Abstract
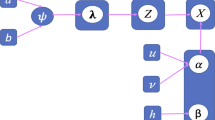
In this work, we develop a statistical framework for data clustering which uses hierarchical Dirichlet processes and Beta-Liouville distributions. The parameters of this framework are leaned using two variational Bayes approaches. The first one considers batch settings and the second one takes into account the dynamic nature of real data. Experimental results based on a challenging problem namely visual scenes categorization demonstrate the merits of the proposed framework.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Source code of PCA-SIFT: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~yke/pcasift.
Database is available at: http://vision.princeton.edu/projects/2010/SUN/.
References
Andrews JL, McNicholas PD, Subedi S (2011) Model-based classification via mixtures of multivariate t-distributions. Comput Stat Data Anal 55(1):520–529
Attias H (1999) A variational Bayes framework for graphical models. In: Proceedings of advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS), pp 209–215
Banerjee A, Langford J (2004) An objective evaluation criterion for clustering. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (KDD). ACM, pp 515–520
Bishop CM (2006) Pattern recognition and machine learning. Springer, Heidelberg
Blei DM, Jordan MI (2005) Variational inference for Dirichlet process mixtures. Bayesian Anal 1:121–144
Bouguila N (2011) Bayesian hybrid generative discriminative learning based on finite liouville mixture models. Pattern Recog 44(6):1183–1200
Bouguila N (2012a) Hybrid generative/discriminative approaches for proportional data modeling and classification. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 24(12):2184–2202
Bouguila N (2012b) Infinite liouville mixture models with application to text and texture categorization. Pattern Recog Lett 33(2):103–110
Bouguila N, Ziou D (2005) Using unsupervised learning of a finite Dirichlet mixture model to improve pattern recognition applications. Pattern Recog Lett 26(12):1916–1925
Bouguila N, Ziou D, Vaillancourt J (2004) Unsupervised learning of a finite mixture model based on the Dirichlet distribution and its application. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(11):1533–1543
Boutell MR, Luo J, Shen X, Brown CM (2004) Learning multi-label scene classification. Pattern Recog 37(9):1757–1771
Cheng H, Jiang X, Sun Y, Wang J (2001) Color image segmentation: advances and prospects. Pattern Recog 34(12):2259–2281
Cohn DA, Ghahramani Z, Jordan MI (1996) Active learning with statistical models. J Artif Intell Res 4:129–145
Corridoni JM, Bimbo AD, Pala P (1999) Image retrieval by color semantics. Multimed Syst 7(3):175–183
Erdem C, Karabulut G, Yanmaz E, Anarim E (2001) Motion estimation in the frequency domain using fuzzy c-planes clustering. IEEE Trans Image Process 10(12):1873–1879
Fan J, Gao Y, Luo H, Keim DA, Li Z (2008) A novel approach to enable semantic and visual image summarization for exploratory image search. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM international conference on multimedia information retrieval (MIR). ACM, pp 358–365
Fan W, Bouguila N (2013a) Learning finite Beta-liouville mixture models via variational Bayes for proportional data clustering. In: Proceedings of the 23rd international joint conference on artificial intelligence (IJCAI)
Fan W, Bouguila N (2013b) Variational learning of finite Beta-liouville mixture models using component splitting. In: Proceedings of the international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN), pp 1–8
Fan W, Bouguila N (2014) Non-gaussian data clustering via expectation propagation learning of finite Dirichlet mixture models and applications. Neural Process Lett 39(2):115–135
Fan W, Bouguila N, Ziou D (2012) Variational learning for finite Dirichlet mixture models and applications. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23(5):762–774
Ferguson TS (1983) Bayesian density estimation by mixtures of normal distributions. Recent Adv Stat 24:287–302
Graepel T, Herbrich R (2008) Large scale data analysis and modelling in online services and advertising. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (KDD), ACM, pp 2–2
Hegerath A, Deselaers T, Ney H (2006) Patch-based object recognition using discriminatively trained gaussian mixtures. In: Proceedings of the British machine vision conference (BMVC), pp 519–528
Ishwaran H, James LF (2001) Gibbs sampling methods for stick-breaking priors. J Am Stat Assoc 96:161–173
Ke Y, Sukthankar R (2004) Pca-sift: a more distinctive representation for local image descriptors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp II–506–II–513 Vol 2
Korwar RM, Hollander M (1973) Contributions to the theory of Dirichlet processes. Ann Probab 1:705–711
Kushner H, Yin G (1997) Stochastic approximation algorithms and applications, applications of mathematics. Springer, Berlin
Laaksonen J, Koskela M, Oja E (2002) Picsom-self-organizing image retrieval with mpeg-7 content descriptors. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 13(4):841–853
Lampert C, Nickisch H, Harmeling S (2009) Learning to detect unseen object classes by between-class attribute transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 951–958
