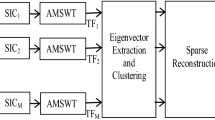
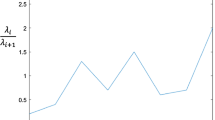
Abstract
In recent years, the number of electrical and electronic devices used in production and life has been increasing. It leads to serious interference and aliasing among electromagnetic signals. To address electromagnetic interference (EMI) issues, we propose a feasible blind source separation method based on wavelet transform and improved equivariant adaptive separation via independence (EASI) algorithm. First, we leverage the wavelet transform algorithm to denoise mixed electromagnetic signals. Second, we use the variable step-size EASI algorithm to separate each signal from the mixed signals. It is inspired by the simulated annealing strategy. We conduct a series of experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of WE method. The experimental results show that WE method can provide support for solving EMI problems.


source signals



source signal waveforms


source signal (blue) waveforms

source signal (blue) waveforms

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang LC (2005) Developing electromagnetic compatibility undertaking in our country. Trans China Electrotech Soc 20:23–28
Wu XL (1980) Control radio interference and achieve electromagnetic compatibility. Radio TV Broadcast Eng 66:42–51
Chen WF, Liu WL, Zhou X (2008) Electromagnetic compatibility and its test technology. Electron Meas Technol 31:101–104
Li M, Zhu ZW, Cai WY (2007) Research status and future treads of electromagnetic compatibility technology. Electron Qual 66:61–64
Hyvärinen A (1999) The fixed-point algorithm and maximum likelihood estimation for independent component analysis. Neural Process Lett 10(1):1–5
Lu JT, Cheng W, Zi YY, He ZJ (2015) Variable step-size algorithm for equivariant adaptive separation via independence. J Xi’an Jiaotong Univ 49:83–89
Li HY, Ma LT, Chen B, Zhao D (2015) A one-stop BSS analysis method of integrated system signals based on wavelet transform, FastICA and SOM. Atlantis Press
Li HY, Lin W, Zhao D (2019) A single-channel BSS method based on ICEEMDAN and FastICA and its application in EMI analysis. In: 14th International conference on computer science and education (ICCSE 2019), pp 780–784
Wu JS, Li GB (2006) An improved adaptive step-size EASI algorithm. Ship Electron Eng 26:137–140
Fu WH, Yang XN, Liu NA, Zen XW (2008) Step-size optimization based EASI algorithm for blind source separation. J Sichuan Univ Eng Sci Ed 40:118–121
Cardoso JF, Laheld BH (1997) Equivariant adaptive source separation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 44(12):3017–3030
Meng DX, Ma JF, Qiao YF (2007) Improved speech separation algorithm based on EASI. Comput Eng Appl 43:214–216
Fu WH, Shi F, Liu NA (2012) Blind source separation algorithm for time varying channel. J Univ Electron Sci Technol China 41:512–515
Gao L, Zhang TQ, Hou RL, He DN (2012) Information and chip sequence blind estimation for DS-CDMA system based on improved EASI algorithm. Telecommun Eng 52:1275–1281
Cao XR, Liu RW (19969) A general approach to blind source separation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 44:562–571
Donoho DL, Johnstone IM (1995) Adapting to unknown smoothness via wavelet shrinkage. J Am Stat Assoc 90(432):1200–1224
Tian ZD, Li SJ, Wang YH, Sha Y (2017) A prediction method based on wavelet transform and multiple models fusion for chaotic time series. Chaos Solitons Fract 98:158–172
Tian ZD (2020) A combined prediction approach based on wavelet transform for crop water requirement. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 20(3):1016–1034
Tian ZD (2020) Network traffic prediction method based on wavelet transform and multiple models fusion. Int J Commun Syst 33:4415
Wu W, Ca PS (2008) Simulation of wavelet denoising based on MATLAB. Inf Electron Eng 6:220–222
Berkner K, Wells RO Jr (1998) Wavelet transforms and denoising algorithm. In: Signal, system & computers, conference record of the thirty-second asilomar conference, pp 1639–1643
Wu PY, Liu SG (2001) Application performance analysis of several common wavelets. China Acad J Electron 66:6
Daubechies I (1994) Ten lectures on wavelets. CBMS SIAM 61:194–202
Yu H, Wu WQ (2009) Research and improvement of blind source separation based on EASI algorithm. Comput Technol Autom 28:76–79
Yu H, Wu WQ, Liu Z (2009) Research and improvement of blind source separation based on EASI algorithm. Ship Electron Eng 29:118–121
Ren HL, Zheng YF, Zhong N, Cao XF (2020) Research on single antenna co-frequency mixed signal separation based on improved EFICA algorithm. J Phys Conf Ser 1651(1):66
Pan Y, Matilainen M, Taskinen S et al (2020) A review of second‐order blind identification methods. Wiley interdisciplinary reviews: computational statistics, 2021
Petkov J, Koldovský H, Zbyněk A (2009) BSSGUI—a package for interactive control of blind source separation algorithms in MATLAB
Acknowledgements
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61771001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Most of Wei Lin’s work was done when he was at Beihang University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Lin, W. & Zhao, D. BSS Method Based on Wavelet Transform and Improved EASI Algorithm and Its Application in EMI. Neural Process Lett 53, 4437–4449 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10621-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10621-8