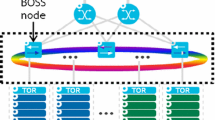
Abstract
Existing performance studies on optical burst switched (OBS) networks have been focusing on channel blocking, i.e., when the required wavelength is not available on a link along a burst’s route. However, we identify another type of blocking as the receiver blocking, i.e., when the receiver at a burst’s destination node is occupied by another burst. Receiver blocking may account for the much larger part of total burst blocking. Receiver blocking has been largely ignored in existing research. In this paper we propose using multiple receivers or fiber delay lines (FDL) in front of the receivers in order to reduce the receiver blocking probability. Extensive simulation results on bi-directional OBS rings are presented to illustrate the problem and the performance of our proposed approaches. The results indicate that receiver blocking can be almost eliminated by using as little as three receivers and can be reduced by using a FDL of small length. To our knowledge, this is the first performance study that covers both channel and receiver blocking for OBS networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battistilli T., & Perros H. (2003). An introduction to optical burst switching. IEEE Communication Magazine 41(8): S10–S15
Vokkarane, V. M., Haridoss, K., & Jue, J. P. (2002). Threshold-based burst assembly policies for qos support in optical burst-switched networks. In Proceedings of SPIE OptiComm’2002, pp. 125–136.
Wei J.Y., Mcfarland R.I. (2000) Just-in-time signalling for wdm optical burst switching network. IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Communications 18(12): 2019–2037
Turner J. (1999) Terabit burst switching. Journal of High Speed Networks 8(1): 3–16
Xiong Y., Vandenhoute M.M., Cankaya H. (2000) Control architecture in optical burst-switched WDM networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 18(10): 1838–1851
Teng, J., & Rouskas, G. N. (2003). A comparison of the jit, jet, and horizon wavelength reservation schemes on a single obs node. In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Optical Burst Switching (co-located with Opticomm 2003).
Gauger, C. M., Kohn, M., & Scharf, J. (2004). Comparison of contention resolution strategies in obs network scenarios. In Proceedings of 6th International Conference on Transport Optical Networks, Vol. 1, pp. 18–21.
Chang, J.-B., & Park, C.-S. (2002). Efficient channel-scheduling algorithm in optical burst switching architecture. In Proceedings of IEEE Workshop on High Performance Switching and Routing, pp. 194–198.
Liu, D. Q., & Liu, M. T. (2002). Differentiated services and scheduling scheme in optical burst-switched wdm networks. In Proceedings of 10th IEEE International Conference on Networks, ICON 2002, pp. 23–27.
Kozlovski, E., Duser, M., De Miguel, I., & Bayvel, P. (2001). Analysis of burst scheduling for dynamic wavelength assignment in optical burst-switched networks. In Proceedings of IEEE LEOS’01, Vol. 1, pp. 161–162.
Duser M., Bayvel P. (2002) Analysis of a dynamically wavelength-routed optical burst switched network architecture. IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology 20(4):574–585
Xu L., Perros H.G., Rouskas G.N. (2003) A simulation study of optical burst switching access protocols for wdm ring networks. Computer Networks 41(2): 143–160
Rosberg Z., Vu H.L., Zukerman M., White J. (2003) Performance analyses of optical burst-switching networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 21(7): 1187–1197
Ge A., Callegati F., Tamil L. (2000) On optical burst switching and self-similar traffic. IEEE Communications Letters 4(3): 98–100
Laevens, K. (2002). Traffic characteristics inside optical burst switched networks. In Proceedings of SPIE OptiComm’2002, pp. 137–148.
Morato, D., Izal, M., Aracil, J., Magana, E., & Miqueleiz, J. (2003). Blocking time analysis of obs routers with arbitrary burst size distribution. In Proceedings of IEEE GLOBECOM’03, Vol. 5, pp. 2488–2492.
Qiao C., Yoo M. (1999) Optical burst switching (OBS) – a new paradigm for an optical internet. Journal of High Speed Networks 8(1): 69–84
Baldine I., Rouskas G.N., Perros H.G., Stevenson D. (2002) Jumpstart: A just-in-time signaling architecture for wdm burst-switched networks. IEEE Communication Magazine 40(2): 82–89
Lu, X., & Mark, B. L. (2002). Analytical modeling of optical burst switching with fiber delay lines. In Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Modeling, Analysis, & Simulation of Computer & Telecommunications Systems, pp. 501–506.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, Y., Battestilli, L. A performance study on optical burst switched networks: the ring topology. Photon Netw Commun 14, 63–70 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-007-0061-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-007-0061-6