Abstract
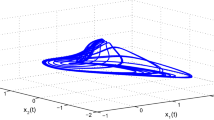
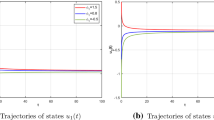
This paper aims at analyzing the impulsive synchronization of fractional-order neural works. Firstly, in view of control theory, by constructing a suitable impulsive response system with the designed controller, the synchronization error system between the drive system and the corresponding response system is given. Afterwards, based on the theory of impulsive differential equation, the theory of fractional differential equation, Lyapunov direct method, and inequality techniques, some effective sufficient criteria are established to guarantee the global Mittag-Leffler stability for the synchronization error system. Finally, several simulation examples are designed to demonstrate the effectiveness and feasibility of the obtained results.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang T, Li C, Yu W, Chen G (2009) Synchronization of delayed chaotic systems with parameter mismatches by using intermittent linear state feedback. Nonlinearity 22:569–584
Sun Z, Xue L, Zhang K (2015) A new approach to finite-time adaptive stabilization of high-order uncertain nonlinear system. Automatica 58:60–66
Sun Z, Li T, Yang S (2016) A unified time-varying feedback approach and its applications in adaptive stabilization of high-order uncertain nonlinear systems. Automatica 70:249–257
Sun Z, Yun M, Li T (2017) A new approach to fast global finite-time stabilization of high-order nonlinear system. Automatica 81:455–463
Hua C, Li Y, Guan X (2017) Finite/fixed time stabilization for nonlinear interconnected systems with dead-zone input. IEEE Trans Autom Control 62(5):2254–2560
Li X, Rakkiyappan R (2013) Impulsive controller design for exponential synchronization of chaotic neural networks with mixed delays. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 18(6):1515–1523
Samidurai R, Anthoni S, Balachandran K (2010) Global exponential stability of neutral-type impulsive neural networks with discrete and distributed delays. Nonlinear Anal Hybrid Syst 4(1):103–112
Huang T, Li C, Duan S, Starzyk J (2012) Robust exponential stability of uncertain delayed neural networks with stochastic perturbation and impulse effects. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23(6):866–875
Yang X, Cao J, Ho D (2015) Exponential synchronization of discontinuous neural networks with time-varying mixed delays via state feedback and impulsive control. Cogn Neurodyn 9(2):113–128
Li C, Yu X, Huang T, Chen G, He X (2016) A generalized Hopfield network for nonsmooth constrained convex optimization: Lie derivative approach. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(3):308–321
Gao X, Zhong S, Gao F (2009) Exponential synchronization of neural networks with time-varying delays. Nonlinear Anal Theory Methods Appl 71(5):2003–2011
Wang K, Teng Z, Jiang H (2008) Adaptive synchronization of neural networks with time-varying delay and distributed delay. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 387(2):631–642
Zhang C, He Y, Wu M (2010) Exponential synchronization of neural networks with time-varying mixed delays and sampled-data. Neurocomputing 74(1):265–273
Chen W, Lu X, Zheng W (2015) Impulsive stabilization and impulsive synchronization of discrete-time delayed neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 26(4):734–748
Zhang W, Tang Y, Miao Q, Du W (2013) Exponential synchronization of coupled switched neural networks with mode-dependent impulsive effects. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24(8):1316–1326
Li P, Cao J, Wang Z (2007) Robust impulsive synchronization of coupled delayed neural networks with uncertainties. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 373:261–272
Li X, Song S (2014) Research on synchronization of chaotic delayed neural networks with stochastic perturbation using impulsive control method. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 19(10):3892–3900
Li C, Yu X, Liu Z, Huang T (2016) Asynchronous impulsive containment control in switched multi-agent systems. Inf Sci 370–371(20):667–679
Lakshmikantham V, Bainov D, Simeonov P (1989) Theory of impulsive differential equations. World Science, Singapore
Yang T (2001) Impulsive control theory. Springer, Berlin
Li C, Liao X, Zhang R (2004) Impulsive synchronization of nonlinear coupled chaotic systems. Phys Lett A 328(1):47–50
Song Q, Huang T (2015) Stabilization and synchronization of chaotic systems with mixed time-varying delays via intermittent control with non-fixed both control period and control width. Neurocomputing 154:61–69
Wang X, Li C, Huang T, Chen L (2014) Impulsive exponential synchronization of randomly coupled neural networks with Markovian jumping and mixed model-dependent time delays. Neural Netw 60:25–32
Yang X, Song Q, Liu Y, Zhao Z (2015) Finite-time stability analysis of fractional-order neural networks with delay. Neurocomputing 152:19–26
