Abstract
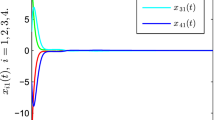
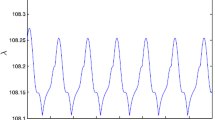
This paper deals with the problem of globally exponential synchronization and bipartite synchronization of coupled neural networks with impulsive interactions. Impulsive interaction means that a number of neural networks only communicate with each other at impulsive instants, while the array of neural networks are independent from each other at the remaining time. The advantage of the scheme is that communication cost can be largely reduced when only discrete communication is required. Moreover the communication links between nodes can be either positive or negative at impulsive instants. Using the Lyapunov method combined with some mathematical analysis and average impulsive interval, some efficient criteria are obtained to guarantee synchronization of impulsive coupled neural networks. Finally, the validity of our theoretical results is demonstrated by two numerical examples.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park MJ, Kwon OM, Park JH, Lee SM, Cha EJ (2013) On synchronization criterion of coupled discrete-time neural networks with interval time-varying delays. Neurocomputing 99:188–196
Arunkumar A, Sakthivel R, Mathiyalagan K, Anthoni SM (2012) Robust stability criteria for discrete-time switched neural networks with various activation functions. Appl Math Comput 218:10803–10816
Yang XS, Song Q, Cao JD, Lu JQ (2019) Synchronization of coupled Markovian reaction–diffusion neural networks with proportional delays via quantized control. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 30(3):951–958
Li YY (2017) Impulsive synchronization of stochastic neural networks via controlling partial states. Neural Process Lett 46:59–69
Xiong XL, Tang RQ, Yang XS (2019) Finite-time synchronization of memristive neural networks with proportional delay. Neural Process Lett 50(2):1139–1152
Pecora LM, Carroll TL (1998) Master stability functions for synchronized coupled systems. Phys Rev Lett 80(10):2109–2112
Arenas A, Díaz-Guilera A, Kurths J, Moreno Y, Zhou CS (2008) Synchronization in complex networks. Phys Rep 469(3):93–153
Li YY, Lou JG, Wang Z, Alsaadi FE (2018) Synchronization of nonlinearly coupled dynamical networks under hybrid pinning impulsive controllers. J Frankl Inst 355:6520–6530
Li LL, Ho DWC, Cao JD, Lu JQ (2016) Pinning cluster synchronization in an array of coupled neural networks under event-based mechanism. Neural Netw 76:1–12
Zhong J, Lu JQ, Huang TW, Ho DWC (2017) Controllability and synchronization analysis of identical-hierarchy mixed-valued logical control networks. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(11):3482–3493
Li YL, Li HT, Xu XJ, Li YY (2018) A semi-tensor product approach to minimal-agent consensus control of networked evolutionary games. IET Control Theory Appl 12(16):2269–2275
Zhu Q, Liu Y, Lu J, Cao J (2018) Further results on the controllability of Boolean control networks. IEEE Trans Autom Control 1(64):440–442
Yang XY, Chen BQ, Li YY, Liu Y, Alsaadi FE (2018) Stabilization of dynamic-algebraic Boolean control networks via state feedback control. J Frankl Inst 355:5520–5533
Liu HC, Liu Y, Li YY, Wang Z, Alsaadi FE (2019) Observability of Boolean networks via STP and graph methods. IET Control Theory Appl 13(7):1031–1037
Zhu Q, Liu Y, Lu J, Cao J (2018) On the optimal control of Boolean control networks. SIAM J Control Optim 56(2):1321–1341
Bainov DD, Simeonov PS (1989) Systems with impulsive effect: stability theory and applications. Ellis Horwood Limited, Chichester
Li X, Fang J, Li H (2017) Master slave exponential synchronization of delayed complex-valued memristor-based neural networks via impulsive control. Neural Netw 93:165–175
Li XD, Yang XY, Huang TW (2019) Persistence of delayed cooperative models: impulsive control method. Appl Math Comput 342:130–146
Huang C, Lu JQ, Ho DWC, Zhai GS, Cao JD (2020) Stabilization of probabilistic Boolean networks via pinning control strategy. Inf Sci 510:205–217
Zhao YS, Li XD, Duan PY (2019) Observer-based sliding mode control for synchronization of delayed chaotic neural networks with unknown disturbance. Neural Netw 116:268–273
Li LL, Shi XH, Liang JL (2019) Synchronization of impulsive coupled complex-valued neural networks with delay: the matrix measure method. Neural Netw 117:285–294
Wang YQ, Lu JQ, Lou JG, Ding CD, Alsaadi FE, Hayat T (2018) Synchronization of heterogeneous partially coupled networks with heterogeneous impulses. Neural Process Lett 1(48):557–575
Yang T (2001) Impulsive systems and control: theory and application. Nova Science, New York
Wang YQ, Lu JQ, Liang JL, Cao JD, Perc M (2019) Pinning synchronization of nonlinear coupled Lure networks under hybrid impulses. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs 66(3):432–436
Yang XS, Cao JD, Qiu JL (2015) pth moment exponential stochastic synchronization of coupled memristor-based neural networks with mixed delays via delayed impulsive control. Neural Netw 65:80–91
Yang T (2001) Impulsive control theory, vol 272. Verlag, Heidelberg
Yang XS, Lu JQ, Ho DWC, Song Q (2018) synchronization of uncertain hybrid switching and impulsive complex networks. Appl Math Model 59:379–392
Lu JQ, Ho DWC, Cao JD (2010) A unified synchronization criterion for impulsive dynamical networks. Automatica 46:1215–1221
Liu XW, Chen TP (2011) Cluster synchronization in directed networks via intermittent pinning control. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(7):1009–1020
Xu C, Yang XS, Lu JQ, Feng JW, Alsaadi FE, Hayat T (2018) Finite-time synchronization of networks via quantized intermittent pinning control. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(10):3021–3027
Yang SF, Guo ZY, Wang J (2017) Global synchronization of multiple recurrent neural networks with time delay via impulsive interactions. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(7):1657–1666
Hu JP, Zhu H (2015) Adaptive bipartite consensus on coopetition networks. Physica D 307:14–21
Lu JQ, Guo X, Huang TW, Wang Z (2019) Consensus of signed networked multi-agent systems with nonlinear coupling and communication delays. Appl Math Comput 350:153–162
Facchetti G, Lacono G, Altafini C (2011) Computing global structural balance in large-scale signed social networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(52):14–21
Wang N, Li XC, Lu JQ, Alsaadi FE (2018) Unified synchronization criteria in an array of coupled neural networks with hybrid impulses. Neural Netw 101:25–32
Altafini C (2013) Consensus problems on networks with antagonistic interactions. IEEE Trans Autom Control 58(4):935–946
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61973078, the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under Grant BK20170019, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Henan Province Nos. 20B110018 and 19B110012, and Foundation of Xuchang University with No. 2019YB030.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, N., Li, X. & Lu, J. Impulsive-Interaction-Driven Synchronization in an Array of Coupled Neural Networks. Neural Process Lett 51, 2685–2700 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-020-10214-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-020-10214-x