Abstract
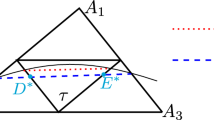
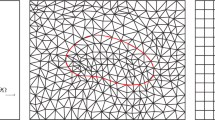
Augmented immersed interface methods have been developed recently for interface problems and problems on irregular domains including CFD applications with free boundaries and moving interfaces. In an augmented method, one or several augmented variables are introduced along the interface or boundary so that one can get efficient discretizations. The augmented variables should be chosen such that the interface or boundary conditions are satisfied. The key to the success of the augmented methods often relies on the interpolation scheme to couple the augmented variables with the governing differential equations through the interface or boundary conditions. This has been done using a least squares interpolation (under-determined) for which the singular value decomposition (SVD) is used to solve for the interpolation coefficients. In this paper, based on properties of the finite element method, a new augmented immersed finite element method (IFEM) that does not need the interpolations is proposed for elliptic interface problems that have a piecewise constant coefficient. Thus the new augmented method is more efficient and simple than the old one that uses interpolations. The method then is extended to Poisson equations on irregular domains with a Dirichlet boundary condition. Numerical experiments with arbitrary interfaces/irregular domains and large jump ratios are provided to demonstrate the accuracy and the efficiency of the new augmented methods. Numerical results also show that the number of GMRES iterations is independent of the mesh size and nearly independent of the jump in the coefficient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braess, D.: Finite elements: Theory, fast solvers, and applications in solid mechanics. Cambridge University Press (2001)
Bramble, J., King, J.: A finite element method for interface problems in domains with smooth boundaries and interfaces. Adv. Comput. Math. 6, 109–138 (1996)
Chang, K., Kwak, D.: Discontinuous bubble scheme for elliptic problems with jumps in the solution. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 200, 494–508 (2011)
Chen, G., Li, Z., Lin, P.: A fast finite difference method for biharmonic equations on irregular domains. Adv. Comput. Math. 29, 113–133 (2008)
He, X., Lin, T., Lin, Y.: Approximation capability of a bilinear immersed finite element space. Numer. Methods Partial Differential Equations 24, 1265–1300 (2008)
He, X., Lin, T., Lin, Y.: A bilinear immersed finite volume element method for the diffusion equation with discontinuous coefficient. Commun. Comput. Phys. 6, 185 (2009)
He, X., Lin, T., Lin, Y.: Immersed finite element methods for elliptic interface problems with non-homogeneous jump conditions. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model. 8, 284–301 (2011)
Hou, S., Liu, X.: A numerical method for solving variable coefficient elliptic equation with interfaces. J. Comput. Phys. 202, 411–445 (2005)
Hou, T., Wu, X., Cai, Z.: Convergence of a multiscale finite element method for elliptic problems with rapidly oscillating coefficients. Math. Comp. 68, 913–943 (1999)
Hou, T., Wu, X., Zhang, Y.: Removing the cell resonance error in the multiscale finite element method via a Petrov-Galerkin formulation. Commun. Math. Sci. 2, 185–205 (2004)
Ito, K., Li, Z., Lai, M.: An augmented method for the Navier-Stokes equations on irregular domains. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 2616–2628 (2009)
Swarztrauber, P., Adams, J., Sweet, R.: Fishpack: Efficient Fortran subprograms for the solution of separable elliptic partial differential equations. Available In: http://www.netlib.org/fishpack/
Ji, H., Chen, J., Li, Z.: A symmetric and consistent immersed finite element method for interface problems. J. Sci. Comput. doi:10.1007/s10915-014-9837-x
Li, Z.: A fast iterative algorithm for elliptic interface problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 35, 230–254 (1998)
Li, Z., Ito, K.: The immersed interface method: numerical solutions of PDEs involving interfaces and irregular domains. Frontiers in Applied Mathematics, vol. 33. SIAM, Philadelphia (2006)
Li, Z., Ito, K., Lai, M.: An augmented approach for Stokes equations with a discontinuous viscosity and singular forces. Comput. Fluids 36, 622–635 (2007)
Li, Z., Lin, T., Wu, X.: New Cartesian grid methods for interface problems using the finite element formulation. Numer. Math. 96, 61–98 (2003)
Li, Z., Wang, W., Chern, I., Lai, M.: New formulations for interface problems in polar coordinates. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 25, 224–245 (2003)
Li, Z., Zhao, H., Gao, H.: A numerical study of electro-migration voiding by evolving level set functions on a fixed Cartesian grid. J. Comput. Phys. 152, 281–304 (1999)
Mayo, A.: The rapid evaluation of volume integrals of potential theory on general regions. J. Comput. Phys. 100, 236–245 (1992)
Mayo, A., Greenbaum, A.: Fast parallel iterative solution of Poisson’s and the biharmonic equations on irregular regions. SIAM J. Sci. Statist. Comput. 13, 101–118 (1992)
Nielsen, B.F.: Finite element discretizations of elliptic problems in the presence of arbitrarily small ellipticity: An error analysis. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 36, 368–392 (1999)
Oevermann, M., Klein, R.: A Cartesian grid finite volume method for elliptic equations with variable coefficients and embedded interfaces. J. Comput. Phys. 219, 749–769 (2006)
Saad, Y., Schultz, M.: Gmres: A generalized minimal residual algorithm for solving nonsymmetric linear systems. SIAM J. Sci. Statist. Comput. 7, 856–869 (1986)
Ying, W., Henriquez, C.: A kernel-free boundary integral method for elliptic boundary value problems. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 1046–1074 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, H., Chen, J. & Li, Z. A new augmented immersed finite element method without using SVD interpolations. Numer Algor 71, 395–416 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-015-9999-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-015-9999-0
Keywords
- Interface problem
- Piecewise constant coefficient
- Immersed finite element
- Augmented immersed finite element method
- Poisson equation on irregular domain
- Fast poisson solver
- Least squares interpolation using SVD