Abstract
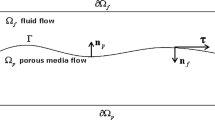
This paper considers the robust numerical methods for solving the time-dependent Stokes-Darcy multiphysics problem that can be implemented by use of existing surface water and groundwater codes. Porous media problem for the groundwater flow is preferable to employ the mixed discretization due to their superior conservation property and the convenience to compute flux on the large domain with relatively coarse meshes. However, the theory of mixed spatial discretizations for the time-dependent problems is far less developed than the non-mixed approaches, even for the one domain problems. Herein, we develop a stabilized mixed discretization technique for the porous media problem coupled with the fluid region across an interface with the physically appropriate coupling conditions. Time discretization is constructed to allow a non-iterative splitting of the coupled problem into two subproblems. The stability and convergence analysis of the coupled and decoupled algorithms are derived rigorously. If the time scale is bounded by a constant which only depends on the physical parameters, we prove the unconditional stability of both schemes. Four numerical experiments are conducted to show the efficiency and accuracy of the numerical methods, which illustrate the exclusive features of the Stokes-Darcy interface system.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable
Code availability
Not applicable
References
Layton, W.J., Schieweck, F., Yotov, I.: Coupling fluid flow with porous media flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 40(6), 2195–2218 (2003)
Jäger, W., Mikelic, M.: On the interface boundary condition of Beavers, Joseph and Saffman. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 60(4), 1111–1127 (2000)
Discacciati, M., Miglio, E., Quarteroni, A.: Mathematical and numerical models for coupling surface and groundwater flows. Appl. Numer. Math. 43, 57–74 (2001)
Payne, L.E., Song, J.C., Straughan, B.: Continuous dependence and convergence results for Brinkman and Forcheimer models with variable viscosity. Proc. Royal Soc, London A 455, 2173–2190 (1999)
Payne, L.E., Straughan, B.: Analysis of the boundary condition at the interface between a viscous fluid and a porous medium and related modeling questions. J. Math. Pure Appl. 77, 1959–1977 (1998)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., Hu, X., Hua, F., Wang, X., Zhao, W.: Finite element approximations for Stokes-Darcy flow with Beavers-Joseph interface conditions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47, 4239–4256 (2010)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., He, X.-M., Wang, X.: Robin-robin domain decomposition methods for the steady Stokes-Darcy model with Beaver-Joseph interface condition. Numer. Math. 117, 601–629 (2011)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., He, X.-M., Wang, X.: Parallel, non-iterative, multi-physics domain decomposition methods for time-dependent Stokes-Darcy systems. Math. Comput. 83, 1617–1644 (2014)
He, X. -M., Li, J., Liu, Y.P., Ming, J.: A domain decomposition method for the steady-state Navier-Stokes-Darcy model with the Beavers-Joseph interface condition. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 37, S264–S290 (2015)
Discacciati, M., Quarteroni, A., Valli, A.: Robin-robin domain decomposition methods for the Stokes-Darcy coupling. SIAMJ. Numer. Anal. 45, 1246–1268 (2007)
Sun, Y., Sun, W., Zheng, H.: Domain decomposition method for the fully-mixed Stokes-Darcy coupled problem 374, 113578 (2021)
Mu, M., Xu, J.: A two-grid method of a mixed Stokes-Darcy model for coupling fluid flow with porous media flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45, 1801–1813 (2007)
Zuo, L., Hou, Y.: A decoupling two-grid algorithm for the mixed Stokes-Darcy model with the Beavers-Joseph interface condition. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 30, 1066–1082 (2014)
Cai, M., Mu, M.: A multilevel decoupled method for a mixed Stokes/Darcy model. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 236, 2452–2465 (2012)
