Abstract
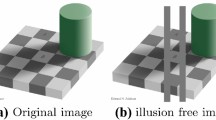
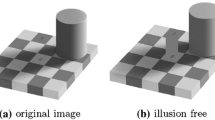
Retinex theory was proposed by Land in the 1970s. Its theoretical basis is that the color of an object is determined by the reflection ability of the object to the light of long wave, medium wave, and short wave, rather than by the absolute value of the reflected light intensity. There is color sense consistency in Retinex theory. The main purpose of Retinex problem is to recover the reflection properties of objects from the images obtained under a certain illumination intensity, so as to obtain the real colors of objects. There are many methods for solving the Retinex problem. In this paper, based on a variational minimization model with physical constraints of reflectance value, we first transform the Retinex problem into a linear complementarity problem, and then propose a class of two-step modulus-based matrix splitting iteration methods to solve this problem. We also prove the convergence of the two-step modulus-based matrix splitting iteration methods for solving the linear complementarity problem. The experimental results show that the convergence speeds of the proposed methods are much faster than the existing methods for solving the Retinex problem, and that the advantages of the new methods over the existing ones could be significant in the quality of the reflectance recovery.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, Z.-Z., Golub, G.H., Ng, M.K.: Hermitian and skew-Hermitian splitting methods for non-Hermitian positive definite linear systems. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 24(3), 603–626 (2003)
Bai, Z.-Z., Golub, G.H., Pan, J.-Y.: Preconditioned Hermitian and skew-Hermitian splitting methods for non-Hermitian positive semidefinite linear systems. Numer. Math. 98(1), 1–32 (2004)
Bai, Z.-Z., Golub, G.H.: Accelerated Hermitian and skew-Hermitian splitting iteration methods for saddle-point problems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 27 (1), 1–23 (2007)
Bai, Z.-Z.: Modulus-based matrix splitting iteration methods for linear complementarity problems. Numer. Linear Algebra Appl. 17 (6), 917–933 (2010)
Bai, -Z.: On the convergence of additive and multiplicative splitting iterations for systems of linear equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 154(1), 195–214 (2003)
Bai, Z.-Z.: On SSOR-like preconditioners for non-Hermitian positive definite matrices. Numer. Linear Algebra Appl. 23(1), 37–60 (2016)
Bai, Z.-Z., Tao, M.: Rigorous convergence analysis of alternating variable minimization with multiplier methods for quadratic programming problems with equality constraints. BIT Numer. Math. 56(2), 399–422 (2016)
Bai, Z.-Z., Tao, M.: On preconditioned and relaxed AVMM methods for quadratic programming problems with equality constraints. Linear Algebra Appl. 516(16), 264–285 (2017)
Bai, Z.-Z., Golub, G. H., Lu, L.-Z., Yin, J.-F.: Block triangular and skew-Hermitian splitting methods for positive definite linear systems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 26(3), 844–863 (2005)
Cooper, T. J., Baqai, F. A.: Analysis and extensions of the Frankle-McCann Retinex algorithm. J. Electron. Imag. 13(1), 85–92 (2004)
Cottle, R.W., Pang, J.-S., Stone, R. E.: The linear complementarity problem. Academic Press, San Diego (1992)
Dong, J.-L., Jiang, M.-Q.: A modified modulus method for symmetric positive-definite linear complementarity problems. Numer. Linear Algebra Appl. 16(2), 129–143 (2009)
Dong, J.-L., Gao, J.-B., Ju, F.-J., Shen, J.-H.: Modulus methods for nonnegatively constrained image restoration. SIAM J. Imag. Sci. 9(3), 1226–1246 (2016)
Funt, B., Ciurea, F.: Retinex in MATLAB. J. Electron. Imag. 13(1), 48–57 (2004)
Hurlbert, A.: Formal connections between lightness algorithms. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 3(10), 1684–1693 (1986)
Jobson, D.J., Rahman, Z., Woodell, G.A.: Properties and performance of a center/surround Retinex. IEEE Trans. Imag. Process. 6(3), 451–462 (1997)
Kimmel, R., Elad, M., Shaked, D., Keshet, R., Sobel, I.: A variational framework for Retinex. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 52(1), 7–23 (2003)
Land, E.H., McCann, J.J.: Lightness and Retinex theory. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 61(1), 1–11 (1971)
Land, E.H.: The Retinex theory of color vision. Sci. Am. 237 (6), 108–128 (1977)
Land, E.H.: Recent advances in retinex theory and some implications for cortical computations: color vision and the natural image. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 80(16), 5163–5169 (1983)
Land, E.H.: An alternative technique for the computation of the designator in the Retinex theory of color vision. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 83(10), 3078–3080 (1986)
Li, H.-F., Zhang, L.-P., Shen, H.-F.: A perceptually inspired variational method for the uneven intensity correction of remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing. 50(8), 3053–3065 (2012)
Liang, J.-W., Zhang, X.-Q.: Retinex by higher order total variation l1 decomposition. J. Math. Imag. Vis. 52(3), 345–355 (2015)
Murty, K.: Linear complementarity, linear and nonlinear programming. Heldermann, Berlin (1988)
Morel, J.M., Petro, A.B., Sbert, C.: A PDE formalization of Retinex theory. IEEE Trans. Imag. Process. 19(11), 2825–2837 (2010)
Mittal, A., Soundararajan, R., Bovik, A.C.: Making a “Completely Blind” image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 20(3), 209–212 (2013)
Ng, M.K., Wang, W.: A total variation model for Retinex. SIAM J. Imag. Sci. 4(1), 345–365 (2011)
Rahman, Z., Jobson, D.J., Woodell, G.A.: Retinex processing for automatic image enhancement. J. Electron. Imag. 13(1), 100–110 (2004)
Wang, W., He, C.-J.: A variational model with barrier functionals for Retinex. SIAM J. Imag. Sci. 8(3), 1955–1980 (2015)
Yang, X., Huang, Y.-M., Sun, L.: A modulus iteration method for Retinex problem. Numer. Linear Algebra Appl. 25(6), 1–12 (2018)
Zhang, L.-L.: Two-step modulus-based matrix splitting iteration method for linear complementarity problems. Numer. Algorithms 57(1), 83–99 (2011)
Zosso, D., Tran, G., Osher, S.J.: Non-local Retinex—a unifying framework and beyond. SIAM J. Imag. Sci. 8(2), 787–826 (2015)
Funding
Fang Chen and Yu Zhu were supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 11501038) and the Science and Technology Planning Projects of Beijing Municipal Education Commission (No. KM201911232010 and No. KM202011232019), P.R. China. Galina V. Muratova was supported by The Grant of the Government of the Russian Federation (No. 075-15-2019-1928).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, F., Zhu, Y. & Muratova, G.V. Two-step modulus-based matrix splitting iteration methods for retinex problem. Numer Algor 88, 1989–2005 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-021-01103-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-021-01103-y