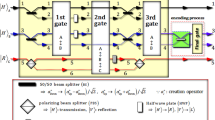
Abstract
We demonstrate the advantages of an optical parity gate using weak cross-Kerr nonlinearities (XKNLs), quantum bus (qubus) beams, and photon number resolving (PNR) measurement through our analysis, utilizing a master equation under the decoherence effect (occurred the dephasing and photon loss). To generate Bell states, parity gates based on quantum non-demolition measurement using XKNL are extensively employed in quantum information processing. When designing a parity gate via XKNL, the parity gate can be diversely constructed according to the measurement strategies. In practice, the interactions of XKNLs in optical fiber are inevitable under the decoherence effect. Thus, by our analysis of the decoherence effect, we show that the designed parity gate employing homodyne measurement would not be expected to provide reliable quantum operation. Furthermore, compared with a parity gate using a displacement operator and PNR measurement, we conclude there is experimental benefit from implementation of a parity gate via qubus beams and PNR measurement under the decoherence effect.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings, 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, vol. 124 (1994)
Loock, P.V., Munro, W.J., Nemoto, K., Spiller, T.P., Ladd, T.D., Braunstein, S.L., Milburn, G.J.: Hybrid quantum computation in quantum optics. Phys. Rev. A 78, 022303 (2008)
Lin, Q., He, B.: Addendum to single-photon logic gates using minimum resources. Phys. Rev. A 82, 064303 (2010)
Wang, H.F., Zhang, S., Zhu, A.D., Yeon, K.H.: Fast and effective implementation of discrete quantum Fourier transform via virtual-photon-induced process in separate cavities. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29, 1078 (2012)
Heo, J., Kang, M.S., Hong, C.H., Yang, H., Choi, S.G.: Discrete quantum Fourier transform using weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity and displacement operator and photon-number-resolving measurement under the decoherence effect. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 4955 (2016)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032302 (2002)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crepeau, C., Jozsa, R., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895 (1993)
Heo, J., Hong, C.H., Lee, D.H., Yang, H.J.: Bidirectional transfer of quantum information for unknown photons via cross-Kerr nonlinearity and photon-number-resolving measurement. Chin. Phys. B 25, 020306 (2016)
Liu, H., Ma, H., Wei, K., Yang, X., Qu, W., Dou, T., Chen, Y., Li, R., Zhu, W.: Multi-group dynamic quantum secret sharing with single photons. Phys. Lett. A 380, 2349 (2016)
Heo, J., Kang, M.S., Hong, C.H., Choi, S.G., Hong, J.P.: Scheme for secure swapping two unknown states of a photonic qubit and an electron-spin qubit using simultaneous quantum transmission and teleportation via quantum dots inside single-sided optical cavities. Phys. Lett. A (2017). doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2017.01.052
Ren, B.C., Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: Two-step hyperentanglement purification with the quantum-state-joining method. Phys. Rev. A 90, 052309 (2014)
Tan, X., Zhang, X.: Controlled quantum secure direct communication by entanglement distillation or generalized measurement. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 2137 (2016)
Huber, T., Ostermann, L., Prilmüller, M., Solomon, G.S., Ritsch, H., Weihs, G., Predojević, A.: Coherence and degree of time-bin entanglement from quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 93, 201301(R) (2016)
Heo, J., Kang, M.S., Hong, C.H., Yang, H., Choi, S.G.: Schemes generating entangled states and entanglement swapping between photons and three-level atoms inside optical cavities for quantum communication. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 24 (2017)