Bao H, Cao J (2015) Projective synchronization of fractional-order memristor-based neural networks. Neural Netw 63:1–9
Li Y, Chen Y, Podlubny I (2009) Mittag-Leffler stability of fractional order nonlinear dynamic systems. Automatica 45:1965–1969
Yu J, Hu C, Jiang H, Fan X (2014) Projective synchronization for fractional neural networks. Neural Netw 49:87–95
Yu J, Hu C, Jiang H (2012) \(\alpha \)-stability and \(\alpha \)-synchronization for fractional order neural networks. Neural Netw 35:82–87
Yang X, Li C, Huang T, Song Q (2017) Mittag-Leffler stability analysis of nonlinear fractional-order systems with impulses. Appl Math Comput 293:416–422
Yang X, Li C, Huang T, Song Q, Chen X (2017) Quasi-uniform synchronization of fractional-order memristor-based neural networks with delay. Neurocomputing 234:205–215
Zhu H, He Z, Zhou S (2011) Lag synchronization of the fractional-order system via nonlinear observer. Int J Mod Phys B 25:3951–3964
Zhang S, Yu Y, Wang H (2015) Mittag-Leffler stability of fractional-order Hopfield neural networks. Nonlinear Anal Hybrid Syst 16:104–121
Wu A, Zeng Z (2016) Boundedness, Mittag-Leffler stability and asymptotical \(\omega \)-periodicity of fractional-order fuzzy neural networks. Neural Netw 74:73–84
Wu A, Zeng Z, Song X (2016) Global Mittag-Leffler stabilization of fractional-order bidirectional associative memory neural networks. Neurocomputing 177:489–496
Boroomand A, Menhaj B (2010) Fractional-order Hopfield neural networks. In: Natural computation international conference, pp 883–890
Diethelm K (2010) The analysis of fractional differential equations. Springer, Berlin
Kilbas A, Srivastava H, Trujillo J (2006) Theory and applications of fractional differential equations. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Podlubny I (1999) Fractional differential equations. Academic Press, San Diego
Chen J, Zeng Z, Jiang P (2014) Global Mittag-Leffler stability and synchronization of memristor-based fractional-order neural networks. Neural Netw 51:1–8
Ding Z, Shen Y, Wang L (2016) Global Mittag-Leffler synchronization of fractional-order neural networks with discontinuous activations. Neural Netw 73:77–85
Kaslik E, Sivasundaram S (2012) Nonlinear dynamics and chaos in fractional order neural networks. Neural Netw 32:245–256
Wu A, Zeng Z (2016) Global Mittag-Leffler stabilization of fractional-order memristive neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(1):206–217
Stamova I (2014) Global stability of impulsive fractional differential equations. Appl Math Comput 237:605–612
Stamova I (2015) Mittag-Leffler stability of impulsive differential equations of fractional order. Q Appl Math 73(3):525–535
Li Y, Chen Y, Podlubny I (2010) Stability of fractional-order nonlinear dynamic systems: Lyapunov direct method and generalized Mittag-Leffler stability. Comput Math Appl 59:1810–1821
Li H, Jiang Y, Wang Z, Hu C (2015) Global stability problem for feedback control systems of impulsive fractional differential equations on networks. Neurocomputing 161:155–161
Wang F, Yang Y, Hu M (2015) Asymptotic stability of delayed fractional-order neural networks with impulsive effects. Neurocomputing 154:239–244
Stamova I (2014) Global Mittag-Leffler stability and synchronization of impulsive fractional-order neural networks with time-varying delays. Nonlinear Dyn 77(4):1251–1260
Aguila-Camacho N, Duarte-Mermoud M, Gallegos J (2014) Lyapunov functions for fractional order systems. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 19(9):2951–2957
Berman A, Plemmons R (1979) Nonnegative matrices in the mathematical sciences. Academic, New York
Hua C, Liu D, Guan X (2014) Necessary and sufficient stability criteria for a class of fractional-order delayed systems. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II 61(1):59–63
Hua C, Guan X (2016) Smooth dynamic output feedback control for multiple time-delay systems with nonlinear uncertainties. Automatica 68:1–8
Sun Z, Zhang C, Wang Z (2017) Adaptive disturbance attenuation for generalized high-order uncertain nonlinear systems. Automatica 80:102–109
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Qatar National Research Fund, a member of the Qatar Foundation, through the National Priorities Research Program under Grant NPRP 9-166-1-031, by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61374078, 61773004 and 11501065, and in part by the Chongqing Research Program of Basic Research and Frontier Technology of cstc2015jcyjBX0052.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Li, C., Huang, T. et al. Global Mittag-Leffler Synchronization of Fractional-Order Neural Networks Via Impulsive Control. Neural Process Lett 48, 459–479 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-017-9744-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-017-9744-x