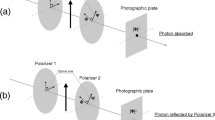
Abstract
In this paper, two schemes for joint remote preparation via linear optics elements are proposed. Firstly, we propose a scheme for joint remote preparation of an arbitrary two-photon state via linear-optical elements by using a five-qubit cluster state as the quantum channel. Then, the JRSP protocol of an arbitrary three-photon state via linear-optical elements, which was rarely considered in previous papers, is investigated. All the senders share the information of prepared state. The senders transform the quantum channel to the target quantum channel according to their information of prepared state, and the receiver can prepare the original state by performing corresponding operations on his entangled particles. Our scheme has advantage of transmitting less particles for joint remote preparing an arbitrary two-qubit state. Moreover, it is more convenience in application since it only requires linear-optical elements for joint remote preparation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Wiesner, S.J.: Communication via one-and two-particle operators on Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69(20), 2881 (1992)
Liu, X.S., Long, G.L., Tong, D.M., et al.: General scheme for superdense coding between multiparties. Phys. Rev. A 65(2), 022304 (2002)
Barreiro, J.T., Wei, T.C., Kwiat, P.G.: Beating the channel capacity limit for linear photonic superdense coding. Nat. Phys. 4(4), 282 (2008)
Liu, D.: Controlled dense coding with six-particle nonmaximal graph state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54(8), 2748 (2015)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bells theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67(6), 661 (1991)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Mermin, N.D.: Quantum cryptography without Bells theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68(5), 557 (1992)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Controlled order rearrangement encryption for quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 68(4), 042315 (2003)
Li, X.H., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Efficient quantum key distribution over a collective noise channel. Phys. Rev. A 78(2), 022321 (2008)
Hillery, M., Buzek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59(3), 1829 (1999)
Karlsson, A., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Quantum entanglement for secret sharing and secret splitting. Phys. Rev. A 59(1), 162 (1999)
Xiao, L., Long, G.L., Deng, F.G., Pan, J.W.: Efficient multiparty quantum-secret-sharing schemes. Phys. Rev. A 69(5), 052307 (2004)
Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y., Long, G.L.: Circular quantum secret sharing. J. Phys. A 39(45), 14089 (2006)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65(3), 032302 (2002)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68(4), 042317 (2003)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Secure direct communication with a quantum one-time-pad. Phys. Rev. A 69(5), 052319 (2004)
Wang, C., Deng, F.G., Li, Y.S., Liu, X.S., Long, G.L.: Quantum secure direct communication with high-dimension quantum superdense coding. Phys. Rev. A 71(4), 044305 (2005)
Bouda, J., Buzek, V.: Entanglement swapping between multi-qudit systems. J. Phys. A 34(20), 4301 (2001)
Bose, S., Vedral, V., Knight, P.L.: Multiparticle generalization of entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. A 57(2), 822 (1998)
Takeda, S., Fuwa, M., van Loock, P., Furusawa, A.: Entanglement swapping between discrete and continuous variables. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114(10), 100501 (2015)
Jin, R.B., Takeoka, M., Takagi, U., Shimizu, R., Sasaki, M.: Highly efficient entanglement swapping and teleportation at telecom wavelength. Sci. Rep. (2015). doi:10.1038/srep09333
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crpeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70(13), 1895 (1993)
Bouwmeester, D., Pan, J.W., Mattle, K., Eibl, M., Weinfurter, H., Zeilinger, A.: Experimental quantum teleportation. Nature 390(6660), 575 (1997)
