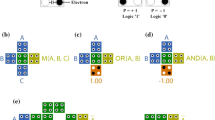
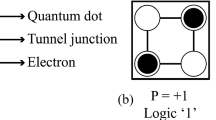
Abstract
Quantum-dot cellular automata (QCA) is a nanoscale technology to design digital circuits in nano-measure which acts based on electron’s interaction. The technology of collecting, processing and distributing information is growing rapidly, but the growth in demand for advanced methods in data processing has always been greater than the speed of growth of these technologies. Hence, computer networks play an important role in providing a resource sharing and facilitating user communications. The circuit-switched network is one of the main components for sending input signals between different users within the network. In this paper, a minimal and optimal design of the circuit-switched network is presented at a single level in QCA. The proposed design is studied and compared with existing designs in terms of fault tolerant under stuck-at 0 and 1. There is also a physical analysis for the proposed circuit-switched network.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadpour, S., Mosleh, M., Heikalabad, S.R.: Robust QCA full-adders using an efficient fault-tolerant five-input majority gate. Int. J. Circ. Theor. App. 47(7), 1037–1056 (2019)
Norouzi, A., Heikalabad, S.R.: Design of reversible parity generator and checker for the implementation of nano-communication systems in quantum-dot cellular automata. Photonic Netw. Commun. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-019-00850-2
Nejad, M.Y., Mosleh, M., Heikalabad, S.R.: An LSB-based quantum audio watermarking using MSB as arbiter. Int. J. Theor. Phys. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04251-z
Lent, C., Tougaw, P.: A device architecture for computing with quantum dots. Proc. IEEE 85(4), 541–557 (1997)
Lent, C.S., Tougaw, P.D., Porod, W.: Bistable saturation in coupled quantum dots for quantum cellular automata. Appl. Phys. Lett. 62(7), 714–716 (1993)
Roohi, A., DeMara, R.F., Khoshavi, N.: Design and evaluation of anultra-area-efficientfault-tolerant QCA full adder. Microelectron. J. 46(6), 531–542 (2015)
Milad, B., Mahya, S., Alireza, A., Keivan, N., Nader, B.: A 3D universal structure based on molecular-QCA and CNT technologies. J. Mol. Struct. 1119(5), 86–95 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.04.025
Mohammad, M., Majid, M., Saeid, G.: An efficient design of full adder in quantum-dot cellular automata (QCA) technology. Microelectron. J. 50, 35–43 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2016.02.004
Heikalabad, S.R., Navin, A.H., Hosseinzadeh, M.: Midpoint memory: a special memory structure for data-oriented models implementation. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 24(5), 1550063 (2015)
Heikalabad, S.R., Navin, A.H., Hosseinzadeh, M.: Content addressable memory cell in quantum-dot cellular automata. Microelectron. Eng. 163, 140–150 (2016)
Karkaj, E.T., Heikalabad, S.R.: Binary to gray and gray to binary converter in quantum-dot cellular automata. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron. Opt. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.11.087
Karkaj, E.T., Heikalabad, S.R.: A testable parity conservative gate in quantum-dot cellular automata. Superlattices Microstruct. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2016.08.054
Gadim, M.R., Navimipour, N.J.: A new three-level fault tolerance arithmetic and logic unit based on quantum dot cellular automata. Microsyst. Technol. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3502-x
Heikalabad, S.R., Asfestani, M.N., Hosseinzadeh, M.: A full adder structure without crosswiring in quantum-dot cellular automata with energy dissipation analysis. J. Supercomput. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-017-2206-4
Barughi, Y.Z., Heikalabad, S.R.: A three-layer full adder/subtractor structure in quantum-dot cellular automata. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56, 2848 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-017-3453-0
Rad, S.K., Heikalabad, S.R.: Reversible flip-flops in quantum-dot cellular automata. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56, 2990 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-017-3466-8
Sadoghifar, A., Heikalabad, S.R.: A content-addressable memory structure using quantum cells in nanotechnology with energy dissipation analysis. Phys. B Condens. Matter 537, 202–206 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.02.024
Asfestani, M.N., Heikalabad, S.R.: A unique structure for the multiplexer in quantum dot cellular automata to create a revolution. Phys. B Condens. Matter 512, 91–99 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2017.02.028
Babaie, S., Sadoghifar, A., Bahar, A.N.: Design of an efficient multilayer arithmetic logic unit in quantum-dot cellular automata (QCA). IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 66, 963–967 (2018)
Salimzadeh, F., Heikalabad, S.R.: Design of a novel reversible structure for full adder/subtractor in quantum-dot cellular automata. Phys. B Phys. Condens. Matter (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.12.028
Heikalabad, S.R., Gadim, M.R.: Design of improved arithmetic logic unit in quantum-dot cellular automata. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(6), 1733–1747 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3699-1
Kamrani, S., Heikalabad, S.R.: A unique reversible gate in quantum-dot cellular automata for implementation of four flip-flops without garbage outputs. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(11), 3340–3358 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3847-7
Ahmadpour, S.S., Mosleh, M., Heikalabad, S.R.: A revolution in nanostructure designs by proposing a novel QCA full-adder based on optimized 3-input XOR. Phys. B 550, 383–392 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.09.029
Mariam, Z., Keivan, N.: Ultra-area-efficient reversible multiplier. Microelectron. J. 43(6), 377–385 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2012.02.004
Basu, S.: Realization of combinational multiplier using quantum cellular automata. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 99(19), 1–6 (2014)
Cho, H., Swartzlander Jr., E.E.: Adder and multiplier design in quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans. Comput. 58(6), 721–727 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TC.2009.21
Dharmendra, K., Debasis, M.: Design of a practical fault-tolerant adder in QCA. Microelectron. J. 53, 90–104 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2016.04.004
Trailokya, N., Ashutosh, K., Anand, M.: An optimal design of full adder based on 5-input majority gate in coplanar quantum-dot cellular automata. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 127(20), 8576–8591 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.06.034
Firdous, A.G., Hossein, K., Saeid, A., Shaahin, A., Keivan, N.: Towards single layer quantum-dot cellular automata adders based on explicit interaction of cells. J. Comput. Sci. 16, 8–15 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2016.02.005
Kianpour, M., Sabbaghi-Nadooshan, R., Navi, K.: A novel design of 8-bit adder/subtractor by quantum-dot cellular automata. J Comput Syst Sci. 80(7), 1404–1414 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcss.2014.04.012
Das, J.C., De, D.: Circuit switching with quantum-dot cellular automata. Nano Commun. Netw. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nancom.2017.09.002
Asfestani, M.N., Heikalabad, S.R.: A novel multiplexer-based structure for random access memory cell in quantum-dot cellular automata. Phys. B Condens. Matter 521, 162–167 (2017)
Sen, B., Sahu, Y., Mukherjee, R., Nath, R.K., Sikdar, B.K.: on the reliability of majority logic structure in quantum-dot cellular automata. Microelectron. J. 47, 7–18 (2016)
Hosseinzadeh, H., Heikalabad, S.R.: A novel fault tolerant majority gate in quantum-dot cellular automata to create a revolution in design of fault tolerant nanostructures, with physical verification. Microelectron. Eng. 192, 52–60 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2018.01.019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heikalabad, S.R., Kamrani, H. Design and implementation of circuit-switched network based on nanoscale quantum-dot cellular automata. Photon Netw Commun 38, 356–377 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-019-00864-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-019-00864-w