Cai, M., Mu, M., Xu, J.: Numerical solution to a mixed Navier-Stokes/Darcy model by the two-grid approach. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47, 3325–3338 (2009)
Du, G., Li, Q., Zhang, Y.: A two-grid method with backtracking for the mixed Navier-Stokes/Darcy model. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 36(6), 1601–1610 (2020)
Nasu, N.J., Mahbub, M.A.A., Hussain, S., Zheng, H.: Two-grid finite element method for the dual-permeability-Stokes fluid flow model. Numer. Algo. 88, 1703–1731 (2021)
Sun, Y., Shi, F., Zheng, H., Li, H., Wang, F.: Two-grid domain decomposition methods for the coupled Stokes-Darcy system. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 385, 114041 (2021)
Gatica, G.N., Heuer, N., Meddahi, S.: On the numerical analysis of nonlinear twofold saddle point problems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 23(2), 301–330 (2003)
Gatica, G.N., Oyarzúa, R., Sayas, F. -J.: Convergence of a family of Galerkin discretizations for the Stokes-Darcy coupled problem. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 27(3), 721–748 (2011)
Gatica, G.N., Oyarzúa, R., Sayas, F. -J.: Analysis of fully-mixed finite element methods for the Stokes-Darcy coupled problem. Math. Comput. 80(276), 1911–1948 (2011)
Du, G., Zuo, L.: Local and parallel finite element method for the mixed Navier-Stokes/Darcy model with Beavers-Joseph interface conditions. Acta Math. Sci. 37(5), 1331–1347 (2017)
Layton, W., Tran, H., Trenchea, S.: Analysis of long time stability and errors of two partitioned methods for uncoupling evolutionary groundwater-surface water flows. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51(1), 248–272 (2013)
Kubacki, M.: Uncoupling evolutionary groundwater-surface water flows using the Crank-Nicolson Leapfrog method. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 29(03), 1192–1216 (2013)
Mu, M., Zhu, X.: Decoupled schemes for a non-stationary mixed Stokes-Darcy model. Math. Comput. 79(270), 707–731 (2010)
Shan, L., Zhang, Y.: Error estimates of the partitioned time stepping method for the evolutionary Stokes-Darcy flows. Comput Math. Appl. 73(4), 713–726 (2017)
Shan, L., Zheng, H.: Partitioned time stepping method for fully evolutionary Stokes-Darcy flow with Beavers-Joseph interface conditions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51, 813–839 (2013)
Connors, J., Howell, J.S., Layton, W.: Partitioned time stepping methods for a parabolic two-domain problem. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47(5), 3526–3549 (2009)
Connors, J., Howell, J.S., Layton, W.: Decoupled time stepping methods for fluid-fluid interaction. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50(3), 1297–1319 (2012)
Shan, L., Zheng, H., Layton, W.J.: A decoupling method with different subdomain time steps for the nonstationary Stokes-Darcy model. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 29(2), 549–583 (2013)
Qin, Y., Hou, Y., Pei, W., Li, J.: A variable time-stepping algorithm for the unsteady Stokes/Darcy model. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 394, 113521 (2021)
Rybak, I., Magiera, J.: A multiple-time-step technique for coupled free flow and porous medium systems. J. Comput. Phys. 272, 327–342 (2014)
Li, Y., Hou, Y.: A second-order partitioned method with different subdomain time steps for the evolutionary Stokes-Darcy system. Numer Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 41(5), 2178–2208 (2018)
Qin, Y., Hou, Y.: The time filter for the non-stationary coupled Stokes/Darcy model. Appl. Numer. Math. 146, 260–275 (2019)
Lai, M.-C., Shiue, M.-C., Ong, K.C.: A simple projection method for the coupled Navier-Stokes and Darcy flows. Comput. Geosci. 23, 21–33 (2019)
Wang, Y., Li, S., Si, Z.: A second order in time incremental pressure correction finite element method for the Navier-Stokes/Darcy problem. ESAIM: M2AN 52(4), 1477–1500 (2018)
Li, J., Yao, M., Mahbub, M.A.A., Zheng, H.: The efficient rotational pressure-correction schemes for the coupling Stokes/Darcy problem. Comput. Math. Appl. 79(2), 337–353 (2020)