Chen, Y.A., Chen, S., Yuan, Z.S., Zhao, B., Chuu, C.S., Schmiedmayer, J., Pan, J.W.: Memory-built-in quantum teleportation with photonic and atomic qubits. Nat. Phys. 4(2), 103 (2008)
Olmschenk, S., Matsukevich, D.N., Maunz, P., Hayes, D., Duan, L.M., Monroe, C.: Quantum teleportation between distant matter qubits. Science 323(5913), 486 (2009)
Xiao, X., Yao, Y., Zhong, W.J., Li, Y.L., Xie, Y.M.: Enhancing teleportation of quantum Fisher information by partial measurements. Phys. Rev. A 93(1), 012307 (2016)
Karlsson, A., Bourennane, M.: Quantum teleportation using three-particle entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 58(6), 4394 (1998)
Deng, F.G., Li, C.Y., Li, Y.S., et al.: Symmetric multiparty-controlled teleportation of an arbitrary two-particle entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 72(2), 022338 (2005)
Deng, F.G., Li, X.H., Li, C.Y., et al.: Multiparty quantum-state sharing of an arbitrary two-particle state with Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pairs. Phys. Rev. A 72(4), 044301 (2005)
Long, L.R., Li, H.W., Zhou, P., Fan, C., Yin, C.L.: Multiparty-controlled teleportation of an arbitrary GHZ- class state by using a d-dimensional (N+2)- particle nonmaximally entangled state as the quantum channel. Sci. China Ser. G Phys. Mech. Astron. 54(3), 484 (2011)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B., Smolin, J.A., Wootters, W.K.: Purification of noisy entanglement and faithful teleportation via noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76(5), 722 (1996)
Deutsch, D., Ekert, A., Jozsa, R., Macchiavello, C., Popescu, S., Sanpera, A.: Quantum privacy amplification and the security of quantum cryptography over noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(13), 2818 (1996)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G.: Deterministic entanglement purification and complete nonlocal Bell-state analysis with hyperentanglement. Phys. Rev. A 81(3), 032307 (2010)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G.: One-step deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 82(4), 044305 (2010)
Li, X.H.: Deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 82(4), 044304 (2010)
Deng, F.G.: One-step error correction for multipartite polarization entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 83(6), 062316 (2011)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L.: Deterministic polarization entanglement purification using time-bin entanglement. Laser Phys. Lett. 11(8), 085203 (2014)
Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Jin, G.: Entanglement purification and concentration of electron-spin entangled states using quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Phys. Rev. A 84(3), 032307 (2011)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Zhao, S.M.: Efficient two-step entanglement concentration for arbitrary W states. Phys. Rev. A 85(4), 042302 (2012)
Ren, B.C., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement purification and concentration assisted by diamond NV centers inside photonic crystal cavities. Laser. Phys. Lett. 10(11), 115201 (2013)
Ren, B.C., Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: Two-step hyperentanglement purification with the quantum-state-joining method. Phys. Rev. A 90(5), 052309 (2014)
Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Jin, G.S.: Polarization-entanglement purification and concentration using cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Quantum Inf. Comput. 11(11–12), 988 (2011)
Li, X.H., Ghose, S.: Efficient hyperconcentration of nonlocal multipartite entanglement via the cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Opt. Express 23(3), 3550 (2015)
Li, T., Deng, F.G.: Heralded high-efficiency quantum repeater with atomic ensembles assisted by faithful single-photon transmission. Sci. Rep. 5, 15610 (2015)
Wang, T.J., Liu, L.L., Zhang, R., Cao, C., Wang, C.: One-step hyperentanglement purification and hyperdistillation with linear optics. Opt. Express 23(7), 9284 (2015)
Shor, P.W.: Proceedings of the 35th Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, p. 124 (1994)
Feng, G.R., Xu, G.F., Long, G.L.: Experimental realization of nonadiabatic holonomic quantum computation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(19), 190501 (2013)