Liu X, Fu H, Jia Y (2008) Gaussian mixture modeling and learning of neighboring characters for multilingual text extraction in images. Pattern Recog 41(2):484–493
Liu Z, Song YQ, Chen JM, Xie CH, Zhu F (2012) Color image segmentation using nonparametric mixture models with multivariate orthogonal polynomials. Neural Comput Appl 21(4):801–811
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 60(2):91–110
Lu G (2002) Techniques and data structures for efficient multimedia retrieval based on similarity. IEEE Trans Multimed 4(3):372–384
Luo J, Boutell M, Gray R, Brown C (2005) Image transform bootstrapping and its applications to semantic scene classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B: Cybern 35(3):563–570
Ma Z, Leijon A (2010) Expectation propagation for estimating the parameters of the Beta distribution. In: Proceedings IEEE international conference on acoustics speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp 2082–2085
Mancas-Thillou C, Gosselin B (2007) Color text extraction with selective metric-based clustering. Comput Vis Image Underst 107(1–2):97–107
Maybeck PS (1982) Stochastic models, estimation and control. Academic Press, New York
McNicholas PD (2010) Model-based classification using latent gaussian mixture models. Stat Plan Inference 140(5):1175–1181
Minka T (2001) Expectation propagation for approximate Bayesian inference. In: Proceedings of the conference on uncertainty in artificial intelligence (UAI), pp 362–369
Minka T, Lafferty J (2002) Expectation propagation for the generative aspect model. In: Proceedings of the conference on uncertainty in artificial intelligence (UAI), pp 352–359
Mojsilovic A, Rogowitz B (2004) Semantic metric for image library exploration. IEEE Trans Multimed 6(6):828–838
Mojsilovic A, Kovacevic J, Hu J, Safranek R, Ganapathy S (2000) Matching and retrieval based on the vocabulary and grammar of color patterns. IEEE Trans Image Process 9(1):38–54
Nilsback ME, Zisserman A (2006) A visual vocabulary for flower classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), vol 2, pp 1447–1454
Ozuysal M, Fua P, Lepetit V (2007) Fast keypoint recognition in ten lines of code. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1–8
Park SH, Yun ID, Lee SU (1998) Color image segmentation based on 3-d clustering: morphological approach. Pattern Recog 31(8):1061–1076
Robert C, Casella G (1999) Monte Carlo statistical methods. Springer, New York
Santago P, Gage H (1995) Statistical models of partial volume effect. IEEE Trans Image Process 4(11):1531–1540
Sato M (2001) Online model selection based on the variational Bayes. Neural Comput 13:1649–1681
Schweitzer H (1999) Organizing image databases as visual-content search trees. Image Vis Comput 17(7):501–511
Seemann E, Leibe B, Mikolajczyk K, Schiele B (2005) An evaluation of local shape-based features for pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the British machine vision conference (BMVC)
Sethuraman J (1994) A constructive definition of Dirichlet priors. Statistica Sinica 4:639–650
Souden M, Kinoshita K, Nakatani T (2013) An integration of source location cues for speech clustering in distributed microphone arrays. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp 111–115
Souden M, Kinoshita K, Delcroix M, Nakatani T (2014) Location feature integration for clustering-based speech separation in distributed microphone arrays. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 22(2):354–367
Teh YW, Jordan MI (2010) Hierarchical Bayesian nonparametric models. In: Hjort N, Holmes C, Müller P, Walker S (eds) Bayesian nonparametrics: principles and practice. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Teh YW, Jordan MI, Beal MJ, Blei DM (2006) Hierarchical Dirichlet processes. J Am Stat Assoc 101(476):1566–1581
Thureson J, Carlsson S (2004) Appearance based qualitative image description for object class recognition. In: Pajdla T, Matas J (eds) ECCV (2), Springer, Lecture notes in computer science, vol 3022, pp 518–529
Wang C, Paisley JW, Blei DM (2011) Online variational inference for the hierarchical Dirichlet process. J Mach Learn Res—Proc Track 15:752–760
Wu Y, Huang TS (2000) Self-supervised learning for visual tracking and recognition of human hand. In: Proceedings of the 7th national conference on artificial intelligence and twelfth conference on on innovative applications of artificial intelligence (AAAI/IAAI), pp 243–248
Xiao J, Hays J, Ehinger K, Oliva A, Torralba A (2010) Sun database: large-scale scene recognition from abbey to zoo. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 3485–3492
Acknowledgments
The completion of this work was supported by the Scientific Research Funds of Huaqiao University (600005-Z15Y0016). The authors would like to thank the anonymous referees and the associate editor for their comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, W., Bouguila, N. Model-Based Clustering Based on Variational Learning of Hierarchical Infinite Beta-Liouville Mixture Models. Neural Process Lett 44, 431–449 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-015-9466-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-015-9466-x