Abstract
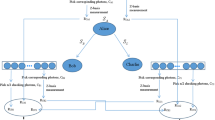
After analyzing Yang’s verifiable quantum secret sharing (VQSS) scheme, we show that in their scheme a participant can prepare a false quantum particle sequence corresponding to a forged share, while other any participant cannot trace it. In addition, an attacker or a participant can forge a new quantum sequence by transforming an intercepted quantum sequence; moreover, the forged sequence can pass the verification of other participants. So we propose a new VQSS scheme to improve the existed one. In the improved scheme, we construct an identity-based quantum signature encryption algorithm, which ensures chosen plaintext attack security of the shares and their signatures transmitted in the quantum tunnel. We employ dual quantum signature and one-way function to trace against forgery and repudiation of the deceivers (dealer or participants). Furthermore, we add the reconstruction process of quantum secret and prove the security property against superposition attack in this process.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shamir, A.: How to share a secret. Commun. ACM 22(11), 612–613 (1979)
Hillery, M., Buzek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829 (1999)
Zheng, S.B.: Splitting quantum information via W states. Phys. Rev. A 74, 054303 (2006)
Nie, Y.Y., Sang, M.H., Li, Y.H., Liu, J.C.: Three-party quantum information splitting of an arbitrary two-qubit state by using six-qubit cluster state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50(5), 1367–1371 (2011)
Paul, N., Menon, J.V., Karumanchi, S., Muralidharan, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Quantum tasks using six qubit cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 10, 619–632 (2011)
Hsu, L.-Y.: Quantum secret-sharing protocol based on Grover’s algorithm. Phys. Rev. A 68(2), 022306 (2003)
Hao, L., Li, J.-L., Long, G.-L.: Eavesdropping in a quantum secret sharing protocol based on Grover algorithm and its solution. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 53(3), 491–495 (2010)
Cleve, R., Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K.: How to share a quantum secret. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 648 (1999)
Lai, H., Orgun, A.M., Xiao, J.H., Pieprzyk, J.: Dynamic (2, 3) threshold quantum secret sharing of secure direct communication. Commun. Theor. Phys. 63(4), 459–465 (2015)
Markham, D., Sanders, B.C.: Graph states for quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 78, 42309 (2008)
Keet, A., Fortescue, B., Markham, D., Sanders, B.C.: Quantum secret sharing with qudit graph states. Phys. Rev. A 82, 62315 (2010)
Chor, B., Goldwasser, S., Micali, S., Awerbuch, B.: Verifiable secret sharing and achieving simultaneity in the presence of faults. In: The 26th IEEE Symposium on Foundations of computer science, pp. 383–395 (1985)
Yang, Y.G., Teng, Y.W., Chai, H.P., Wen, Q.Y.: Verifiable quantum \((k, n)\)-threshold secret key sharing. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50(3), 792–798 (2011)
Gottesman, D., Chuang, I.: Quantum Digital Signatures. Technical Report. http://arxiv.org/abs/quant-ph/0105032 (2001)
Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia: Quantum Digital Signature. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantum_digital_signature#Quantum_Digital_Signature
Boneh, D., and Zhandry, M.: Secure signatures and chosen ciphertext security in a post-quantum world. In: The 33rd Annual Cryptology Conference, pp. 361–379 (2013)
Lü, X., Feng, D.G.: Quantum digital signature based on quantum one-way functions. In: The 7th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology, pp. 514–517 (2005)
Buhrman, H., Cleve, R., Watrous, J., Wolf, R.D.: Quantum fingerprinting. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87(16), 175–196 (2001)
Gentry, C., Peikert, C., Vaikuntanathan, V.: Trapdoors for hard lattices and new cryptographic constructions. Electron. Colloq. Comput. Complex. 14, 197–206 (2008)
Agrawal, S., Dan, B., Boyen, X.: Efficient lattice (H)IBE in the standard model. In: Advances in Cryptology - EUROCRYPT 2010, pp. 553–572 (2010)
Zhandry, M.: Secure identity-based encryption in the quantum random oracle model. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 7417, 758–775 (2015)
Li, Q., Long, D.Y., Chan, W.H., Qiu, D.W.: Sharing a quantum secret without a trusted party. Quantum Inf. Process. 10(1), 97–106 (2011)
Hwang, W.Y.: Quantum key distribution with high loss: toward global secure communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91(5), 508–508 (2003)
Somma, R.D., Hughes, R.J.: Security of decoy-state protocols for general photon-number-splitting attacks. Phys. Rev. A. 87(6), 1993–2001 (2013)
Zou, X., Qiu, D.: Attack and improvements of fair quantum blind signature schemes. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(6), 2071–2085 (2013)
Lin, S., Yu, C.H., Guo, G.D.: Reexamining the security of fair quantum blind signature schemes. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(11), 2407–2415 (2014)
Zhang, P., Matsumoto, R.: Quantum strongly secure ramp secret sharing. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(2), 715–729 (2014)
Zeng, G.H. (2008) Reply to “comment on ‘arbitrated quantum-signature scheme’ ”. Phys. Rev. A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.78.016301
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Guo, F.Z., Wen, Q.Y.: Cryptanalysis of the arbitrated quantum signature protocols. Phys. Rev. A 84(2), 022344 (2011)
Damgard, I., Funder, J., Nielsen, J.B., et al.: Superposition attacks on cryptographic protocols. In: The 7th International Conference on Information Theoretic Security, pp. 142–161 (2013)
Ogawa, T., Sasaki, A., Iwamoto, M., Yamamoto, H.: Quantum secret sharing schemes and reversibility of quantum operations. Phys. Rev. A 72(3), 032318 (2005)
Acknowledgments
This work is partially supported by Program for Innovation Team Building at Institutions of Higher Education in Chongqing under Grant No. KJTD201310, National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61272400, and Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing Science & Technology Commission of China under Grant No. cstc2014jcyjA40028.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Liu, Y. Cryptanalysis and improvement of verifiable quantum (k, n) secret sharing. Quantum Inf Process 15, 851–868 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-015-1199-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-015-1199-2