Ren, B.C., Deng, F.G.: Hyper-parallel photonic quantum computation with coupled quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 4, 4623 (2014)
Ren, B.C., Wang, G.Y., Deng, F.G.: Universal hyperparallel hybrid photonic quantum gates with dipole-induced transparency in the weak-coupling regime. Phys. Rev. A 91(3), 032328 (2015)
Li, C.Y., Zhang, Z.R., Sun, S.H., Jiang, M.S., Liang, L.M.: Logic-qubit controlled-NOT gate of decoherence-free subspace with nonlinear quantum optics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30(7), 1872 (2013)
Huelga, S.F., Vaccaro, J.A., Chefles, A., Plenio, M.B.: Quantum remote control: teleportation of unitary operations. Phys. Rev. A 63(4), 042303 (2001)
Huelga, S.F., Plenio, M.B., Vaccaro, J.A.: Remote control of restricted sets of operations: teleportation of angles. Phys. Rev. A 65(4), 042316 (2002)
Zhang, Y.S., Ye, M.Y., Guo, G.C.: Conditions for optimal construction of two-qubit nonlocal gates. Phys. Rev. A 71(6), 062331 (2005)
Xing, H., Liu, Y.M., Xie, C.M., Ji, Q.B., Zhan, Z.J.: Four-party deterministic operation sharing with six-qubit cluster state. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(7), 1553 (2014)
He, Y.H., Lu, Q.C., Liao, Y.M., Qin, X.C., Qin, J.S., Zhou, P.: Bidirectional controlled remote implementation of an arbitrary single qubit unitary operation with EPR and cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54(5), 1726 (2015)
Pati, A.K.: Minimum classical bit for remote preparation and measurement of a qubit. Phys. Rev. A 63(1), 014302 (2000)
Lo, H.K.: Classical-communication cost in distributed quantum-information processing: a generalization of quantum-communication complexity. Phys. Rev. A 62(1), 012313 (2000)
Bennett, C.H., DiVincenzo, D.P., Shor, P.W., Smolin, J.A., Terhal, B.M., Wootters, W.K.: Remote state preparation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87(7), 077902 (2001)
Peng, X.H., Zhu, X.W., Fang, X.M., et al.: Experimental implementation of remote state preparation by nuclear magnetic resonance. Phys. Lett. A 306(5), 271 (2003)
Liu, W.T., Wu, W., Ou, B.Q., Chen, P.X., Li, C.Z., Yuan, J.M.: Experimental remote preparation of arbitrary photon polarization states. Phys. Rev. A 76(2), 022308 (2007)
Wu, W., Liu, W.T., Chen, P.X., Li, C.Z.: Deterministic remote preparation of pure and mixed polarization states. Phys. Rev. A 81(4), 042301 (2010)
Yan, F.L., Zhang, G.H.: Remote preparation of the two-particle state. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 6(03), 485 (2008)
Wang, D., Hu, Y.D., Wang, Z.Q., et al.: Efficient and faithful remote preparation of arbitrary three-and four-particle W-class entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(6), 2135 (2015)
Wang, D., Hoehn, R.D., Ye, L., et al.: Efficient and faithful remote preparation of arbitrary three-and four-particle W-class entangled states. Entropy 17(4), 1755 (2015)
Wang, D., Huang, A.J., Sun, W.Y., et al.: Practical single-photon-assisted remote state preparation with non-maximally entanglement. Quantum Inf. Process. (2016). doi:10.1007/s11128-016-1346-4
Nguyen, B.A.: Joint remote preparation of a general two-qubit state. J Phys. B 42(12), 125501 (2009)
Luo, M.X., Chen, X.B., Ma, S.Y., Niu, X.X., Yang, Y.X.: Joint remote preparation of an arbitrary three-qubit state. Opt. Commun. 283(23), 4796 (2010)
Xiao, X.Q., Liu, J.M., Zeng, G.: Joint remote state preparation of arbitrary two-and three-qubit states. J Phys. B 44(7), 075501 (2011)
Xia, Y., Chen, Q.Q., An, N.B.: Deterministic joint remote preparation of an arbitrary three-qubit state via Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pairs with a passive receiver. J Phys. A 45(33), 335306 (2012)
Chen, Q.Q., Xia, Y.: Joint remote preparation of an arbitrary two-qubit state via a generalized seven-qubit brown state. Laser Phys. 26(1), 015203 (2016)
Wang, D., Zha, X.W., Lan, Q.: Joint remote state preparation of arbitrary two-qubit state with six-qubit state. Opt. Commun. 284(24), 5853 (2011)
Peng, J.Y., Luo, M.X., Mo, Z.W.: Joint remote state preparation of arbitrary two-particle states via GHZ-type states. J Phys. A 12(7), 2325 (2013)
