Abstract
The effect of variable entangling on the dynamics of a spatial quantum formulation of the iterated prisoner’s dilemma game is studied in this work. The game is played in the cellular automata manner, i.e., with local and synchronous interaction. The effect of spatial structure is assessed when allowing the players to adopt quantum and classical strategies, both in the two- and three-parameter strategy spaces.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Cellular automata are spatially extended dynamical systems that are discrete in all their constitutional components: space, time and state-variable. Uniform, local and synchronous interactions, as assumed here, are landmark features of CA [34].
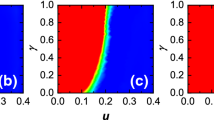
Provided that \(P-S \le \mathfrak {T}-R\), the critical values are to be: \(\gamma ^*= \arcsin \big (\sqrt{\displaystyle \frac{P-S}{\mathfrak {T}-S}}\big )\), and \(\gamma ^+= \arcsin \big (\sqrt{\displaystyle \frac{\mathfrak {T}-R}{\mathfrak {T}-S}}\big )\). Thus, (0.524,0.785) with the (5,3,2,1)-PD parameters, and \(\gamma ^*=\gamma ^+=0.616\) with the (4,3,2,1)-PD parameters.
The reference [14] is also relevant in this respect, but the occasional reader should be warned about the variation of the \(\alpha \) and \(\beta \) parameters in the \([-\pi ,\pi ]\) interval instead of in \([0,\pi /2]\), as proposed for \(\alpha \) in the seminal EWL paper.
References
Alonso-Sanz, R.: A quantum prisoner’s dilemma cellular automaton. Proc. R. Soc. A 470, 20130793 (2014)
Alonso-Sanz, R.: On a three-parameter quantum battle of the sexes cellular automaton. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(5), 1835–1850 (2013)
Alonso-Sanz, R.: A quantum battle of the sexes cellular automaton. Proc. R. Soc. A 468, 3370–3383 (2012)
Alonso-Sanz, R.: Dynamical Systems with Memory. World Scientific Pub., Singapore (2011)
Benjamin, S.C., Hayden, P.M.: Comment on “quantum games and quantum strategies”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87(6), 069801 (2001)
Binmore, K.: Fun and Games. D.C.Heath, Lexington (1992)
Bleiler, S. : A Formalism for Quantum Games and an Application. http://arxiv.org/abs/0808.1389 (2008)
Branderburger, A.: The relationship between quantum and classical correlation games. Games Econ. Behav. 89, 157–183 (2010)
Du, J.F., Xu, X.D., Li, H., Zhou, X., Han, R., et al.: Entanglement playing a dominating role in quantum games. Phys. Lett. A 289(1–2), 9–15 (2001)
Du, J.F., Li, H., Xu, X.D., Zhou, X., Han, R.: Phase-transition-like behaviour of quantum games. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 36(23), 6551–6562 (2003)
Du, J.F., Xu, X.D., Li, H., Zhou, X., Han, R.: Entanglement enhanced multiplayer quantum games. Phys. Lett. A 302, 222–233 (2002)
Eisert, J., Wilkens, M., Lewenstein, M.: Quantum games and quantum strategies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83(15), 3077–3080 (1999)
Eisert, J., Wilkens, M.: Quantum games. J. Mod. Opt. 47(14–15), 2543–2556 (2000)
Flitney, A.P., Hollenberg, L.C.L.: Nash equilibria in quantum games with generalized two-parameter strategies. Phys. Lett. A 363, 381–388 (2007)
Flitney, A.P., Abbott, D.: Advantage of a quantum player over a classical one in 2x2 quantum games. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 459(2038), 2463–2474 (2003)
Flitney A.P., Abbott, D.: An introduction to quantum game theory. Fluct. Noise Lett. 02, R175. http://arxiv.org/pdf/quant-ph/0208069 (2002)
Khan, F.S., Phoenix, S.J.D.: Gaming the quantum. Quantum Inf. Comput. 13(3–4), 231–244. http://arxiv.org/pdf/1202.1142 (2013)
Landsburg, S.E.: Quantum game theory. In: The Wiley Encyclopedia of Operations Research and Management Science. http://arxiv.org/pdf/1110.6237v1 (2011)
Landsburg, S.E.: Quantum game theory. Not. AMS. http://www.ams.org/notices/200404/fea-landsburg (2004)
Levine, D.K. : Quantum Games Have No News for Economists. http://levine.sscnet.ucla.edu/papers/quantumnonews (2005)
Li, Q., Iqbal, A., Perc, M., Chen, M., Abbott, D.: Coevolution of quantum and classical strategies on evolving random networks. PloS One 8(7), e68423 (2013)
Li, Q., Iqbal, A., Chen, M., Abbott, D.: Quantum strategies win in a defector-dominated population. Physica A 391, 3316–3322 (2012)
Li, Q., Iqbal, A., Chen, M., Abbott, D.: Evolution of quantum and classical strategies on networks by group interactions. New J. Phys. 14(10), 103034 (2012)
Marinatto, L., Weber, T.: A quantum approach to static games of complete information. Phys. Lett. A 272, 291–303 (2000)
Meyer, D.A.: Quantum strategies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 1052–1055 (1999)
Miszczak, J.A., Pawela, L., Sladkowski, J. : General model for an entanglement-enhanced composed quantum game on a two-dimensional lattice. Fluct. Noise Lett. 13(2), 1450012. http://arxiv.org/abs/1306.4506 (2014)
Nawaz, A., Toor, A.H.: Dilemma and quantum battle of sexes. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 37(15), 4437–4443 (2004)
Nawaz, A., Toor, A.H.: Generalized quantization scheme for two-person non-zero sum games. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 37(42), 365305 (2004)
Nowak, N.M., May, R.M.: Evolutionary games and spatial chaos. Nature 359, 826–829 (1992)
Nowak, M.A., May, R.M.: The spatial dilemmas of evolution. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 3(11), 35–78 (1993)
Owen, G.: Game Theory. Academic Press, Waltham (1995)
Phoenix, S.J.D., Khan, F.S.: The role of correlations in classical and quantum games. Fluct. Noise Lett. 12(3), 1350011 (2013)
Piotrowski, E.W., Sladkowski, J.: An invitation to quantum game theory. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 42(5), 1089–1099 (2003)
Schiff, J.L.: Cellular Automata: A Discrete View of the World. Wiley, New York (2008)
Wiesner, K.: Quantum Cellular automata. Encycl. Complex. Syst. Sci., 7154–7164. http://arxiv.org/abs/0808.0679 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Spanish Grant M2012-39101-C02-01. Part of the computations of this work were performed in EOLO and FISWULF, HPC machines of the International Campus of Excellence of Moncloa, funded by the Spanish Government and Feder Funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alonso-Sanz, R. Variable entangling in a quantum prisoner’s dilemma cellular automaton. Quantum Inf Process 14, 147–164 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0834-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0834-7