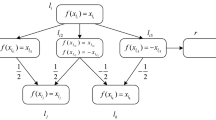
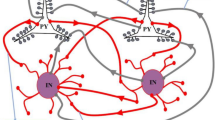
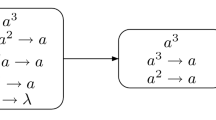
Abstract
Spiking neural P systems (namely SN P systems, for short) are bio-inspired neural-like computing models under the framework of membrane computing, which are also known as a new candidate of the third generation of neural networks. In this work, a parallel image skeletonizing method is proposed with SN P systems with weights. Specifically, an SN P system with weighs is constructed to achieve the Zhang–Suen image skeletonizing algorithm. Instead of serial calculation like Zhang–Suen image skeletonizing algorithm, the proposed method can parallel process a certain number of pixels of an image by spiking multiple neurons simultaneously at any computation step. Demonstrating via the experimental results, our method shows higher efficiency in data-reduction and simpler skeletons with less noise spurs than the method developed in Diazpernil (Neurocomputing 115:81–91, 2013) in skeletonizing images like hand-written words.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akerkar R, Sajja PS (2009) Bio-inspired computing: constituents and challenges. Int J Bio-inspired Comput 1(3):135–150
Păun G, Rozenberg G, Salomaa A (2010) The Oxford handbook of membrane computing. Oxford University Press Inc, Oxford
Ionescu M, Păun G, Yokomori T (2006) Spiking neural P systems. Fundam Inform 71(2):279–308
Maass W (1997) Networks of spiking neurons: the third generation of neural network models. Neural Netw 10(9):1659–1671
Gerstner W, Kistler WM (2002) Spiking neuron models: single neurons, populations, plasticity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Chen H, Freund R, Ionescu M, Păun G, Pérez-Jiménez MJ (2007) On string languages generated by spiking neural P systems. Fundam Inform 75(1):141–162
Zhang X, Liu Y, Luo B, Pan L (2014) Computational power of tissue P systems for generating control languages. Inf Sci 278:285–297
Păun A, Păun G (2007) Small universal spiking neural P systems. Biosystems 90(1):48–60
Zhang G, Rong H, Neri F, Pérez-Jiménez MJ (2014) An optimization spiking neural p system for approximately solving combinatorial optimization problems. Int J Neural Syst 24(05):1440006
Pan L, Păun G (2009) Spiking neural P systems with anti-spikes. Int J Comput Commun Control 4(3):273–282
Metta VP, Krithivasan K, Garg D (2012) Computability of spiking neural P systems with anti-spikes. New Math Nat Comput 8(03):283–295
Song T, Pan L, Jiang K, Song B, Chen W (2013) Normal forms for some classes of sequential spiking neural P systems. IEEE Trans NanoBioscience 12(3):255–264
Song T, Wang X (2015) Homogenous spiking neural p systems with inhibitory synapses. Neural Process Lett 42(1):199–214
Zeng X, Zhang X, Pan L (2009) Homogeneous spiking neural P systems. Fundam Inf 97(1):275–294
Song T, Wang X, Zhang Z, Chen Z (2014) Homogenous spiking neural P systems with anti-spikes. Neural Comput Appl 24:1833–1841
Wang J, Hoogeboom HJ, Pan L, Paun G, Pérez-Jiménez MJ (2010) Spiking neural P systems with weights. Neural Comput 22(10):2615–2646
Ibarra OH, Păun A, Rodríguez-Patón A (2009) Sequential SNP systems based on min/max spike number. Theor Comput Sci 410(30):2982–2991
Zhang X, Luo B, Fang X, Pan L (2012) Sequential spiking neural P systems with exhaustive use of rules. Biosystems 108(1):52–62
Ionescu M, Păun G, Yokomori T (2007) Spiking neural P systems with an exhaustive use of rules. Int J Unconv Comput 3(2):135–153
Zhang X, Wang B, Pan L (2014) Spiking neural P systems with a generalized use of rules. Neural Comput 26(12):2925–2943
Pan L, Păun G, Pérez-Jiménez MJ (2011) Spiking neural P systems with neuron division and budding. Sci China Inf Sci 54(8):1596–1607
Song T, Pan L (2014) Spiking neural P systems with rules on synapses working in maximum spikes consumption strategy. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience 14(1):38–44
Song T, Pan L (2015) Spiking neural P systems with rules on synapses working in maximum spikes consumption strategy. IEEE Trans NanoBioscience 14(1):38–44
Song T, Pan L (2015) Spiking neural P systems with rules on synapses working in maximum spiking strategy. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience 14(4):465–477
Cavaliere M, Ibarra OH, Păun G, Egecioglu O, Ionescu M, Woodworth S (2009) Asynchronous spiking neural P systems. Theor Comput Sci 410(24):2352–2364
Song T, Pan L, Păun G (2012) Asynchronous spiking neural P systems with local synchronization. Inf Sci 219:197–207
Păun G (2007) Spiking neural P systems with astrocyte-like control. J Univ Comput Sci 13(11):1707–1721
Binder A, Freund R, Oswald M, Vock L (2007) Extended spiking neural p systems with excitatory and inhibitory astrocytes. In: Proceedings of fifth brainstorming week on membrane computing, pp 63–72
Macías-Ramos LF, Pérez-Jiménez MJ (2012) Spiking neural P systems with functional astrocytes. In: Lecture notes in computer science, vol 7762, pp 228–242
