Abstract
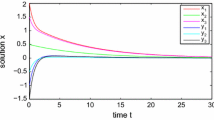
A novel method to analyze the dynamics of the BSB (Brain State in a Box) model is presented. The method is able to determine if a proposed interconnection matrix generated with the CMM rule can achieve the desired behavior, and what are the parameters that should be changed in case of obtaining an incorrect final rest point. By means of an application of the techniques used in control system theory it is possible to evaluate the evolution of each of the training points individually and also to establish what are the points of the training set that are competing between them. So, this kind of analysis can be useful not only as a medium to modify the learning rule to obtain a better performance, but also as a tool to understand the limitations that the initial learning rule has. As an example of the application of this tool some simulated experiments were carried out in order to show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSB:
-
Brain State in a Box
References
A.J. Anderson J.W. Silverstein S.A. Ritz R.S. Jones (1977) ArticleTitleDistinctive features, categorical perception, and probability learning: Some applications of a neural model Psychological Review 84 413–451
Bellman R.E. Introduction to Matrix Analysis, Mcgraw-Hill Book Company, 1970.
M.A. Cohen S. Grossberg (1983) ArticleTitleAbsolute stability of global pattern formation and parallel memory storage by competitive neural networks IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics 13 815–826 Occurrence Handle85e:92002
Duda, R. O. and Hari, P. E.: Pattern classification and scene analysis, John Wiley & Sons, 1963.
R.M. Golden (1986) ArticleTitleThe Brain-State-in-a-Box neural model is a gradient descendent algorithm Journal of Mathematical Psychology 30 73–80 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-2496(86)90043-X Occurrence Handle0587.92028 Occurrence Handle87e:92045
J.J. Hopfield (1982) ArticleTitleNeural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 79 2554–2558 Occurrence Handle1982PNAS...79.2554H Occurrence Handle83g:92024
S. Hui S.H. Zak (1992) ArticleTitleDynamical analysis of the Brain-State-in-a-Box (BSB) neural model IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 3 86–94 Occurrence Handle10.1109/72.105420
Kwakernaak, H. and Sivan, R.: Linear Optimal Control Systems, John Wiley & Sons, 1972.
J.H. Li A.N. Michel W. Porod (1989) ArticleTitleAnalysis and synthesis of a class of neural networks: Linear systems operating on a closed hypercube IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems 36 1405–1422 Occurrence Handle90k:92015
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pelle, P., D’attellis, C. Analysis of the BSB Model Dynamics Using Control Theory. Neural Process Lett 22, 345–359 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-005-1001-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-005-1001-z