Abstract
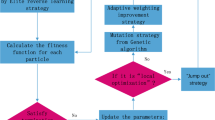
In order to improve the convergence speed and solution accuracy of particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm and avoid premature convergence, an enhanced PSO with fusing multiple strategies, namely CWBPSO is proposed in this paper. In the proposed CWBPSO algorithm, a fast convergence strategy is employed to accelerate the particles toward the optimal value. Meanwhile, an improved strategy of the acceleration factor is designed to improve the local search ability of the particles and strengthen the global search ability. A new linear decreasing strategy of inertia weight factor is designed to avoid premature maturation and oscillation phenomenon, improve the overall optimization performance and reduce the time complexity. Four typical test functions in CEC2014 and CEC2017 and a real train delay scheduling problem are selected to verify the effectiveness of the proposed CWBPSO algorithm. The comparative analysis of experimental results shows that the CWBPSO algorithm improves the convergence speed and convergence accuracy, avoids premature convergence and oscillation phenomena. The CWBPSO algorithm can effectively schedule the delay trains, reduce train delay time and avoid delay propagation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, pp 39–43
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of ICNN'95 - International Conference on Neural Networks 4:1942–1948
Sabir Z, Ali MR, Raja MAZ et al (2021) Computational intelligence approach using Levenberg–Marquardt backpropagation neural networks to solve the fourth-order nonlinear system of Emden-Fowler model. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01427-2
Ayub A, Sabir Z, Altamirano GC et al (2021) Characteristics of melting heat transport of blood with time-dependent cross-nanofluid model using Keller-Box and BVP4C method. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01406-7
Ali MR, Ma WX, Sadat R (2021) Lie symmetry analysis and invariant solutions for (2+1) dimensional Bogoyavlensky-Konopelchenko equation with variable-coefficient in wave propagation. J Ocean Eng Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joes.2021.08.006
Ali MR, Sadat R, Ma WX (2021) Investigation of new solutions for an extended (2+ 1)-dimensional Calogero-Bogoyavlenskii-Schif equation. Front Math China 16(4):925–936
Ali MR, Ma WX (2020) New exact solutions of Bratu Gelfand model in two dimensions using Lie symmetry analysis. Chin J Phys 65:198–206
Wagle R, Sharma P (2021) Bio-inspired hybrid BFOA-PSO algorithm-based reactive power controller in a standalone wind-diesel power system. Int Trans Electric Energy Syst 31(3):2050–7038
Moharam A, El-Hosseini M, Ali H (2016) Design of optimal PID controller using hybrid differential evolution and particle swarm optimization with a-n aging leader and challengers. Appl Soft Comput 38:727–737
Sreesudha P, Malleswari BL (2021) A hybridization approach of PSO and GSO algorithm for minimum-BER based multi-user detection in STBC-MIMO MC-CDMA systems. Multimedia Tools Appl 80(21):31967–31992
Mistry K, Zhang L, Neoh S (2017) A Micro-GA embedded PSO feature selection approach to intelligent facial emotion recognition. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(6):1–14
Cui HJ, Guan Y, Chen H (2021) Rolling element fault diagnosis based on VMD and sensitivity MCKD. IEEE Access 9:120297–120308
Wei YY, Zhou YQ, Luo QF et al (2021) Optimal reactive power dispatch using an improved slime mould algorithm. Energy Rep 7:8742–8759
Guedria N (2016) Improved accelerated PSO algorithm for mechanical engineering optimization problems. Appl Soft Comput 40:455–467
Rengasamy S, Murugesan P (2021) PSO based data clustering with a different perception. Swarm Evol Comput 64:100895
Zhang ZH, Min F, Chen GS et al (2021) Tri-partition state alphabet-based sequential pattern for multivariate time series. Cogn Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-021-09871-4
Ran XJ, Zhou XB, Lei MM et al (2021) A novel k-means clustering algorithm with a noise algorithm for capturing urban hotspots. Appl Sci 11:11202
Deng W, Xu JJ, Gao XZ et al (2020) An enhanced MSIQDE algorithm with novel multiple strategies for global optimization problems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybernet. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2020.3030792
Wu Q, Hu DW, Deng PY et al (2020) Non-parametric Bayesian prior inducing deep network for automatic detection of cognitive status. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.2977267
Li TY, Qian ZJ, Deng W et al (2021) Forecasting crude oil prices based on variational mode decomposition and random sparse Bayesian learning. Appl Soft Comput 113:108032
Cui H, Guan Y, Chen HY et al (2021) A novel advancing signal processing method based on coupled multi-stable stochastic resonance for fault detection. Appl Sci 11:5385
Wu Q, Zhou MC, Hu DW et al (2020) Self-paced dynamic infinite mixture model for fatigue evaluation of pilots’ brain. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.3033005
Deng W, Zhang XX, Zhou YQ et al (2022) An enhanced fast non-dominated solution sorting genetic algorithm for multi-objective problems. Inf Sci 585:441–453
Ali MR, Sadat R (2021) Construction of Lump and optical solitons solutions for (3+ 1) model for the propagation of nonlinear dispersive waves in inhomogeneous media. Opt Quant Electron 53(5):1–13
Ali MR, Sadat R (2021) Lie symmetry analysis, new group invariant for the (3+ 1)-dimensional and variable coefficients for liquids with gas bubbles models. Chin J Phys 71:539–547
Shi Y, Eberhart, RC (1998) Parameter selection in particle swarm optimization. Int Conf Evolut Program 1447:591–600