Girault, V., Rivière, B.: DG approximation of coupled Navier-Stokes and Darcy equations by Beaver-Joseph-Saffman interface condition. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47, 2052–2089 (2009)
Lipnikov, K., Vassilev, D., Yotov, I.: Discontinuous Galerkin and mimetic finite difference methods for coupled Stokes-Darcy flows on polygonal and polyhedral grids. Numer Math. 126, 321–360 (2014)
Rivière, B.: Analysis of a discontinuous finite element method for coupled Stokes and Darcy problems. J. Sci. Comput. 22-23(1-3), 479–500 (2005)
Gatica, G.N., Sequeira, F.A.: Analysis of the HDG method for the Stokes-Darcy coupling. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 33(3), 885–917 (2017)
Egger, H., Waluga, C.: A Hybrid Discontinuous Galerkin Method for Darcy-Stokes Problems. In: Bank, R., Holst, M., Widlund, O., Xu, J. (eds.) Domain decomposition methods in science and engineering xx. lecture notes in computational science and engineering, vol. 91. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Igreja, I., Loula, A.F.D.: A stabilized hybrid mixed DGFEM naturally coupling Stokes-Darcy flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 339, 739–768 (2018)
Camaño, J., Gatica, G.N., Oyarzúa, R., Ruiz-Baier, R., Venegas, P.: New fully-mixed finite element methods for the Stokes-Darcy coupling. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 295, 362–395 (2015)
Yu, J., Mahbub, M.A.A., Shi, F., Zheng, H.: Stabilized finite element method for the stationary mixed Stokes-Darcy problem. Adv. Diff. Equa., vol. 46, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-018-1809-2 (2018)
Mahbub, M.A.A., He, X. -M., Nasu, N.J., Qiu, C., Zheng, H.: Coupled and decoupled stabilized mixed finite element methods for non-stationary dual-porosity-Stokes fluid flow model. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 120 (6), 803–830 (2019)
Mahbub, M.A.A., Shi, F., Nasu, N.J., Wang, Y., Zheng, H.: Mixed stabilized finite element method for the stationary Stokes-dual-permeability fluid flow model. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 358, 112616 (2020)
Yu, J., Sun, Y., Shi, F., Zheng, H.: Nitsche’s type stabilized finite element method for the fully mixed Stokes-Darcy problem with Beavers-Joseph conditions. ppl. Math. Lett. 110, 106588 (2020)
Yu, J., Zhang, Y.: Nitsche’s type stabilization for the fully mixed Navier-Stokes/Darcy problem. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 11(3), 1481–1493 (2021)
Burman, E., Fernández, M. A.: Stabilized explicit coupling for fluid-structure interaction using Nitsche’s method. Comptes Rendus Mathematique 345(8), 467–472 (2007)
Burman, E., Fernández, M. A.: Stabilization of explicit coupling in fluid-structure interaction involving fluid incompressibility. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 198, 766–784 (2009)
Fernández, M. A., Gerbeau, J.F., Smaldone, S.: Explicit coupling schemes for a fluid-fluid interaction problem arising in hemodynamics. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 36(6), A2557–A2583 (2014)
Blank, L., Caiazzo, A., Chouly, F., Lozinski, A., Mura, J.: Analysis of a stabilized penalty-free Nitsche method for the Brinkman, Stokes, and Darcy problems. ESAIM:, M2AN 52, 2149–2185 (2018)
Burman, E.: A penalty-free nonsymmetric Nitsche-type method for the weak imposition of boundary conditions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50(4), 1959–1981 (2012)
He, X.-M., Jiang, N., Qiu, C.: An artificial compressibility ensemble algorithm for a stochastic Stokes-Darcy model with random hydraulic conductivity and interface conditions. Int. J. Numer. Methods. Eng. 121, 712–739 (2020)
Li, Y., Hou, Y., Rong, Y.A.: Second-order artificial compression method for the evolutionary Stokes-Darcy system. Numer. Algo. 84, 1019–1048 (2020)
Lee, H., Rife, K.: Least squares approach for the time-dependent nonlinear Stokes-Darcy flow. Comput. Math. Appl. 67(10), 1806–1815 (2014)
Münzenmaier, S.: First-order system least squares for generalized-Newtonian coupled Stokes-Darc flow. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 31(4), 1150–1173 (2015)