Song T, Gong F, Liu X, Zhao Y, Zhang X (2016) Spiking neural P systems with white hole neurons. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience 15(7):666–673
Wang T, Zhang G, Zhao J, He Z, Wang J, Pérez-Jiménez MJ (2015) Fault diagnosis of electric power systems based on fuzzy reasoning spiking neural P systems. IEEE Trans Power Syst 30(3):1182–1194
Metta VP, Krithivasan K, Garg D (2011) Modelling and analysis of spiking neural P systems with anti-spikes using pnet lab. Nano Commun Netw 2(2):141–149
Ionescu M, Sburlan D (2007) Several applications of spiking neural P systems. In: 5th Proceedings of the workshop on membrane computing, Thessaloniki, pp 383–394
Ionescu M, Sburlan D (2012) Some applications of spiking neural P systems. Comput Inform 27(3):515–528
Song T, Zheng P, Wong MD, Wang X (2016) Design of logic gates using spiking neural P systems with homogeneous neurons and astrocytes-like control. Inf Sci 372:380–391
Adl A, Badr A, Farag I, Towards a spiking neural P systems OS, arXiv preprint arXiv:1012.0326
Zeng X, Song T, Zhang X, Pan L (2012) Performing four basic arithmetic operations with spiking neural P systems. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience 11(4):366–374
Ghosh-Dastidar S, Adeli H (2007) Improved spiking neural networks for EEG classification and epilepsy and seizure detection. Integr Comput Aided Eng 14(3):187–212
Gupta A, Long LN (2007) Character recognition using spiking neural networks. In: 2007 International joint conference on neural networks, IEEE, pp 53–58
Kang M, Palmer-Brown D (2008) A modal learning adaptive function neural network applied to handwritten digit recognition. Inf Sci 178(20):3802–3812
Diazpernil D, Penacantillana F, Gutierreznaranjo MA (2013) A parallel algorithm for skeletonizing images by using spiking neural P systems. Neurocomputing 115:81–91
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1097–1105
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–9
Hinton GE, Salakhutdinov RR (2006) Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 313(5786):504–507
Hong C, Yu J, Wan J, Tao D, Wang M (2015) Multimodal deep autoencoder for human pose recovery. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5659–5670
Hong C, Yu J, Tao D, Wang M (2015) Image-based three-dimensional human pose recovery by multiview locality-sensitive sparse retrieval. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(6):3742–3751
Hong C, Chen X, Wang X, Tang C (2016) Hypergraph regularized autoencoder for image-based 3D human pose recovery. Signal Process 124:132–140
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Yu Z, Yu J, Xiang C, Fan J, Tao D (2018) Beyond bilinear: generalized multimodal factorized high-order pooling for visual question answering. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 99:1–13
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2015) Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 91–99
Yu Z, Yu J, Fan J, Tao D (2017) Multi-modal factorized bilinear pooling with co-attention learning for visual question answering. In: Proceedings of IEEE international on conference computer visualization, vol 3
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3431–3440
Mitkov R (2005) The Oxford handbook of computational linguistics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Zhang T, Suen CY (1984) A fast parallel algorithm for thinning digital patterns. Commun ACM 27(3):236–239
Penacantillana DMF, Berciano A (2012) Parallel skeletonizing of digital images by using cellular automata. Comput Topol Image Context 115:81–91
Wang X, Song T, Gong F, Zheng P (2016) On the computational power of spiking neural P systems with self-organization. Sci Rep 6:27624
Zhang X, Pan L, Paun A (2015) On the universality of axon P systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 26(11):2816–2829
Song T, Rodrłguez-Patn A, Zheng P, Zeng X (2017) Spiking neural P systems with colored spikes. IEEE Trans Cogn Dev Syst 99:1–1
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61873280, 61502535, 61672033 and 61672248), Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province (2017GGX10147), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (16CX02006A, 18CX02152A), Talent introduction project of China University of Petroleum (YJ201601003), and research project TIN2016-81079-R (AEI/FEDER, Spain-EU) and grant 2016-T2/TIC-2024 from Talento-Comunidad de Madrid, project TIN2016-81079-R (MINECO AEI/FEDER, SpainEU) and and InGEMICS-CM project (B2017/BMD-3691, FSE/FEDER, Comunidad de Madrid-EU).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, T., Pang, S., Hao, S. et al. A Parallel Image Skeletonizing Method Using Spiking Neural P Systems with Weights. Neural Process Lett 50, 1485–1502 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-018-9947-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-018-9947-9