Chen B, Qi J, Zhang D (2021) An adaptive parameters adjustment and planning method for robotic belt grinding using modified quality model. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B 235(4):605–615
Liu M, Lin R, Yang M (2021) Active disturbance rejection motion control of spherical robot with parameter tuning. Ind Robot. https://doi.org/10.1108/IR-05-2021-0099
Nobile M, Cazzaniga P, Besozzi D (2018) Fuzzy self-tuning PSO: A settings-free algorithm for global optimization. Swarm Evol Comput 39:70–85
Marinakis Y, Migdalas A, Sifaleras A (2017) A hybrid particle swarm optimization–variable neighborhood search algorithm for constrained shortest pa-th problems. Eur J Oper Res 261(3):819–834
Liang J, Suganthan P (2005) Dynamic multi-swarm particle swarm optimizer with local search. IEEE Congress Evolut Comput 1:522–528
Lim W, Isa N (2014) Particle swarm optimization with increasing topology connectivity. Eng Appl Artif Intell 27:80–102
Chen Y, Li L, Peng H (2017) Dynamic multi-swarm differential learning particle swarm optimizer. Swarm Evol Comput 39:209–221
Wang L, Yang B, Chen Y (2014) Improving particle swarm optimization using multi-layer searching strategy. Inf Sci 274:70–94
Xia X, Xie C, Wei B (2017) Particle swarm optimization using multi-level adaptation and purposeful detection operators. Inform Sci 385–386:174–195
Liu Q, Wei W, Yuan H (2016) Topology selection for particle swarm optimization. Inf Sci 363:154–173
Liu ZH, Wei HL, Zhong QC (2016) Parameter estimation for VSI-fed PMSM based on a dynamic PSO with learning strategies. IEEE Trans Power Electron 32(4):3154–3165
Xu G, Cui Q, Shi X (2019) Particle swarm optimization based on dimensional learning strategy. Swarm Evol Comput 45:33–51
Wu G, Qiu D, Yu Y (2014) Superior solution guided particle swarm optimization combined with local search techniques. Expert Syst Appl 41(16):7536–7548
Tanweer M, Suresh S, Sundararajan N (2015) Self regulating particle swarm optimization algorithm. Inf Sci 294:182–202
Tanweer M, Suresh S, Sundararajan N (2016) Dynamic mentoring and self-regulation based particle swarm optimization algorithm for solving comple-x real-world optimization problems. Inf Sci 326:1–24
Liang B, Zhao Y, Li Y (2021) A hybrid particle swarm optimization with crisscross learning strategy. Eng Appl Artif Intell 105:104418
Cheng R, Jin Y (2015) A social learning particle swarm optimization algorithm for scalable optimization. Inf Sci 291:43–60
Wang H, Jin Y, Doherty J (2017) Committee-Based active learning for surrogate-assisted particle swarm optimization of expensive problems. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(9):2664–2677
Shieh H, Kuo C, Chiang C (2011) Modified particle swarm optimization algorithm with simulated annealing behavior and its numerical verification. Appl Math Comput 218(8):4365–4383
Li J, Zhang J, Jiang C (2015) Composite particle swarm optimizer with historical memory for function optimization. IEEE Trans Cybern 45(10):2350–2363
Ouyang H, Gao L, Kong X (2016) Hybrid harmony search particle swarm optimization with global dimension selection. Inf Sci 346–347:318–337
Chen X, Tianfield H, Mei C (2018) Biogeography-based learning particle swarm optimization. Appl Soft Comput 21:7519–7541
Aydilek I (2018) A hybrid firefly and particle swarm optimization algorithm for computationally expensive numerical problems. Appl Soft Comput 66:232–249
Chen YG, Li LX, Peng HP (2017) Particle swarm optimizer with two differential mutation. Appl Soft Comput 61:314–330
Bouyer A, Hatamlou A (2018) An efficient hybrid clustering method based on improved cuckoo optimization and modified particle swarm optimization algorithms. Appl Soft Comput 67:172–182
Lynn N, Suganthan P (2015) Heterogeneous comprehensive learning particle swarm optimization with enhanced exploration and exploitation. Swarm Evol Appl Soft Comput 24:11–24
Haklı H, Guz HU (2014) A novel particle swarm optimization algorithm with Levy flight. Appl Soft Comput 23:333–345
Tanabe R, Fukunaga A (2013) Success-history based parameter adaptation for differential evolution. In Proceedings of IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, 7: 71–78
Mallipeddi R, Suganthan P, Pan Q (2010) Differential evolution algorithm with ensemble of parameters and mutation strategies. Appl Soft Comput 11(2):1679–1696
Draa A, Bouzoubia S, Boukhalfa I (2014) A sinusoidal differential evolution algorithm for numerical optimization. Appl Soft Comput 27:99–126
Wang H, Wu Z, Rahnamayan S (2014) Multi-strategy ensemble artificial bee colony algorithm. Inf Sci 279:587–603
Naik M, Nath M, Wunnava A (2015) A new adaptive cuckoo search algorithm. In IEEE 2nd International Conference on Recent Trends inInformation Systems, 7, pp 1–5
Zhang X (2018) A novel hybrid algorithm based on biogeography-based optimization and grey wolf optimizer. Appl Soft Comput 67:197–214
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant U2133205, U2033214 and 61771087, the Research and Innovation Funding Project for Postgraduates of Tianjin (Aviation Project) under Grant 2021YJSO2S12, the China National Key R&D Program under Grant 2018YFB1601200, the Research Foundation for Civil Aviation University of China under Grant 3122022PT02 and 2020KYQD123, and the Central University Basic Scientific Research Business Fee Project of Civil Aviation University of China under Grant 2000420534.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Xu, J., Liu, Y. et al. Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm with Multi-strategies for Delay Scheduling. Neural Process Lett 54, 4563–4592 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10821-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10821-w