane computing for control of time-varying unstable plants. Inf Sci 181(11):2370–2391
Jiao LC, Wang L (2000) A novel genetic algorithm based on immunity. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 30(5):552–561
Jiao LC, Liu J, Zhong WC (2006) An organizational co-evolutionary algorithm for classification. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 10(1):67–80
Jin Y, Branke J (2005) Evolutionary optimization in uncertain environments—a survey. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 9(3):303–317
Leung Y-W, Wang YP (2003) U-measure: a quality measure for multiobjective programming. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 33(3):337–343
Liu RC, Sheng ZC, Jiao LC, Zhang W (2010) Immunodomaince based clonal selection clustering algorithm. IEEE Congr Evolut Comput 2010:1–7
Lung RI, Dumitrescu D (2010) Evolutionary swarm cooperative optimization in dynamic environments. Nat Comput 9(1):83–94. doi:10.1007/s11047-009-9129-9
Nusawardhana, Zak SH (2004) Simultaneous perturbation extremum seeking method for dynamic optimization problems. In: Proceedings of the 2004 American control conference. IEEE Press, Piseataway, 2004, pp 2805–2810
Shang RH, Jiao LC, Gong MG, Lu B (2005) Clonal selection algorithm for dynamic muitiobjective optimization. In: Hao Y et al (Eds) Proceedings of the 2005 international conference on computational intelligence and security LNCS, vol 3801. Springer, Berlin, 2005, pp 846–851
Shang RH, Jiao LC, Liu F, Ma WP (2012) A novel immune clonal algorithm for MO problems. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 16(1):35–50
Sun J, Fang W, Palade V, Wu XJ, Xu WB (2011) Quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization with Gaussian distributed local attractor point. Appl Math Comput 218:3763–3775
Ursem RK, Krink T, Jensen MT, Michalewicz Z (2002) Analysis and modeling of control tasks in dynamic systems. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 6(4):378–389
Van Veldhuizen DA, Lamont GB (2000) On measuring multiobjective evolutionary algorithm performance. Congress on evolutionary computation (CEC 2000). IEEE Press, Piscataway, pp 204–211
Wang YP, Dang CY (2008) An evolutionary algorithm for dynamic multi-objective optimization. Appl Math Comput 205(1):6–18
Wang HF, Yang SX, Ip WH, Wang DW (2010) A particle swarm optimization based memetic algorithm for dynamic optimization problems. Nat Comput 9(3):703–725. doi:10.1007/s11047-009-9176-2
Woolley NC, Milanović JV (2011) An immune system inspired clustering and classification method to detect critical areas in electrical power networks. Nat Comput 10(1):305–333. doi:10.1007/s11047-010-9204-2
Yang DD, Jiao LC, Gong MG (2009) Adaptive multiobjective optimization based on nondominated solutions. Comput Intell 25(2):84–108. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8640.2009.00332.x
Zitzler E, Thiele L (2005) A simple mulf-membered evolution strategy to solve constraint optimization problems. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 9(1):1–17
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere appreciation to the anonymous reviewers for their insightful and valuable comments, which have greatly helped us in improving the quality of the paper. This work was partially supported by the National Basic Research Program (973 Program) of China under Grant 2013CB329402, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, under Grants 61371201, 61001202, 61203303, and 61272279, the National Research Foundation for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China, under Grants 20100203120008, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, under Grant K5051302028, the Fund for Foreign Scholars in University Research and Teaching Programs (the 111 Project) under Grant B07048, and the Program for Cheung Kong Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University under Grant IRT1170.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, R., Jiao, L., Ren, Y. et al. Immune clonal coevolutionary algorithm for dynamic multiobjective optimization. Nat Comput 13, 421–445 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11047-014-9415-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11047-014-9415-z