Gao, C.Y., Wang, G.Y., Zhang, H., Deng, F.G.: Multi-photon self-error-correction hyperentanglement distribution over arbitrary collective-noise channels. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 11 (2017)
Heo, J., Kang, M.S., Hong, C.H., Choi, S.G., Hong, J.P.: Constructions of secure entanglement channels assisted by quantum dots inside single-sided optical cavities. Opt. Commun. (2017). doi:10.1016/j.optcom.2017.01.056
Nemoto, K., Munro, W.J.: Nearly deterministic linear optical controlled-NOT gate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 250502 (2004)
Barrett, S.D., Kok, P., Nemoto, K., Beausoleil, R.G., Munro, W.J., Spiller, T.P.: Symmetry analyzer for nondestructive Bell-state detection using weak nonlinearities. Phys. Rev. A 71, 060302 (2005)
Lin, Q., Li, J.: Quantum control gates with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Phys. Rev. A 79, 022301 (2009)
Guo, Q., Bai, J., Cheng, L.Y., Shao, X.Q., Wang, H.F., Zhang, S.: Simplified optical quantum-information processing via weak cross-Kerr nonlinearities. Phys. Rev. A 83, 054303 (2011)
Zhao, R.T., Guo, Q., Cheng, L.Y., Sun, L.L., Wang, H.F., Zhang, S.: Two-qubit and three-qubit controlled gates with cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Chin. Phys. B 22, 030313 (2013)
Heo, J., Hong, C.H., Lim, J.I., Yang, H.J.: Bidirectional quantum teleportation of unknown photons using path-polarization intra-particle hybrid entanglement and controlled-unitary gates via cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Chin. Phys. B 24, 050304 (2015)
Jin, G.S., Lin, Y., Wu, B.: Generating multiphoton Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger states with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Phys. Rev. A 75, 054302 (2007)
Zheng, C.H., Zhao, J., Shi, P., Li, W.D., Gu, Y.J.: Generation of three-photon polarization-entangled GHZ state via linear optics and weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Opt. Commun. 316, 26 (2014)
Heo, J., Hong, C.H., Lim, J.I., Yang, H.J.: Simultaneous quantum transmission and teleportation of unknown photons using intra- and inter-particle entanglement controlled-not gates via cross-kerr nonlinearity and P-homodyne measurements. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54, 2261 (2015)
Louis, S.G.R., Nemoto, K., Munro, W.J., Spiller, T.P.: The efficiencies of generating cluster states with weak nonlinearities. New J. Phys. 9, 193 (2007)
He, B., Ren, Y., Bergou, J.A.: Creation of high-quality long-distance entanglement with flexible resources. Phys. Rev. A 79, 052323 (2009)
Lin, Q., He, B.: Single-photon logic gates using minimal resources. Phys. Rev. A 80, 042310 (2009)
Lin, Q., He, B., Bergou, J.A., Ren, Y.: Processing multiphoton states through operation on a single photon: methods and applications. Phys. Rev. A 80, 042311 (2009)
Lin, Q., He, B.: Weaving independently generated photons into an arbitrary graph state. Phys. Rev. A 84, 062312 (2011)
Zhu, M.Z., Ye, L.: Efficient distributed controlled Z gate without ancilla single-photons via cross-phase modulation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 31, 405 (2014)
Zhu, M.Z., Ye, L.: Efficient entanglement purification for Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger states via the distributed parity-check detector. Opt. Commun. 334, 51 (2015)
Lin, Q., He, B.: Highly efficient processing of multi-photon states. Sci. Rep. 5, 12792 (2015)
Munro, W.J., Nemoto, K., Spiller, T.P.: Weak nonlinearities: a new route to optical quantum computation. New J. Phys. 7, 137 (2005)
Jeong, H.: Using weak nonlinearity under decoherence for macroscopic entanglement generation and quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 72, 034305 (2005)
Jeong, H.: Quantum computation using weak nonlinearities: robustness against decoherence. Phys. Rev. A 73, 052320 (2006)