Wang, Y., Ji, X.: Deterministic joint remote state preparation of arbitrary two-and three-qubit states. Chin. Phys. B 22(2), 020306 (2013)
Zhan, Y.B., Ma, P.C.: Deterministic joint remote preparation of arbitrary two- and three-qubit entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(2), 997 (2013)
Peng, J.Y., Luo, M.X., Mo, Z.W.: Joint remote state preparation of arbitrary two-particle states via GHZ-type states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(7), 2325 (2013)
Li, H.N., Ping, Y., Pan, X.Q., et al.: Joint remote preparation of an arbitrary three-qubit state with mixed resources. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52(12), 4265 (2013)
Chen, N., Quan, X.D., Xu, F.F., et al.: Deterministic joint remote state preparation of arbitrary single- and two-qubit states. Chin. Phys. B 24(10), 100307 (2015)
Wang, Z.Y., Liu, Y.M., Zou, X.Q., Zhang, Z.J.: Controlled remote state preparation. Commun. Theor. Phys. 52(2), 235 (2009)
Chen, X.B., Ma, S.Y., Su, Y., Zhang, R., Yang, Y.X.: Controlled remote state preparation of arbitrary two and three qubit states via the Brown state. Quantum Inf. Process. 11(6), 1653 (2012)
Liao, Y.M., Qin, X.C., He, Y.H., et al.: Controlled remote preparing of an arbitrary 2-qudit state with two-particle entanglements and positive operator-valued measure. Commun. Theor. Phys. 61(3), 315 (2014)
Wang, C., Zeng, Z., Li, X.H.: Controlled remote state preparation via partially entangled quantum channel. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(3), 1077 (2015)
Wang, D., Ye, L.: Multiparty-controlled joint remote state preparation. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(10), 3223 (2013)
Chen, N., Quan, D.X., Yang, H., et al.: Deterministic controlled remote state preparation using partially entangled quantum channel. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(4), 1719 (2016)
Zhang, D., Zha, X.W., Duan, Y.J., et al.: Deterministic controlled bidirectional remote state preparation via a six-qubit entangled state. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(5), 2169 (2016)
Fan, Q.B.: Remote preparation of photon polarization states within a network. Chin. Phys. Lett. 25(1), 20 (2008)
Xia, Y., Song, J., Song, H.S., Guo, J.L.: Multiparty remote state preparation with linear optical elements. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 6(05), 1127 (2008)
Xia, Y., Song, J., Ning, Y., Lu, P.M., Song, H.S.: Remote preparation of N photon GHZ polarization entangled states within a network. JETP lett. 90(11), 735 (2010)
Lu, Q.C., Liu, D.P., He, Y.H., et al.: Linear-optics-based bidirectional controlled remote state preparation via five-photon cluster-type states for quantum communication network. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(1), 535 (2016)
Xia, Y., Song, J., Lu, P.M., et al.: Controlled teleportation of a multi-photon GHZ polarization-entangled state using linear optical elements. Eur. Phys. J. D 61(2), 493 (2011)
Ren, B.C., Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement concentration for two-photon four-qubit systems with linear optics. Phys. Rev. A 88(1), 012302 (2013)
Li, T., Deng, F.G.: Linear-optics-based entanglement concentration of four-photon \(\chi \)-type states for quantum communication network. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(9), 3026 (2014)
Liao, Y.M., Zhou, P., Qin, X.C., et al.: Efficient joint remote preparation of an arbitrary two-qubit state via cluster and cluster-type states. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(3), 615 (2014)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 11564004 and 61501129, Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi under Grant No. 2014GXNSFAA118008, Special Funds of Guangxi Distinguished Experts Construction Engineering and Xiangsihu Young Scholars and Innovative Research Team of GXUN (Min-Da 2015-13-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, RF., Lin, YJ. & Zhou, P. Joint remote preparation of arbitrary two- and three-photon state with linear-optical elements. Quantum Inf Process 15, 4785–4803 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1424-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1424-7