Abstract
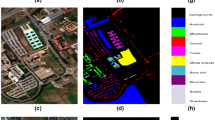
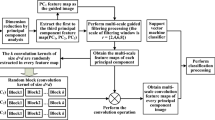
With the development of remote sensing technology, hyperspectral sensors can record reflectance of ground objects in hundreds of bands, which undoubtedly brings great benefits for hyperspectral remote sensing image that contains abundant information of the land covers. At present, some hyperspectral images are contaminated by the noise and a lack of spatial information, this phenomenon hinders the improvement of classification accuracy. To further mine the spatial features of hyperspectral image, we propose an effective feature extraction method based on Spectral-Gabor space discriminant analysis (SGDA). The framework of SGDA is roughly divided into four steps: firstly, we obtain \(p_i\) \(\{p_i|1\le i<d\}\) principal components by PCA, where d denotes the number of features; secondly, we filter the \(p_i\) principal components with Gabor filter on five different scales and eight different orientations and obtain Gabor spatial features; thirdly, incorporating the spectral features of original hyperspectral data into the Gabor spatial features to form the Spectral-Gabor space features F; finally, we project the fusion features to a low-dimensional subspace, and then maximize the Spectral-Gabor space between-class scatter matrix (\(S_b^{SG}\)) and minimize the Spectral-Gabor space within-class scatter matrix (\(S_w^{SG}\)) at the same time inspired by the idea of Fisher line discriminant analysis. Also, in the above fusion process, the proportion of spectral and spatial information can be controlled by using a penalty factor \(\alpha \). Experimental results on three hyperspectral datasets show the better classification performance of the SGDA method than the state-of-art methods on the condition of small sample size by Maximum Likelihood Classifier (MLC).

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar B, Dikshit O, Gupta A et al (2020) Feature extraction for hyperspectral image classification: a review [J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing 41(16):6248–6287
Jia X, Kuo BC, Crawford MM (2013) Feature mining for hyperspectral image classification[J]. Proc IEEE 101(3):676–697
Hosseini SA, Ghassemian H (2016) Hyperspectral Data Feature Extraction Using Rational Function Curve Fitting[J]. Int J Pattern Recognit Artif Intell 30(01):1650001. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218001416500014
Hosseini SA, Ghassemian H (2016) Rational function approximation for feature reduction in hyperspectral data[J]. Remote Sensing Letters 2:101–110
Imani M, Ghassemian H (2017) High-dimensional image data feature extraction by double discriminant embedding[J]. Pattern Anal Appl 20(2):473–484
Imani M, Ghassemian H (2016) Binary coding based feature extraction in remote sensing high dimensional data[J]. Inf Sci 342:191–208
Kelam H, Venkatesan M (2019) Optimal band selection using generalized covering-based rough sets on hyperspectral remote sensing big data. Advances in big data and cloud computing. Springer, Singapore, pp 263–273
Shang, R., Lan, Y., Jiao, L. et al. A dynamic local cluster ratio-based band selection algorithm for hyperspectral images. Soft Comput, 2019, 23: 8281–8289. DOI: 10.1007/s00500-018-3464-7
Veera Senthil Kumar G, Vasuki S Clustering based band selection for endmember extraction using simplex growing algorithm in hyperspectral images. Multimed Tools Appl, 2017, 76: 8355–8371. DOI: 10.1007/s11042-016-3420-4
Dernoncourt D, Hanczar B, Zucker JD (2014) Analysis of feature selection stability on high dimension and small sample data[J]. Comput Stat Data Anal 71:681–693
Agrawal N, Verma K (2020) Dimensionality reduction on hyperspectral data set. In: Proceedings of the 2020 First international conference on power, control and computing technologies (ICPC2T). IEEE, pp 139–142
Hotelling H (1933) Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components[J]. J Educ Psychol 24(6):417–441
Liao W, Pizurica A, Scheunders P et al (2013) Semisupervised local discriminant analysis for feature extraction in hyperspectral images[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 51(1):184–198
Dong P, Liu J (2011) Hyperspectral Image Classification Using Support Vector Machines with an Efficient Principal Component Analysis Scheme. Foundations of Intelligent Systems. Advances in Intelligent and Soft. Computing 122:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25664-6-17
Fauvel M, Chanussot J, Benediktsson JA (2009) Kernel principal component analysis for the classification of hyperspectral remote sensing data over urban areas [J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing 2009(1):783194
Scholkopf B, Smola A, Muller KR (1998) Nonlinear component analysis as a kernel eigenvalue problem[J]. Neural Comput 10:1299–1319
Villa A, Chanussot J, Benediktsson JA et al (2013) Unsupervised methods for the classification of hyperspectral images with low spatial resolution[J]. Pattern Recogn 46(6):1556–1568
Wen J, Tian Z, Liu X et al (2013) Neighborhood preserving orthogonal PNMF feature extraction for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE J Select Top Appl Earth Observ Remote Sens 6(2):759–768
Hosseini A, Ghassemian H (2012) Classification of hyperspectral and multispectral images by using fractal dimension of spectral response curve. In: Proceedings of the 2012 20th Iranian conference on electrical engineering (ICEE). IEEE, pp 1452–1457
Hosseini SA, Ghassemian H (2013) A new hyperspectral image classification approach using fractal dimension of spectral response curve. In: Proceedings of the 2013 21st Iranian conference on electrical engineering (ICEE). IEEE, pp 1–6
Li L, Ge H, Gao J et al (2019) Hyperspectral Image Feature Extraction Using Maclaurin Series Function Curve Fitting[J]. Neural Process Lett 49(1):357–374
Chang CI, Ren H (2000) An experiment-based quantitative and comparative analysis of target detection and image classification algorithms for hyperspectral imagery[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 38(2):1044–1063