Barrett, S.D., Milburn, G.J.: Quantum-information processing via a lossy bus. Phys. Rev. A 74, 060302 (2006)
Wittmann, C., Andersen, U.L., Takeoka, M., Sych, D., Leuchs, G.: Discrimination of binary coherent states using a homodyne detector and a photon number resolving detector. Phys. Rev. A 81, 062338 (2010)
Knill, E., Laflamme, R., Milburn, G.: A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409, 46 (2001)
Wang, X.W., Zhang, D.Y., Tang, S.Q., Xie, L.J., Wang, Z.Y., Kuang, L.M.: Photonic two-qubit parity gate with tiny cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Phys. Rev. A 85, 052326 (2012)
Wang, X.W., Tang, S.Q., Xie, L.J., Zhang, D.Y.: Nondestructive two-photon parity detector with near unity efficiency. Opt. Commun. 296, 153 (2013)
Ding, D., Yan, F.L., Gao, T.: Entangler and analyzer for multiphoton Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger states using weak nonlinearities. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 57, 2098 (2014)
Liu, Q., Wang, G.Y., Ai, Q., Zhang, M., Deng, F.G.: Complete nondestructive analysis of two-photon six-qubit hyperentangled Bell states assisted by cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Sci. Rep. 6, 22016 (2016)
Dong, L., Wang, J.X., Li, Q.Y., Dong, H.K., Xiu, X.M., Gao, Y.J.: Teleportation of a general two-photon state employing a polarization-entangled \(\chi \) state with nondemolition parity analyses. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 2955 (2016)
Phoenix, S.J.D.: Wave-packet evolution in the damped oscillator. Phys. Rev. A 41, 5132 (1990)
Kok, K., Braunstein, S.L.: Postselected versus nonpostselected quantum teleportation using parametric down-conversion. Phys. Rev. A 61, 042304 (2000)
Lukin, M.D., Imamoğlu, A.: Nonlinear optics and quantum entanglement of ultraslow single photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 1419 (2000)
Lukin, M.D., Imamoğlu, A.: Controlling photons using electromagnetically induced transparency. Nature 413, 273 (2001)
Kok, P., Munro, W.J., Nemoto, K., Ralph, T.C., Dowling, J.P., Milburn, G.J.: Linear optical quantum computing with photonic qubits. Rev. Mod. Phys. 79, 135 (2007)
Gea-Banacloche, J.: Impossibility of large phase shifts via the giant Kerr effect with single-photon wave packets. Phys. Rev. A 81, 043823 (2010)
He, B., Lin, Q., Simon, C.: Cross-Kerr nonlinearity between continuous-mode coherent states and single photons. Phys. Rev. A 83, 053826 (2011)
He, B., Scherer, A.: Continuous-mode effects and photon–photon phase gate performance. Phys. Rev. A 85, 033814 (2012)
Kok, P.: Effects of self-phase-modulation on weak nonlinear optical quantum gates. Phys. Rev. A 77, 013808 (2008)
Sanders, B.C., Milburn, G.J.: Complementarity in a quantum nondemolition measurement. Phys. Rev. A 39, 694 (1989)
Sanders, B.C., Milburn, G.J.: Quantum limits to all-optical phase shifts in a Kerr nonlinear medium. Phys. Rev. A 45, 1919 (1992)
Kanamori, H., Yokota, H., Tanaka, G., Watanabe, M., Ishiguro, Y., Yoshida, I., Kakii, T., Itoh, S., Asano, Y., Tanaka, S.: Transmission characteristics and reliability of pure-silica-core single-mode fibers. J. Lightwave Technol. 4, 1144 (1986)
Nagayama, K., Matsui, M., Kakui, M., Saitoh, T., Kawasaki, K., Takamizawa, H., Ooga, Y., Tsuchiya, I., Chigusa, Y.: Ultra low loss (0.1484 dB/km) pure silica core fiber. SEI Tech. Rev. 57, 3 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. NRF-2015R1A2A2A03004152).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heo, J., Hong, CH., Yang, HJ. et al. Analysis of optical parity gates of generating Bell state for quantum information and secure quantum communication via weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity under decoherence effect. Quantum Inf Process 16, 110 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1560-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1560-8