Abstract
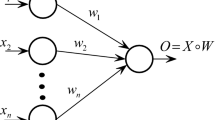
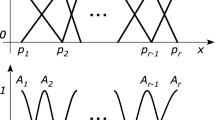
By combining of the benefits of high-order network and TSK (Tagaki-Sugeno-Kang) inference system, Pi-Sigma network is capable to dispose with the nonlinear problems much more effectively, which means it has a compacter construction, and quicker computational speed. The aim of this paper is to present a gradient-based learning method for Pi-Sigma network to train TSK fuzzy inference system. Moreover, some strong convergence results are established based on the weak convergence outcomes, which indicates that the sequence of weighted fuzzy parameters gets to a fixed point. Simulation results show the modified learning algorithm is effective to support the theoretical results.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh P, Borah B (2009) High-order fuzzy-neuro expert system for time series forecasting. Knowl Based Syst 46:12–21. doi:10.1016/j.knosys.2013.01.030
Lin Y, Chang J, Lin C (2013) Identification and prediction of dynamic systems using an interactively recurrent self-evolving fuzzy neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24(2):310–321. doi:10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2231436
Chen P, Fei M, Tian E (2013) Networked control for a class of T–S fuzzy systems with stochastic sensor faults. Fuzzy Sets Syst 212:62–77. doi:10.1016/j.fss.2012.09.015
Takagi T, Sugeno M (1985) Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 15(2):116–132. doi:10.1109/TSMC.1985.6313399
Tseng C, Chen B, Uang H (2001) Fuzzy tracking control design for nonlinear dynamic systems via TS fuzzy model. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 9(3):381–392. doi:10.1109/91.928735
Shin Y, Ghosh J (1991) The Pi-Sigma networks: an efficient higher-order neural network for pattern classification and function approximation. Proc Int Joint Conf Neural Netw 1:13–18. doi:10.1109/IJCNN.1991.155142
Ghazali R, Hussain AJ, Nawi NM, Mohamad B (2009) Non-stationary and stationary prediction of financial time series using dynamic ridge polynomial neural network. Neurocomputing 72(10–12):2359–2367. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2008.12.005
Jin Y, Jiang J, Zhu J (2012) Neural network based fuzzy identification and its application to modeling and control of complex systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 25(6):990–997. doi:10.1109/21.384264
Yu W, Li MQ, Luo J, Su S, Li C (2010) Prediction of the mechanical properties of the post-forged TiC6AlC4V alloy using fuzzy neural network. Mater Des 31(7):3282–3288. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2010.02.009
Zhang C, Wu W, Chen X, Xiong Y (2008) Convergence of BP algorithm for product unit neural networks with exponential weights. Neurocomputing 72(1–3):513–520. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2007.12.004
Sun Z, Au KF, Choi TM (2007) A neuro-fuzzy inference system through integration of fuzzy logic and extreme learning machines. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 37(5):1321–1331. doi:10.1109/TSMCB.2007.901375
Campo I, Echanobe J, Bosque G, Tarela J (2008) Efficient hardware/software implementation of an adaptive neuro-fuzzy system. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 16(3):761–778. doi:10.1109/TFUZZ.2007.905918
Liu Y, Yang J, Yang D, Wu W (2014) A modified gradient-based neuro-fuzzy learning algorithm for pi-sigma network based on first-order takagi-sugeno system. J Math Res Appl 34(1):114–126
Faria FA, Geraldo NS, Vilma AO (2013) Reducing the conservatism of LMI-based stabilisation conditions for TS fuzzy systems using fuzzy Lyapunov functions. Int J Syst Sci 44(10):1956–1969. doi:10.1080/00207721.2012.670307
Chen D et al (2013) Application of Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy model to a class of chaotic synchronization and anti-synchronization. Nonlinear Dyn 73(3):1495–1505. doi:10.1007/s11071-013-0880-1
Jang JSR (1993) ANFIS adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 23(3):665–685. doi:10.1109/21.256541
Charurved K, Pandit M, Srivastava L (2007) Modified neo-fuzzy neuron-based approach for economic and environmental optimal power dispatch. Appl Soft Comput 8(4):1428–1438. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2007.10.010
Yuan YX, Sun WY (2001) Optimization theory and method. Science Press, Beijing
Wu W, Li L, Yang J, Liu Y (2010) A modified gradient-based neuro-fuzzy learning algorithm and its convergence. Inf Sci 180(9):1630–1642. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2009.12.030
Ampazis N, Perantonis SJ (2002) Two highly efficient second-order algorithms for training feedforward networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 13(5):1064–1074. doi:10.1109/TNN.2002.1031939
Mackay DJC (1992) Bayesian interpolation. Neural Comput 4(3):415–447. doi:10.1162/neco.1992.4.3.415
Liu Y, Yang J, Li L, Wu W (2012) Negative effects of sufficiently small initial weights on back-propagation neural networks. J of Zhejiang Univ Sci C (Comput & Electron) 13(8):585–592. doi:10.1631/jzus.C1200008
Chen D, Han W (2013) Prediction of multivariate chaotic time series via radial basis function neural network. Complexity 18(4):55–66. doi:10.1002/cplx.21441
Meng D, Leung Y, Xu Z (2013) The strong convergence of visual classification method and its applications. Inf Sci 249(10):85–95. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2013.06.028
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61403056 and 61473059), Foundation of Liaoning Educational Committee (No. L2014218) and Foundation of major platform for National Engineering Research Center of Seafood ([2011]191).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Yang, D., Nan, N. et al. Strong Convergence Analysis of Batch Gradient-Based Learning Algorithm for Training Pi-Sigma Network Based on TSK Fuzzy Models. Neural Process Lett 43, 745–758 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-015-9445-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-015-9445-2