Mohapatra, S., Dutt, P., Kumar, B.V.R., Gerritsma, M.I.: Non-conforming least-squares spectral element method for Stokes equations on non-smooth domains. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 372, 112696 (2020)
Danisch, G., Starke, G.: First-order system least-squares for Darcy-Stokes flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45(2), 731–745 (2015)
Hessari, P.: Psedospectral least square method for Stokes-Darcy equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 53(3), 1195–1213 (2015)
Li, R., Gao, Y., Li, J., Chen, Z.-X.: Discontinuous finite volume element method for a coupled nonstationary Stokes-Darcy problem. J. Sci. Comput. 74, 693–727 (2018)
Li, R., Li, J., He, X.-M., Chen, Z.-X.: Stabilized finite volume element method for a coupled Stokes-Darcy problem. Appl. Numer. Math. 133, 2–24 (2018)
Li, Y., Hou, Y., Li, R.: A stabilized finite volume method for the evolutionary Stokes-Darcy system. Comput. Math. Appl. 75(2), 596–613 (2018)
Discacciati, M.: Iterative methods for Stokes/Darcy coupling. In: Domain decomposition methods in science and engineering. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Eng. vol. 40, pp. 563–570. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Discacciati, M., Quarteroni, A.: Convergence analysis of a subdomain iterative method for the finite element approximation of the coupling of Stokes and Darcy equations. Comput. Vis. Sci. 6, 93–103 (2004)
Huang, P., Chen, J., Cai, M.: A mixed and nonconforming FEM with nonmatching meshes for a coupled Stokes-Darcy model. J. Sci. Comput. 53, 377–394 (2012)
Layton, W., Tran, H., Xiong, X.: Long time stability of four methods for splitting the evolutionary Stokes-Darcy problem into Stokes and Darcy subproblems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 236, 3198–3217 (2012)
Ervin, V.J., Jenkins, E.W., Lee, H.: Approximation of the Stokes-Darcy system by optimization. J. Sci. Comput. 59, 775–794 (2014)
Moraiti, M.: On the quasistatic approximation in the Stokes–Darcy model of groundwater-surface water flows. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 394, 796–708 (2012)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., Hua, F., Wang, X.: Coupled Stokes-Darcy model with Beavers-Joseph interface boundary conditio. Comm. Math. Sci. 8, 1–25 (2010)
Kim, M.-Y., Park, E.-J.: Fully discrete mixed finite element approximations for non-Darcy flows in porous media. Comput. Math. Appl. 38, 113–129 (1999)
Ansari, S.U., Hussain, M., Rashid, A., Mazhar, S., Ahmad, S.M.: Numerical solution and analysis of three-dimensional transient Darcy flow. Trans. Porous Med. 123, 289–305 (2018)
Bernardi, C., Maarouf, S., Yakoubi, D.: Spectral discretization of an unsteady flow through a porous solid. Calcolo 53, 659–690 (2016)
Hussain, M., Ansari, S.U., Manzoor, T., Ahmad, A., Khan, K.I.: Performance analysis of parallel stabilized mixed Galerkin method for three-dimensional transient Darcy flow using mesh reordering techniques. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 176, 621–631 (2019)
Ansari, S.U., Hussain, M., Ahmad, S.M., Rashid, A., Mazhar, S.: Stabilized mixed finite element method for transient Darcy flow. Trans. Cana. Soci. Mech. Eng. 41(1), 85–97 (2017)
Ibragimov, A., Kieu, T.T.: An expanded mixed finite element method for generalized Forchheimer flows in porous media. Comput. Math. Appl. 72, 1467–1483 (2016)
Qian, Y., Wang, F., Zhang, Y., Han, W.: A mixed discontinuous Galerkin method for an unsteady incompressible Darcy equation. Appl. Anal. 101(4), 1176–1198 (2022)
Wilfrid, H.K., Jamal, A., Mohamed, A.: A posteriori error analysis for a new fully mixed isotropic discretization of the stationary Stokes-Darcy coupled problem. Abst. Appl. Anal., (8628739), pp. 1-12 (2020)
Almonacid, J.A., Díaz, H. S., Gatica, G.N., Márquez, A.: A fully mixed finite element method for the coupling of the Stokes and Darcy-Forchheimer problems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 40(2), 1454–1502 (2020)
Caucao, S., Gatica, G.N., Oyarzúa, R., Šebestová, I.: A fully-mixed finite element method for the Navier-Stokes/Darcy coupled problem with nonlinear viscosity. J. Numer. Math. 25(2), 55–88 (2017)