Landgrebe DA (2005) Signal theory methods in multispectral remote sensing[M]. John Wiley and Sons
Kuo BC, Landgrebe DA (2004) Nonparametric weighted feature extraction for classification[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 42(5):1096–1105
Mika S, Ratsch G, Weston J (1999) Fisher discriminant analysis with kernels. Neural networks for signal processing IX, et al (1999). In: Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE signal processing society workshop. IEEE pp 41–48
Baudat G, Anouar F (2000) Generalized discriminant analysis using a kernel approach[J]. Neural Comput 12(10):2385–2404
Imani M, Ghassemian H (2015) Feature space discriminant analysis for hyperspectral data feature reduction[J]. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 102:1–13
Cai D, He X, Han J (2007) Semi-supervised discriminant analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 11th international conference on computer vision, 2007. ICCV 2007. IEEE, pp 1–7
Chen S, Zhang D (2011) Semisupervised dimensionality reduction with pairwise constraints for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 8(2):369–373
Sugiyama M, Nakajima S et al (2010) Semi-supervised local Fisher discriminant analysis for dimensionality reduction[J]. Mach Learn 78(1–2):35
He X, Cai D, Yan S (2005) Neighborhood preserving embedding. Computer Vision, et al (2005) ICCV 2005. Tenth IEEE International Conference on. IEEE (2):1208–1213
He X, Niyogi P (2004) Locality preserving projections. Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 153–160
He X, Cai D, Han J (2008) Learning a maximum margin subspace for image retrieval[J]. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 20(2):189–201
Li L, Ge H, Gao J (2017) A spectral-spatial kernel-based method for hyperspectral imagery classification[J]. Adv Space Res 59(4):954–967
Gao J, Xu L (2016) A novel spatial analysis method for remote sensing image classification[J]. Neural Process Lett 43(3):805–821
Gao J, Xu L, Shen J et al (2015) A novel information transferring approach for the classification of remote sensing images[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing 2015(1):38
Gao J, Xu L, Huang F (2016) A spectral-textural kernel-based classification method of remotely sensed images[J]. Neural Comput Appl 27(2):431–446
Gao J, Xu L (2015) An efficient method to solve the classification problem for remote sensing image. AEU-Int J Elect Commun 69(1):198–205
Gao J, Xu L, Shi A et al (2014) A kernel-based block matrix decomposition approach for the classification of remotely sensed images[J]. Appl Math Comput 228:531–545
Huang X, Zhang L (2012) An SVM ensemble spproach combining spectral, structural, and semantic features for the classification of high-resolution remotely sensed imagery[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 51(1):257–272
Wan WM (2018) A band selection method for airborne hyperspectral image based on chaotic binary coded gravitational search algorithm[J]. Neurocomputing 273(1):57–67
Huang H, Shi G, He H et al (2019) Dimensionality reduction of hyperspectral imagery based on spatial-spectral manifold learning. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(6). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2905793
Fauvel M, Chanussot J, Benediktsson JA et al (2007) Spectral and spatial classification of hyperspectral data using SVMs and morphological profiles. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium. IEEE, pp 4834–4837
Tuia D, Volpi M et al (2014) Automatic feature learning for spatio-spectral image classification with sparse SVM[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 52(10):6062–6074
Jia S, Zhang X et al (2015) Spectral-Spatial Hyperspectral Image Classification Using 1/2 Regularized Low-Rank Representation and Sparse Representation-Based Graph Cuts[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 8(6):2473–2484
Li J, Marpu PR, Plaza A et al (2013) Generalized composite kernel framework for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 51(9):4816–4829
Saqui, D; Saito, JH; Jorge, LADC; Ferreira, EJ; Lima, DC (2017) Methodology for band selection of hyperspectral images using genetic algorithms and gaussian maximum likelihood classifier. Int Conf Comput Sci Comput Intell 51(1): 733-738
Jia S, Wu K, Zhu J et al (2018) Spectral-spatial Gabor surface feature fusion approach for hyperspectral imagery classificationa. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 99:1–13
Meshgini S, Aghagolzadeh A, Seyedarabi H (2013) Face recognition using Gabor-based direct linear discriminant analysis and support vector machine[J]. Comput Electr Eng 39(3):727–745
Koc M, Barkana A (2011) A new solution to one sample problem in face recognition using FLDA[J]. Appl Math Comput 217(24):10368–10376
Gao J, Fan L, Xu L (2013) Median null (Sw)-based method for face feature recognition[J]. Appl Math Comput 219(12):6410–6419
Jain A, Zongker D. Feature selection: evaluation, application, and small sample performance. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 1997, 19(2):153–158
Purdue Research Foundation (2015) Hyperspectral images by multiSpec. https://engineering.purdue.edu/biehl/MultiSpec/
Universidad-del-Pais-Vasco (2014) Hyperspectral remote sensing scenes. http://www.ehu.eus/ccwintco/index.php?title=HyperspectralRemoteSensingScenes
Acknowledgements
This work is partly supported by the Doctoral Research Foundation of Jining Medical University under Grant No.2018JYQD03, and the Doctoral Research Foundation of Jining Medical University for Dr. Li Li, and a Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program under Grant No.J18KA217, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Gao, J., Ge, H. et al. An Effective Feature Extraction Approach Based on Spectral-Gabor Space Discriminant Analysis for Hyperspectral Image. Neural Process Lett 54, 909–959 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10665-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10665-w