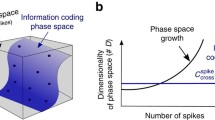
Abstract
This paper provides new insights regarding the transfer of information between input signal and the output of neurons. Simulations of the Hodgkin-Huxley (HH) model combined with computational techniques are used to estimate this transfer of information. Our analysis shows that comparatively, mutual information (MI) between input signal and sodium flux is about two times that between input signal and output spikes during each spike within a millisecond-level time domain. This higher transfer of information provided by ionic fluxes extends the working frequency domain of neural cells beyond those accessible to information transfer within spikes alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.K. Adair (2003) ArticleTitleNoise and stochastic resonance in voltage-gated ion channels, Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100 12099–12104 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.2034447100 Occurrence Handle2003PNAS..10012099A
Asdi A.S., Tewfik A.H.: Detection of weak signals using adaptive stochastic resonance. IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust. Speech, Signal Process., Vol. 2. 1995.
W.M. Bartlett (2002) ArticleTitleHave we been hebbing down the wrong path? Neuron 34 IssueID2, 11 175–177
N. Berglun B. Gentz (2002) ArticleTitleA sample-paths approach to noise-induced synchronization: Stochastic resonance in a double-well potential Ann. Appl. Probab. 12 IssueID4 1419–1470 Occurrence Handle2003h:60083
C.C. Chow J.A. White (1996) ArticleTitleSpontaneous action potentials due to channel fluctuations Biophys. J. 71 3013–3021
T.M. Cover Thomas J.A. (1991) Elements of Information Theory John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York
G.A. Darbellay I. Vajda (1999) ArticleTitleEstimation of the information by an adaptive partitioning of the observation space IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 45 IssueID4 1315–1321 Occurrence Handle10.1109/18.761290 Occurrence Handle2000a:94005
H.B. Eichenbaum J.L. Davis (1998) Neuronal Ensembles: Strategies for Recording and Decoding Wiley-Liss New York
S. Fauve F. Heslot (1983) ArticleTitleStochastic resonance in a bistable system Phys Lett. 97A 5–7 Occurrence Handle1983PhLA...97....5F
M.S. Goldman (2004) ArticleTitleEnhancement of information transmission efficiency by synaptic failures Neural Comput. 16 IssueID6 1137–1162 Occurrence Handle10.1162/089976604773717568 Occurrence Handle1054.92010
R.M. Gray (1990) Entropy and Information Theory Springer-Verlag New York
J.P. Hales C.S-Y. Lin H. Bostock (2004) ArticleTitleVariations in excitability of single human motor axons, related to stochastic properties of nodal sodium channels J. Physiol 559 IssueID3 953–964
D.A. Harris L. Stark (1973) ArticleTitleSynaptic delay: Its effect on information transmission in the crayfish caudal photoreceptor system Brain Res. 15 IssueID51 340–344
B. Hille (2001) Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes EditionNumber3 Sinauer Associates Sunderland, MA
A.L. Hodgkin A. Huxley (1952) ArticleTitleQuantitative description of ion currents and its applications to conduction and excitation in nerve membranes J. Physiol. (Lond.) 117 500–544
M.S. Jog C.I. Connolly Y. Kubota D.R. Iyengar L. Garrido R. Harlan A.M. Graybiel (2002) ArticleTitleTetrode technology: Advances in implantable hardware, neuroimaging, and data analysis techniques J. Neurosci. Meth. 117 141–152
M.S. Jog Y. Kubota C.I. Connolly V. Hillegaar A.M. Graybiel (1999) ArticleTitleBuilding neural representations of habit Science 286 1745–1759 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.286.5445.1745
W. Maass (2001) ArticleTitleOn the relevance of time in neural computation and learning Theoretical Comp. Sci. 261 IssueID1 157–178 Occurrence Handle0974.68168 Occurrence Handle2002c:68078
L. Nerad D.K. Bilkey (2005) ArticleTitleTen- to 12-Hz EEG oscillation in the rat hippocampus and rhinal cortex that is modulated by environmental familiarity J. Neurophysiol. 93 1246–1254
S. Panzeri R.S. Petersen S.R. Schultz M. Lebedev M.E. Diamond (2001) ArticleTitleThe role of spike timing in the coding of stimulus location in rat somatosensory cortex Neuron 29 IssueID3 769–777 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0896-6273(01)00251-3
Press W., Flannery H., Teukolsky B.P., Vetterling W.T. Adaptive Step Size Control for Runge-Kutta, Section 16.2 in Numerical Recipes in FORTRAN: The Art of Scientific Computing, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 2nd edition (1992), pp. 704–716.
D.S. Reich F. Mechle J.D. Victor (2001) ArticleTitleFormal and attribute-specific information in primary visual cortex J. Neurophysiol. 85 305–318
F. Rieke D. Warland R. Steveninck W. Bialek (1997) Spikes: Exploring the Neural Code MIT Press Cambridge, MA
K. Sobczyk (2001) ArticleTitleInformation dynamics: premises, challenges and results Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 15 IssueID3 475–498 Occurrence Handle10.1006/mssp.2000.1378 Occurrence Handle2001MSSP...15..475S
S.P. Strong R Koberle R.R. Steveninck W. Bialek (1998) ArticleTitleEntropy and information in neural spike trains Phys. Rev. Let. 80 197–200 Occurrence Handle1998PhRvL..80..197S
J.D. Victor (2002) ArticleTitleBinless strategies for estimation of information from neural data Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 66 IssueID5–1 051903 Occurrence Handle2002PhRvE..66E1903V
J.S. Walker (1996) Fast Fourier Transfor EditionNumber2 CRC Press Boca Raton, FL
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aur, D., Connolly, C.I. & Jog, M.S. Computing Information in Neuronal Spikes. Neural Process Lett 23, 183–199 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-006-6266-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-006-6266-3