Caucao, S., Gatica, G.N., Sandoval, F.: A fully-mixed finite element method for the coupling of the Navier-Stokes and Darcy-Forchheimer equations. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 37(3), 2550–2587 (2021)
Peng, H., Zhai, Q., Zhang, R., Zhang, S.: A weak Galerkin-mixed finite element method for the Stokes-Darcy problem. Sci. China Math. 64, 2357–2380 (2021)
Wang, G., Wang, F., Chen, L., He, Y.: A divergence free weak virtual element method for the Stokes-Darcy problem on general meshes. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 344, 998–1020 (2019)
Gatica, G.N., Meddahi, S., Oyarzú, R.: A conforming mixed finite-element method for the coupling of fluid flow with porous media flow. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 29, 86–108 (2009)
D’Angelo, C., Zunino, P.: Numerical approximation with Nitsche’s coupling of transient Stokes’/Darcy’s flow problems applied to hemodynamics. Appl. Numer. Math. 62, 378–395 (2012)
Zhou, G., Kashiwabara, T., Oikawa, I., Chung, E., Shiue, M.-C.: An analysis on the penalty and Nitsche’s methods for the Stokes-Darcy system with a curved interface. Appl. Numer. Math. 165, 83–118 (2021)
Zhang, J., Rui, H.: A stabilized Crouzeix-Raviart element method for coupling stokes and Darcy-Forchheimer flows. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 33(4), 1070–1094 (2017)
Fu, G., Lehrenfeld, C.: A strongly conservative hybrid DG/mixed FEM for the coupling of Stokes and Darcy flow. J. Sci. Comput. 77, 1605–1620 (2018)
Beavers, G., Joseph, D.: Boundary conditions at a naturally impermeable wall. J. Fluid Mech. 30(1), 197–207 (1967)
Saffman, P.: On the boundary condition at the surface of a porous media. Stud. Appl. Math. 50, 93–101 (1971)
Jones, I.P.: Low Reynolds number flow past a porous spherical shell. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 73, 231–238 (1973)
Adams, R.A., Fournier, J.J.F.: Sobolev spaces, 2nd edn.,Pure Appl. Mat (Amst.), vol. 140. Elsevier/Academic Press, Amsterdam (2003)
Heywood, J.G., Rannacher, R.: Finite-element approximation of the nonstationary Navier-Stokes problem. part IV: Error analysis for second-order time discretization. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 27(2), 353–384 (1990)
Arnold, D.N., Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: A stable finite element for the stokes equations. Calcolo 21, 337–344 (1984)
Brezzi, F., Douglas, J.J., Marini, L.D.: Two families of mixed elements for second order elliptic problems. Numer. Math. 47, 217–235 (1985)
Brezzi, F., Douglas, Jr.J., Fortin, M., Marini, L.D.: Efficient rectangular mixed finite elements in two and three space variables. Math. Modeling Numer. Anal. 21, 581–604 (1987)
Yu, J., Zheng, H., Shi, F., Zao, R.: Two-grid finite element method for the stabilization of mixed Stokes-Darcy model, Discrete. Contin. Dyn. Syst.-Ser. B 24(1), 387–402 (2019)
Li, R., Li, J., Chen, Z.-X., Gao, Y.L.: A stabilized finite element method based on two local Gauss integrations for a coupled Stokes-Darcy problem. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 292, 92–104 (2016)
Funding
H. Zheng is partially supported by NSF of China (Grant No. 11971174), NSF of Shanghai (Grant No. 19ZR1414300) and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant Nos. 22JC1400900, 21JC1402500, 18dz2271000). L. Shan is supported by Shantou University Scientific Research Fund for Talents (NTF21006) and Scientific Research Fund of Liaoning Provincial Education Department (LJ2020JCL009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
This paper is in final form and no version of it will be submitted for publication elsewhere.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahbub, M.A.A., Shan, L. & Zheng, H. Uncoupling evolutionary groundwater-surface water flows: stabilized mixed methods in both porous media and fluid regions. Numer Algor 92, 1837–1874 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-022-01370-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-022-01370-3
Keywords
- Stokes-Darcy coupling
- partitioned method
- stabilized mixed formulation
- Beavers-Joseph-Saffman interface condition