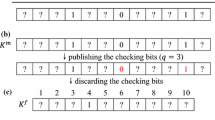
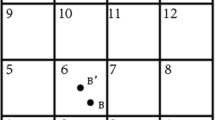
Abstract
Secure multiparty computational geometry is an essential field of secure multiparty computation, which computes a computation geometric problem without revealing any private information of each party. Secure two-party distance computation is a primitive of secure multiparty computational geometry, which computes the distance between two points without revealing each point’s location information (i.e., coordinate). Secure two-party distance computation has potential applications with high secure requirements in military, business, engineering and so on. In this paper, we present a quantum solution to secure two-party distance computation by subtly using quantum private query. Compared to the classical related protocols, our quantum protocol can ensure higher security and better privacy protection because of the physical principle of quantum mechanics.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yao, A.: Protocols for secure computations. In: Proceedings of 23rd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS ’82), Chicago, USA, pp. 160–164. IEEE Computer Society Press, New York (1982)
Du, W., Atallah, M.J.: Secure multi-party computation problems and their applications: a review and open problems. In: Proceedings of the 2001 Workshop on New Security Paradigms, pp. 13–22. ACM, New York (2001)
Atallah, M.J., Du, W.: Secure multi-party computational geometry. In: Proceedings of 7th International Workshop on Algorithms and Data Structures, pp. 165–179. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (2001)
Li, S.D., Dai, Y.Q.: Secure two-party computational geometry. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 20(2), 258–263 (2005)
Frikken, K.B., Atallah, M.J.: Privacy preserving route planning. In: Proceedings of the 2004 ACM workshop on Privacy in the electronic society, pp. 8–15. ACM, New York (2004)
Yang, B., Sun, A., Zhang, W.: Secure two-party protocols on planar circles. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 8(1), 29–40 (2011)
Luo, Y., Huang, L., Jing, W., et al.: Privacy protection in the relative position determination for two spatial geometric objects. Comput. Res. Dev. 43(3), 410–416 (2006)
Liu, W., Luo, S., Yang, Y., et al.: A study of secure two-party circle computation problem. J. Beijing Univ. Posts Telecommun. 32, 32–35 (2009)
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings of 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Santa Fe, New Mexico, pp. 124–134. IEEE, New York (1994)
Grover, L.K.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Coimbra, Portugal, pp. 212–219. ACM, New York (1996)
Jia, H.Y., Wen, Q.Y., Song, T.T., et al.: Quantum protocol for millionaire problem[J]. Opt. Commun. 284(1), 545–549 (2011)
Tseng, H.Y., Lin, J., Hwang, T.: New quantum private comparison protocol using EPR pairs[J]. Quantum Inf. Process. 11(2), 373–384 (2011)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., et al.: Robust and efficient quantum private comparison of equality with collective detection over collective-noise channels[J]. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 56(9), 1670–1678 (2013)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., et al.: Quantum anonymous ranking[J]. Phys. Rev. A 89(3), 87–90 (2014)
Vaccaro, J.A., Spring, J., Chefles, A.: Quantum protocols for anonymous voting and surveying[J]. Phys. Rev. A 75(1), 10064–10070 (2007)
Wang, Q., Yu, C., Gao, F., et al.: Self-tallying quantum anonymous voting[J]. Phys. Rev. A 94, 022333 (2016)
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S., Maccone, L.: Quantum private queries. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100(23), 230502 (2008)
Olejnik, L.: Secure quantum private information retrieval using phase-encoded queries. Phys. Rev. A 84(2), 022313 (2011)
Shi, R., Mu, Y., Zhong, H., et al.: An efficient quantum scheme for Private Set Intersection. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(1), 363–371 (2016)
Shi, R., Mu, Y., Zhong, H., et al.: Quantum private set intersection cardinality and its application to anonymous authentication. Inf. Sci. 370, 147–158 (2016)
Vaidya, J., Shafiq, B., Fan, W., Mehmood, D., Lorenzi, D.: A random decision tree framework for privacy-preserving data mining. IEEE Trans. Depend. Sec. Comput. 11(5), 399–411 (2014)
Jakobi, M., Simon, C., Gisin, N., et al.: Practical private database queries based on a quantum-key-distribution protocol[J]. Phys. Rev. A 83(2), 022301 (2011)
Yang, Y.G., Sun, S.J., Xu, P., et al.: Flexible protocol for quantum private query based on B92 protocol[J]. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(3), 805–813 (2014)
Gao, F., Liu, B., Huang, W., et al.: Postprocessing of the oblivious key in quantum private query[J]. IEEE J. Select. Top. Quantum Electron. 21(3), 98–108 (2014)
Liu, B., Fei, G., Wei, H., et al.: QKD-based quantum private query without a failure probability[J]. Sci. China 58(10), 100301 (2015)
Wei, C.Y., Wang, T.Y., Gao, F.: Practical quantum private query with better performance in resisting joint-measurement attack[J]. Phys. Rev. A 93(4), 042318 (2016)
Shi, R., Mu, Y., Zhong, H., et al.: Quantum oblivious set-member decision protocol. Phys. Rev. A 92(2), 022309 (2015)
Shi, R., Mu, Y., Zhong, H., et al.: Privacy-preserving point-inclusion protocol for an arbitrary area based on phase-encoded quantum private query. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(1), 8 (2017)
Shi, R., Mu, Y., Zhong, H., et al.: Comment on “Secure quantum private information retrieval using phase-encoded queries”. Phys. Rev. A 94(6), 066301 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61772001 and 11301002) and Talents Youth Fund of Anhui Province Universities (2013SQRL006ZD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Zw., Shi, Rh., Zhong, H. et al. A novel quantum scheme for secure two-party distance computation. Quantum Inf Process 16, 316 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1766-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1766-9